Sustainable development focuses on balancing economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity to meet the needs of present and future generations. Implementing sustainable practices can help your community thrive while preserving natural resources. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective strategies for achieving sustainability in various sectors.
Table of Comparison
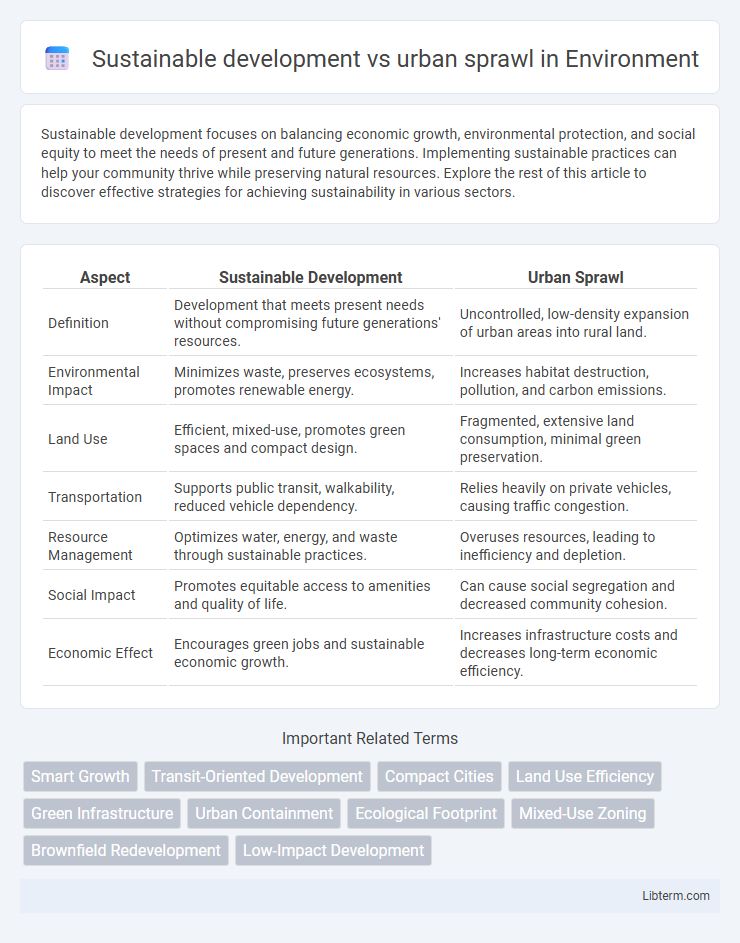
| Aspect | Sustainable Development | Urban Sprawl |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development that meets present needs without compromising future generations' resources. | Uncontrolled, low-density expansion of urban areas into rural land. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes waste, preserves ecosystems, promotes renewable energy. | Increases habitat destruction, pollution, and carbon emissions. |
| Land Use | Efficient, mixed-use, promotes green spaces and compact design. | Fragmented, extensive land consumption, minimal green preservation. |
| Transportation | Supports public transit, walkability, reduced vehicle dependency. | Relies heavily on private vehicles, causing traffic congestion. |
| Resource Management | Optimizes water, energy, and waste through sustainable practices. | Overuses resources, leading to inefficiency and depletion. |
| Social Impact | Promotes equitable access to amenities and quality of life. | Can cause social segregation and decreased community cohesion. |
| Economic Effect | Encourages green jobs and sustainable economic growth. | Increases infrastructure costs and decreases long-term economic efficiency. |
Defining Sustainable Development and Urban Sprawl
Sustainable development is defined as meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, emphasizing environmental protection, economic growth, and social equity. Urban sprawl refers to the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into peripheral rural land, characterized by low-density residential and commercial development, increased reliance on automobiles, and fragmented land use. The contrast between these concepts lies in sustainable development's focus on planned, efficient resource use versus urban sprawl's tendency toward inefficient, sprawling land consumption and environmental degradation.
Key Characteristics of Sustainable Cities
Sustainable cities prioritize efficient land use, promoting high-density development to minimize urban sprawl and preserve natural habitats. They integrate green infrastructure, renewable energy sources, and robust public transportation systems to reduce carbon footprints and enhance residents' quality of life. Emphasis on mixed-use zoning and walkability fosters economic vitality while limiting environmental degradation characteristic of sprawling urban growth.
Causes and Consequences of Urban Sprawl
Urban sprawl is primarily caused by population growth, affordable housing demands, and increased reliance on automobiles, leading to the expansion of low-density, car-dependent communities. This uncontrolled expansion results in habitat loss, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and inefficient land use, counteracting goals of sustainable development. The consequences also include elevated infrastructure costs, traffic congestion, and reduced access to essential services, undermining both environmental health and community well-being.
Environmental Impacts: Sustainability vs. Sprawl
Sustainable development prioritizes efficient land use, reducing habitat destruction and preserving biodiversity, whereas urban sprawl leads to extensive land consumption and fragmentation of ecosystems. Sprawl increases greenhouse gas emissions due to reliance on automobiles and higher energy consumption in dispersed housing. In contrast, sustainable urban planning promotes compact, mixed-use communities that lower carbon footprints and enhance environmental resilience.
Economic Implications of Urban Growth Patterns
Urban sprawl often leads to increased infrastructure costs, including transportation, utilities, and public services, which strain municipal budgets and reduce economic efficiency. In contrast, sustainable development promotes compact urban growth that maximizes land use and fosters local economies through higher-density housing and mixed-use developments. Efficient resource allocation and reduced commute times in sustainable urban models enhance productivity and attract investment, supporting long-term economic resilience.
Urban Planning Strategies for Sustainability
Urban planning strategies for sustainability actively combat urban sprawl by promoting compact, mixed-use developments that reduce land consumption and preserve natural habitats. Integrating public transportation networks and green infrastructure minimizes carbon emissions and enhances resource efficiency. Smart growth policies prioritize walkability and affordable housing, ensuring equitable access while maintaining ecological balance in expanding urban areas.
Transportation and Mobility: Compact vs. Sprawling Cities
Compact cities promote sustainable transportation by supporting public transit, biking, and walking, which reduce greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion. Urban sprawl leads to car-dependent communities with longer commutes and higher fuel consumption, contributing to increased pollution and energy use. Efficient land use in sustainable development enhances mobility options and decreases reliance on private vehicles, fostering healthier, more accessible urban environments.
Social Equity in Urban Development
Sustainable development promotes social equity in urban development by ensuring equal access to resources, affordable housing, and public services for all residents, particularly marginalized communities. Urban sprawl exacerbates social inequities by creating segregated neighborhoods, increasing transportation costs, and limiting access to essential amenities. Prioritizing compact, mixed-use urban planning reduces disparities and fosters inclusive, resilient communities.
Case Studies: Successful Sustainable Urban Models
Curitiba, Brazil, exemplifies sustainable development through its integrated public transportation system and extensive green spaces that effectively counter urban sprawl. Singapore's urban planning emphasizes vertical growth and mixed-use developments, reducing land consumption while enhancing resource efficiency. Masdar City in the UAE combines renewable energy and smart infrastructure to create a low-carbon urban model that addresses the challenges of rapid urban expansion.
Policy Recommendations for Controlling Urban Sprawl
Effective policy recommendations for controlling urban sprawl emphasize smart growth strategies, such as implementing urban growth boundaries, promoting mixed-use zoning, and enhancing public transit infrastructure. Prioritizing compact, walkable neighborhoods contributes to reduced carbon emissions and preserves natural habitats, aligning with sustainable development goals. Incentives for infill development and stringent land-use regulations further support controlled expansion and resource-efficient urbanization.
Sustainable development Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com