Patchy canopy refers to a forest cover with uneven gaps where sunlight penetrates through breaks in the tree layers, affecting ecosystem dynamics and habitat quality. This variability influences soil moisture, plant diversity, and wildlife distribution by creating microhabitats. Discover how patchy canopy impacts your local environment and what it means for forest conservation by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
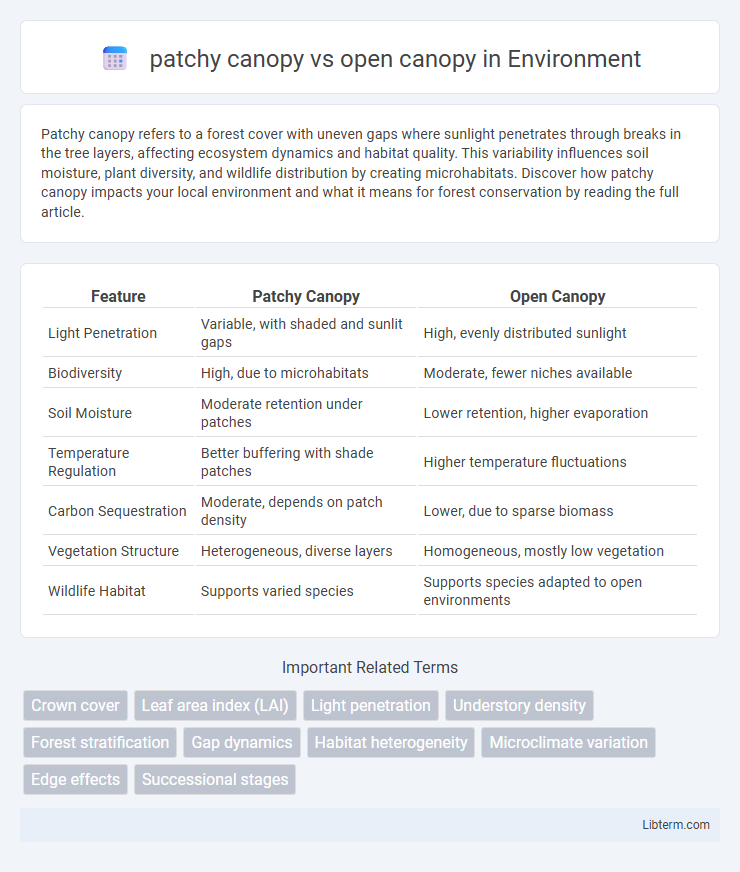
| Feature | Patchy Canopy | Open Canopy |
|---|---|---|
| Light Penetration | Variable, with shaded and sunlit gaps | High, evenly distributed sunlight |
| Biodiversity | High, due to microhabitats | Moderate, fewer niches available |
| Soil Moisture | Moderate retention under patches | Lower retention, higher evaporation |
| Temperature Regulation | Better buffering with shade patches | Higher temperature fluctuations |
| Carbon Sequestration | Moderate, depends on patch density | Lower, due to sparse biomass |
| Vegetation Structure | Heterogeneous, diverse layers | Homogeneous, mostly low vegetation |
| Wildlife Habitat | Supports varied species | Supports species adapted to open environments |
Introduction to Forest Canopies
Patchy canopy and open canopy represent distinct forest canopy structures that influence light penetration, microclimate, and biodiversity. Patchy canopies consist of irregular foliage clusters creating variable light gaps, promoting diverse understory vegetation and habitat heterogeneity. Open canopies feature widely spaced trees with extensive gaps, allowing higher light levels and favoring sun-adapted species and dynamic ecological processes.
Defining Patchy Canopy and Open Canopy
Patchy canopy refers to an irregular vegetation cover characterized by clusters of foliage interspersed with open spaces, resulting in uneven light distribution and microhabitat variability. Open canopy describes a vegetation structure where tree crowns are widely spaced, allowing substantial light penetration to the understory and promoting diverse plant growth. These differences in canopy density directly influence ecosystem dynamics, including photosynthesis rates and habitat availability.
Ecological Roles of Patchy vs. Open Canopies
Patchy canopies create heterogeneous light environments that promote biodiversity by supporting diverse understory plant and animal species, while open canopies allow more sunlight penetration, enhancing primary productivity but often reducing habitat complexity. The fragmented shading patterns in patchy canopies facilitate microhabitats crucial for moisture retention and temperature regulation, influencing species distributions and ecosystem resilience. Open canopies typically accelerate nutrient cycling and soil warming, impacting decomposition rates and carbon sequestration differently compared to the more stabilized microclimates found under patchy canopy structures.
Light Penetration Differences
Patchy canopies exhibit uneven light penetration, with sunlight filtering through gaps and creating a mosaic of shaded and illuminated areas on the forest floor. Open canopies allow more uniform and intense light exposure, resulting in higher overall light availability beneath the canopy. These variations in light penetration significantly influence understory vegetation growth and species composition in different forest ecosystems.
Influence on Understory Vegetation
Patchy canopy structures create variable light conditions that promote a diverse understory vegetation by allowing partial sunlight penetration, which supports shade-tolerant and light-demanding species simultaneously. Open canopies allow more uniform light exposure, often favoring fast-growing, light-dependent understory plants but reducing species richness due to increased competition. The variation in microclimates caused by patchy canopies enhances spatial heterogeneity and biodiversity in the understory vegetation community.
Effects on Biodiversity
Patchy canopies support higher biodiversity by creating diverse microhabitats that accommodate various species, promoting ecological niches and species richness. Open canopies, with increased sunlight and reduced structural complexity, often favor sun-tolerant species but may limit habitat availability for shade-dependent flora and fauna. These differences in light penetration and habitat heterogeneity directly influence species composition, abundance, and ecosystem resilience.
Canopy Structure and Wildlife Habitat
Patchy canopy features irregular tree cover creating a mosaic of shaded and sunlit gaps, which enhances biodiversity by providing diverse microhabitats and resources for various wildlife species. Open canopy consists of widely spaced trees with extensive sunlight reaching the ground, promoting understory vegetation growth that supports ground-dwelling and edge-adapted animals. Wildlife species composition and abundance are strongly influenced by canopy complexity, with patchy canopies generally supporting greater habitat heterogeneity and niche availability compared to open canopies.
Soil Moisture and Microclimate Impacts
Patchy canopies create heterogeneous soil moisture conditions by allowing variable sunlight penetration, which promotes uneven evaporation rates and localized microclimates with fluctuating humidity and temperature levels. Open canopies, on the other hand, expose the soil surface to direct sunlight, resulting in higher soil temperature, reduced soil moisture retention, and increased evaporation compared to denser canopy covers. These differences in canopy structure significantly influence microclimate regulation, soil microbial activity, and plant water availability, impacting overall ecosystem resilience and productivity.
Human Impacts and Canopy Fragmentation
Patchy canopy structures result from selective logging and land-use changes, causing uneven forest cover that disrupts wildlife habitats and microclimates. Open canopies often emerge from extensive deforestation, leading to increased soil erosion and reduced carbon sequestration capacity. Both canopy fragmentation forms exacerbate biodiversity loss and hinder ecosystem resilience by isolating species populations and diminishing habitat connectivity.
Conservation Strategies for Canopy Types
Patchy canopy conservation strategies emphasize maintaining habitat heterogeneity to support diverse species by protecting core forest areas and promoting natural regeneration. Open canopy management prioritizes enhancing understory growth and biodiversity through controlled thinning and periodic disturbances that mimic natural processes. Both approaches require adaptive monitoring to balance light availability, microclimate stabilization, and species habitat requirements for ecosystem resilience.
patchy canopy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com