A wildlife sanctuary preserves natural habitats, ensuring the protection of diverse species from endangerment and human interference. These sanctuaries play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and promoting biodiversity conservation. Discover how visiting or supporting a wildlife sanctuary can benefit Your understanding of nature and contribute to global environmental efforts. Read on to learn more about the importance and impact of wildlife sanctuaries.
Table of Comparison
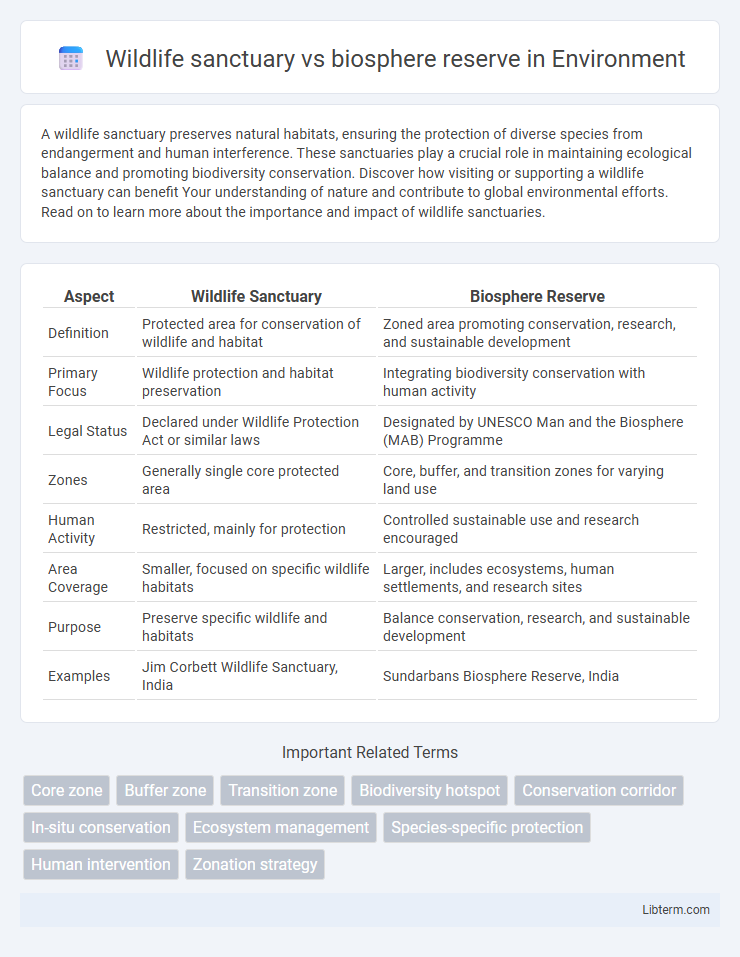
| Aspect | Wildlife Sanctuary | Biosphere Reserve |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protected area for conservation of wildlife and habitat | Zoned area promoting conservation, research, and sustainable development |
| Primary Focus | Wildlife protection and habitat preservation | Integrating biodiversity conservation with human activity |
| Legal Status | Declared under Wildlife Protection Act or similar laws | Designated by UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme |
| Zones | Generally single core protected area | Core, buffer, and transition zones for varying land use |
| Human Activity | Restricted, mainly for protection | Controlled sustainable use and research encouraged |
| Area Coverage | Smaller, focused on specific wildlife habitats | Larger, includes ecosystems, human settlements, and research sites |
| Purpose | Preserve specific wildlife and habitats | Balance conservation, research, and sustainable development |
| Examples | Jim Corbett Wildlife Sanctuary, India | Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve, India |
Introduction to Wildlife Sanctuaries and Biosphere Reserves
Wildlife sanctuaries protect specific animal species and their habitats, emphasizing conservation and minimal human interference. Biosphere reserves serve a broader ecological purpose, integrating core protected areas with buffer zones for sustainable development and research. Both aim to preserve biodiversity but differ in management scope and human activity involvement.
Definition of Wildlife Sanctuary
A wildlife sanctuary is a protected area designated to conserve and protect wild animals and their habitats, restricting human activities to prevent disturbance and poaching. It focuses on preserving native species by maintaining a safe and natural environment, often prohibiting hunting and commercial exploitation. Unlike biosphere reserves that integrate conservation with sustainable development and research, wildlife sanctuaries primarily emphasize species protection and habitat conservation.
Definition of Biosphere Reserve
A biosphere reserve is a designated area that promotes the conservation of biodiversity, supports sustainable development, and facilitates research and monitoring of ecosystems. Unlike wildlife sanctuaries, which primarily focus on protecting specific animal species and their habitats, biosphere reserves encompass multiple zones including core protected areas, buffer zones, and transition areas to balance ecological preservation with human activity. These reserves are often recognized by UNESCO and serve as global models for integrating conservation with community engagement and environmental education.
Key Objectives: Wildlife Sanctuary vs Biosphere Reserve
Wildlife sanctuaries primarily aim to protect specific animal species and their habitats by minimizing human interference and preserving biodiversity in a confined area. In contrast, biosphere reserves focus on balancing conservation of ecosystems with sustainable use of natural resources and promoting research, education, and community involvement. While wildlife sanctuaries emphasize species protection, biosphere reserves serve as sites for ecological conservation combined with sustainable development practices.
Geographical Coverage and Zonation
Wildlife sanctuaries typically cover smaller, specific areas dedicated to the protection of particular species and their habitats, with minimal zoning and restricted human activities to reduce interference. Biosphere reserves encompass larger geographic regions that include core protected areas, buffer zones, and transition areas promoting sustainable use and biodiversity conservation alongside human activity. The zonation in biosphere reserves integrates conservation with development objectives, whereas wildlife sanctuaries primarily emphasize strict wildlife protection within defined boundaries.
Legal Protection and Management
Wildlife sanctuaries are legally protected areas primarily established to conserve specific species and their habitats, often allowing limited human activity under strict regulations enforced by wildlife protection laws. Biosphere reserves are designated under UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme, combining core protected areas with buffer zones and transition areas to promote biodiversity conservation alongside sustainable development. Management of biosphere reserves involves cooperation between local communities, governments, and scientists to balance ecological preservation with socio-economic benefits, whereas wildlife sanctuaries focus predominantly on habitat preservation and minimizing human interference.
Biodiversity Conservation Approaches
Wildlife sanctuaries primarily focus on protecting specific animal species and their habitats through strict regulation of human activities, thereby maintaining local biodiversity. Biosphere reserves adopt a holistic approach by integrating conservation with sustainable development, allowing controlled human interaction while preserving genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Both approaches contribute to biodiversity conservation, but biosphere reserves emphasize a balance between ecological protection and community livelihoods.
Role in Community Involvement and Sustainable Use
Wildlife sanctuaries primarily focus on protecting specific animal species and their habitats, often limiting human activities to preserve biodiversity, which restricts community involvement but ensures minimal disturbance. Biosphere reserves integrate conservation with sustainable development by involving local communities in resource management, promoting sustainable use practices that balance ecological preservation with economic benefits. Community participation in biosphere reserves enhances traditional knowledge application, supports livelihoods, and fosters stewardship, making them vital models for harmonizing human activity with environmental protection.
Notable Examples Around the World
Kaziranga Wildlife Sanctuary in India is renowned for its population of the Indian one-horned rhinoceros, while Yellowstone National Park in the USA serves as a premier example of a wildlife sanctuary protecting diverse fauna. In contrast, UNESCO-designated biosphere reserves like the Galapagos Islands in Ecuador and the Great Barrier Reef in Australia emphasize conservation alongside sustainable use of natural resources and human activity. These biosphere reserves integrate core protected areas with zones that support research, education, and local livelihoods under international conservation frameworks.
Conclusion: Comparing Wildlife Sanctuaries and Biosphere Reserves
Wildlife sanctuaries primarily focus on protecting specific animal species and their habitats, often restricting human activities to minimize disturbances. Biosphere reserves encompass broader ecological zones, integrating conservation with sustainable development and research to balance human presence and nature. Both play crucial roles in biodiversity preservation, but biosphere reserves offer a more comprehensive approach combining conservation, education, and sustainable use.
Wildlife sanctuary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com