Blackfield blends atmospheric rock with melancholic melodies, creating a unique soundscape that resonates deeply with listeners. The project, led by Steven Wilson and Aviv Geffen, explores themes of introspection and emotional complexity through haunting vocals and intricate instrumentation. Discover how Blackfield's evocative music can connect with your inner emotions by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
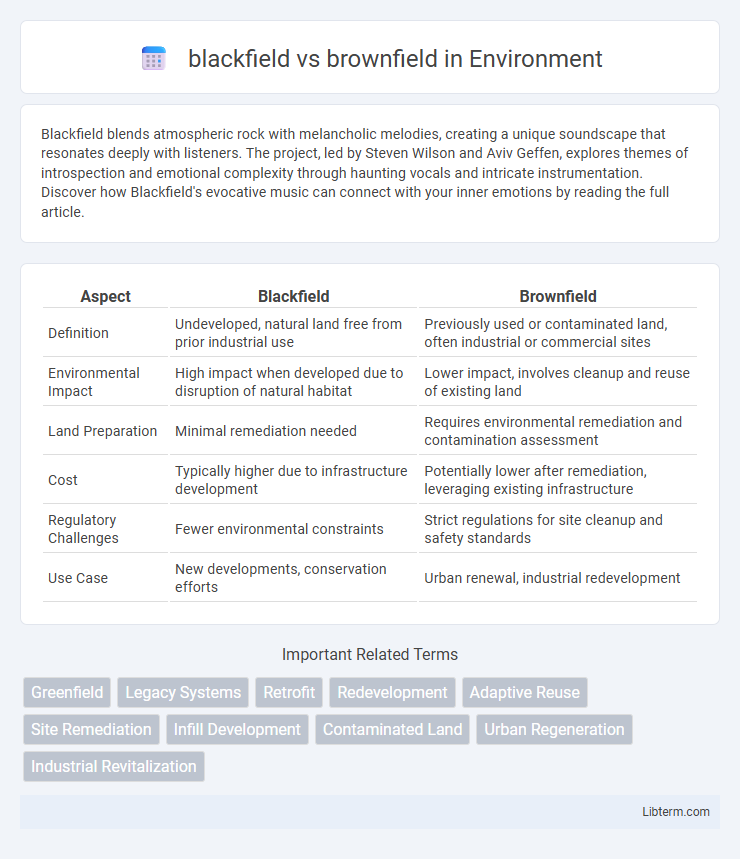
| Aspect | Blackfield | Brownfield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Undeveloped, natural land free from prior industrial use | Previously used or contaminated land, often industrial or commercial sites |
| Environmental Impact | High impact when developed due to disruption of natural habitat | Lower impact, involves cleanup and reuse of existing land |
| Land Preparation | Minimal remediation needed | Requires environmental remediation and contamination assessment |
| Cost | Typically higher due to infrastructure development | Potentially lower after remediation, leveraging existing infrastructure |
| Regulatory Challenges | Fewer environmental constraints | Strict regulations for site cleanup and safety standards |
| Use Case | New developments, conservation efforts | Urban renewal, industrial redevelopment |
Introduction to Blackfield and Brownfield Concepts
Blackfield projects involve new developments on undeveloped land, typically characterized by untouched natural environments and blank slates for construction, whereas brownfield projects focus on redeveloping existing urban sites previously used for industrial or commercial purposes, often requiring environmental remediation. Understanding the distinctions between blackfield and brownfield sites is essential for urban planners, developers, and environmental scientists, as it influences project costs, regulatory requirements, and sustainability strategies. The challenges in brownfield redevelopment include managing soil contamination and integrating infrastructure, while blackfield projects offer flexibility but may face ecological and zoning constraints.
Defining Blackfield and Brownfield Projects
Blackfield projects involve developing new infrastructure or facilities on undeveloped land, often in rural or suburban areas, emphasizing greenfield sites untouched by prior construction. Brownfield projects focus on the redevelopment or renovation of existing sites previously used for industrial or commercial purposes, requiring environmental cleanup and remediation efforts. Understanding the distinction highlights blackfield's emphasis on new construction and brownfield's on redevelopment within urban or industrial contexts.
Key Differences Between Blackfield and Brownfield
Blackfield projects involve development on previously unused or undeveloped land, while brownfield projects focus on revitalizing and repurposing land that has been previously used and may require environmental cleanup. Blackfield development typically offers a blank slate for construction with fewer regulatory hurdles, whereas brownfield redevelopment often faces more stringent environmental assessments and remediation costs. The key difference lies in the starting conditions: blackfield sites are raw and undeveloped, while brownfield sites are contaminated or underutilized lands requiring significant preparation before new development.
Advantages of Blackfield Developments
Blackfield developments offer significant advantages such as lower initial costs and fewer regulatory hurdles compared to brownfield projects, which often require extensive site cleanup and remediation. These greenfield locations provide flexible planning opportunities, enabling developers to design infrastructure and layouts from scratch without constraints imposed by existing structures. Moreover, blackfield sites typically attract higher investor interest due to their potential for scalable growth and modern amenities integration.
Challenges of Blackfield Development
Blackfield development faces significant challenges including complex contamination cleanup, extensive regulatory compliance, and high remediation costs. Environmental hazards such as soil and groundwater pollution require thorough site assessments and specialized mitigation strategies. Limited existing infrastructure and potential legal liabilities further complicate redevelopment efforts on blackfield sites.
Benefits of Brownfield Redevelopment
Brownfield redevelopment revitalizes underutilized or contaminated industrial sites, boosting urban renewal and reducing urban sprawl by making efficient use of existing infrastructure. This approach promotes environmental remediation, improving public health and restoring ecosystems while preserving historical structures. Economically, brownfield projects attract investment, create jobs, and increase property values, enhancing community sustainability and resilience.
Common Issues in Brownfield Projects
Brownfield projects frequently encounter challenges such as contamination from previous industrial use, which requires extensive environmental remediation to meet safety standards. Unforeseen structural degradation and outdated infrastructure often lead to increased costs and delays in project timelines. Regulatory compliance complexities and community opposition also pose significant hurdles, impacting project feasibility and execution.
Environmental Impact: Blackfield vs Brownfield
Brownfield sites often present significant environmental challenges due to prior industrial contamination, including hazardous waste and soil pollutants that require extensive remediation efforts. In contrast, blackfield development typically involves undeveloped land with minimal environmental degradation, reducing the need for costly cleanup processes. Addressing contamination on brownfield properties enhances urban regeneration and mitigates potential health risks, while blackfield projects focus more on preserving existing ecosystems and minimizing land disturbance.
Economic Considerations for Developers
Blackfield developments often require higher initial investments due to infrastructure installation, increasing upfront economic risks for developers. Brownfield projects benefit from existing utilities and structures, potentially lowering redevelopment costs but may involve expensive environmental remediation. Developers must weigh site acquisition expenses, regulatory compliance costs, and long-term land value appreciation when assessing economic viability.
Choosing Between Blackfield and Brownfield Strategies
Choosing between blackfield and brownfield strategies hinges on project goals and resource availability. Blackfield projects offer fresh development opportunities with complete control over design but require higher initial investment and longer timelines. Brownfield strategies leverage existing infrastructure, reducing costs and accelerating deployment while facing challenges like legacy system integration and regulatory compliance.
blackfield Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com