Elliptical leaves feature a symmetrical, elongated oval shape that tapers at both ends, making them highly efficient for maximizing sunlight absorption in various plant species. Their smooth edges and balanced proportions contribute to enhanced photosynthetic performance and water runoff, supporting healthier plant growth. Discover more about the unique benefits and adaptations of elliptical leaves in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
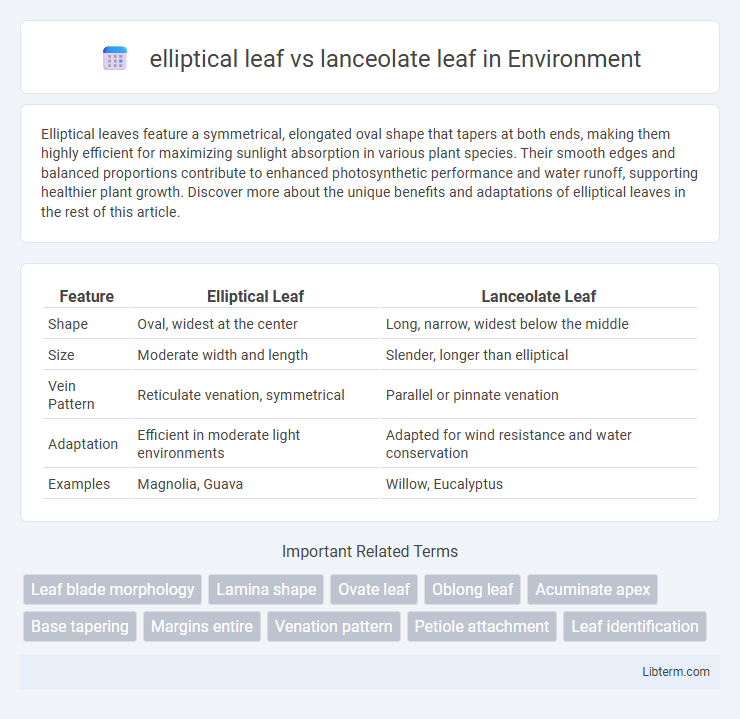
| Feature | Elliptical Leaf | Lanceolate Leaf |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Oval, widest at the center | Long, narrow, widest below the middle |
| Size | Moderate width and length | Slender, longer than elliptical |
| Vein Pattern | Reticulate venation, symmetrical | Parallel or pinnate venation |
| Adaptation | Efficient in moderate light environments | Adapted for wind resistance and water conservation |
| Examples | Magnolia, Guava | Willow, Eucalyptus |
Introduction to Leaf Shapes
Elliptical leaves feature a broad, oval shape with smooth edges, maximizing photosynthetic efficiency by capturing abundant sunlight. Lanceolate leaves are narrow and elongated, tapering to a pointed tip, which reduces water loss and enhances wind resistance in dry or windy environments. Understanding these leaf shapes helps in identifying plant species and adapting to different ecological conditions.
Defining Elliptical Leaves
Elliptical leaves are characterized by their broad, symmetrical shape with the widest part at the center, tapering equally toward both ends, resembling an ellipse. This leaf type typically has smooth margins and a length-to-width ratio ranging from 2:1 to 3:1, distinguishing it from the narrower, spear-shaped lanceolate leaves. The venation in elliptical leaves is pinnate, supporting efficient photosynthesis and water transport throughout the balanced leaf surface.
Defining Lanceolate Leaves
Lanceolate leaves are narrow and taper to a pointed tip, resembling the shape of a lance, typically longer than they are wide, with the widest point below the middle of the leaf blade. In contrast, elliptical leaves have a more oval shape with symmetrical tapering at both ends, widest at the center. The distinct lanceolate form enhances water runoff and sunlight capture, adapting plants to specific environmental conditions.
Key Morphological Differences
Elliptical leaves exhibit a broad, oval shape with evenly curved edges and a length-to-width ratio close to 2:1, while lanceolate leaves are significantly narrower, tapering to a pointed tip and possessing a length-to-width ratio typically exceeding 3:1. The elliptical leaf's symmetrical outline contrasts with the lanceolate leaf's asymmetrical taper, affecting their surface area and light absorption efficiency. Venation patterns differ as well, with elliptical leaves featuring more evenly spaced secondary veins parallel to the margin, whereas lanceolate leaves show prominent midribs supporting a gradual narrowing toward the apex.
Comparative Visual Identification
Elliptical leaves are broadest at the center and taper equally toward both ends, forming a smooth oval shape, while lanceolate leaves are longer, narrower, and taper to a pointed tip, resembling a lance. The elliptical leaf surface is generally wider and more rounded, facilitating easy distinction from the slender, sharply pointed lanceolate leaf. Visual identification relies on noting the overall leaf proportions: elliptical leaves have a length-to-width ratio closer to 2:1, whereas lanceolate leaves often exceed a 3:1 ratio.
Ecological Significance of Each Leaf Shape
Elliptical leaves, with their broad surface area, optimize photosynthesis in shaded environments by capturing diffused sunlight effectively, supporting plant survival in understory ecosystems. Lanceolate leaves, characterized by their narrow and elongated form, reduce water loss and wind resistance, making them advantageous in arid or windy habitats. This leaf shape variation influences plant adaptation strategies, affecting ecosystem dynamics such as water cycling and habitat suitability for diverse organisms.
Anatomical Adaptations
Elliptical leaves exhibit broad, evenly curved surfaces that maximize light capture and enhance photosynthetic efficiency, while their thick cuticles reduce water loss in diverse environments. Lanceolate leaves possess elongated, narrow shapes with tapered ends, facilitating efficient water runoff and minimizing wind resistance, which is advantageous in arid or windy habitats. Both leaf types display specialized vascular arrangements that support optimal nutrient transport and mechanical strength tailored to their anatomical adaptations.
Examples of Plants with Elliptical Leaves
Examples of plants with elliptical leaves include the magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora), avocado (Persea americana), and eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus). These elliptical leaves feature a broad middle with tapered ends, optimizing photosynthesis by maximizing sunlight capture. This leaf shape contrasts with lanceolate leaves, which are narrower and more elongated, such as those seen in willow (Salix spp.) and oleander (Nerium oleander).
Examples of Plants with Lanceolate Leaves
Lanceolate leaves, characterized by a narrow shape tapering to a point, are common in plants like willow (Salix spp.), oleander (Nerium oleander), and eucalyptus (Eucalyptus spp.). These plants thrive in various climates, with lanceolate leaves optimizing water runoff and sunlight capture. In contrast, elliptical leaves, found in species such as magnolia (Magnolia spp.) and camellia (Camellia spp.), have a broader, oval shape that supports efficient photosynthesis in shaded environments.
Importance of Leaf Shape in Plant Identification
Elliptical leaves, characterized by their broad, oval shape with a smooth margin, contrast with lanceolate leaves, which are narrower and taper to a pointed tip. The distinct shapes of elliptical and lanceolate leaves play a crucial role in plant identification by providing key morphological markers that help differentiate species within botanical families. Recognizing these leaf shapes enhances accurate field identification and supports ecological studies by indicating adaptations to specific environmental conditions.
elliptical leaf Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com