Shrubs provide versatile landscaping options with their dense foliage and varying heights, enhancing garden aesthetics and offering habitat for wildlife. These hardy plants require minimal maintenance, making them ideal for both beginners and experienced gardeners looking to add structure and color year-round. Discover how to choose the perfect shrubs to transform Your outdoor space by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
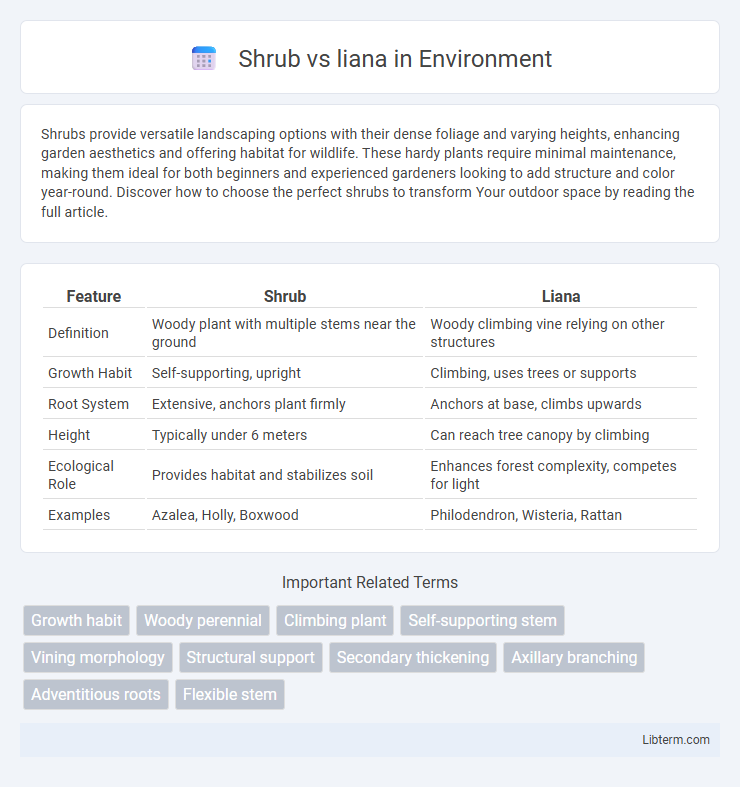
| Feature | Shrub | Liana |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Woody plant with multiple stems near the ground | Woody climbing vine relying on other structures |
| Growth Habit | Self-supporting, upright | Climbing, uses trees or supports |
| Root System | Extensive, anchors plant firmly | Anchors at base, climbs upwards |
| Height | Typically under 6 meters | Can reach tree canopy by climbing |
| Ecological Role | Provides habitat and stabilizes soil | Enhances forest complexity, competes for light |
| Examples | Azalea, Holly, Boxwood | Philodendron, Wisteria, Rattan |
Introduction to Shrubs and Lianas
Shrubs are woody plants with multiple stems that typically grow less than 6 meters tall and are known for their bushy, dense foliage suitable for landscaping and habitat creation. Lianas are long-stemmed, woody vines rooted in the ground that climb trees and other structures to reach sunlight, playing a crucial role in tropical forest ecosystems by connecting trees and facilitating animal movement. Both shrubs and lianas contribute to biodiversity but differ significantly in growth form, ecological function, and structural adaptation.
Defining Characteristics of Shrubs
Shrubs are woody plants characterized by multiple stems arising at or near the ground, typically growing less than 6 meters tall, which distinguishes them from trees and climbing plants like lianas. Unlike lianas, which are climbing vines relying on other structures for support, shrubs have self-supporting, rigid stems that provide a bushy appearance. Their dense branching and permanent woody tissue enable shrubs to thrive in diverse environments, offering important ecological functions such as habitat and soil stabilization.
Unique Features of Lianas
Lianas are climbing woody vines that rely on other structures or trees for support, allowing them to reach sunlight in dense forests, unlike self-supporting shrubs with rigid stems. They have flexible, elongated stems with strong tensile strength, enabling extensive vertical growth and lateral spread in tropical and subtropical ecosystems. Their unique root systems and stem adaptations facilitate efficient water transport and mechanical stability, distinguishing them from shrubs in structural and ecological roles.
Growth Habits: Shrub vs Liana
Shrubs are woody plants with multiple stems growing from the base and maintain a self-supporting, upright structure throughout their life. Lianas are long-stemmed, woody vines that rely on other structures or plants for support, allowing them to climb and reach sunlight in dense forests. The growth habit differences enable shrubs to occupy lower vegetation layers, while lianas primarily exploit vertical space for access to light.
Ecological Roles in Ecosystems
Shrubs contribute to ecosystems by providing habitat and food for wildlife, stabilizing soil, and supporting biodiversity through dense foliage that offers shelter and nesting sites. Lianas play a critical role in forest dynamics by connecting trees, facilitating arboreal animal movement, and influencing tree growth patterns and forest structure. Both growth forms enhance nutrient cycling, but lianas increase light penetration in forests by climbing trees, affecting understory plant communities.
Habitat Preferences and Adaptations
Shrubs thrive in a variety of habitats including temperate forests, grasslands, and arid regions, exhibiting adaptations like deep root systems for water uptake and thick, woody stems to withstand environmental stress. Lianas predominantly inhabit tropical rainforests, relying on other trees for physical support through flexible, climbing stems and aerial roots, which allow efficient access to sunlight in dense canopy layers. These distinct habitat preferences and structural adaptations reflect their evolutionary strategies for survival and resource acquisition in contrasting ecosystems.
Benefits to Wildlife and Biodiversity
Shrubs provide dense habitat and nesting sites for birds and small mammals, supporting diverse insect populations through abundant flowers and fruits. Lianas enhance forest structural complexity by connecting tree canopies, facilitating animal movement and increasing habitat diversity for arboreal species. Both growth forms contribute to ecosystem resilience by promoting species richness and supporting varied food webs in forested environments.
Common Examples of Shrubs and Lianas
Common examples of shrubs include azaleas, boxwoods, and hydrangeas, which are typically woody plants with multiple stems growing close to the ground. Lianas, such as wisteria, poison ivy, and grapevines, are woody vines that rely on other structures or trees for support to reach sunlight. Both play significant roles in ecosystems, but their growth habits and ecological functions differ markedly.
Horticultural Uses and Landscaping Value
Shrubs provide structured greenery with their dense, woody stems, making them ideal for hedges, borders, and foundation plantings in landscaping designs. Lianas, being woody vines, are valued for their vertical growth and ability to cover trellises, pergolas, and fences, adding vertical interest and natural shade to gardens. In horticulture, shrubs offer year-round form and often seasonal flowers or fruits, while lianas contribute dynamic growth patterns and are effective for creating living walls and enhancing garden biodiversity.
Which is Right for Your Garden?
Shrubs are woody plants with multiple stems that typically grow within a manageable height, making them ideal for structured garden borders and low-maintenance landscapes. Lianas are climbing woody vines that rely on other structures or plants for support, adding vertical interest and dense foliage to garden spaces with limited horizontal area. Choosing between shrubs and lianas depends on your garden's spatial constraints, desired aesthetic, and maintenance capabilities, with shrubs suited for defining spaces and lianas perfect for vertical coverage.
Shrub Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com