Riparian zones are critical ecosystems located along the banks of rivers and streams, playing a vital role in maintaining water quality and providing habitat for diverse wildlife. These areas act as natural buffers that reduce erosion, filter pollutants, and support biodiversity. Explore this article to discover how protecting your local riparian zones benefits both the environment and your community.
Table of Comparison
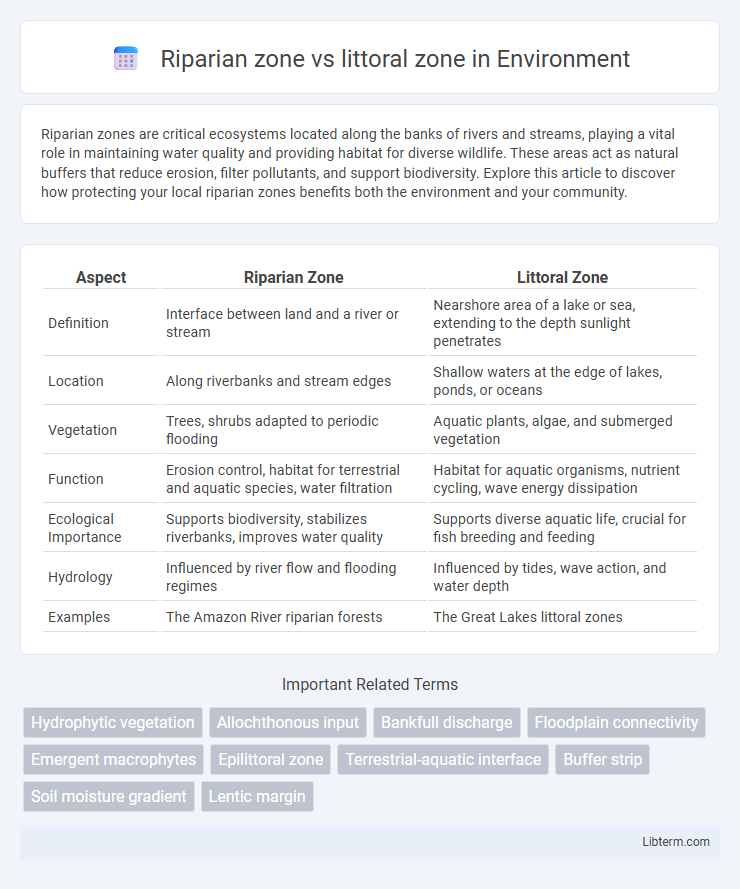
| Aspect | Riparian Zone | Littoral Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interface between land and a river or stream | Nearshore area of a lake or sea, extending to the depth sunlight penetrates |
| Location | Along riverbanks and stream edges | Shallow waters at the edge of lakes, ponds, or oceans |
| Vegetation | Trees, shrubs adapted to periodic flooding | Aquatic plants, algae, and submerged vegetation |
| Function | Erosion control, habitat for terrestrial and aquatic species, water filtration | Habitat for aquatic organisms, nutrient cycling, wave energy dissipation |
| Ecological Importance | Supports biodiversity, stabilizes riverbanks, improves water quality | Supports diverse aquatic life, crucial for fish breeding and feeding |
| Hydrology | Influenced by river flow and flooding regimes | Influenced by tides, wave action, and water depth |
| Examples | The Amazon River riparian forests | The Great Lakes littoral zones |
Introduction to Riparian and Littoral Zones
Riparian zones are the interface areas between land and a river or stream, characterized by unique vegetation and soil conditions supporting diverse aquatic and terrestrial species. Littoral zones refer to the nearshore areas of lakes, ponds, or oceans where sunlight penetrates to the sediment, enabling photosynthesis and sustaining a wide range of aquatic plants and animals. Both zones play crucial roles in maintaining ecosystem health, water quality, and habitat connectivity in freshwater and coastal environments.
Defining the Riparian Zone
The riparian zone is the interface between land and a river or stream, characterized by distinct vegetation and soil conditions influenced by the presence of flowing freshwater. This zone plays a critical role in maintaining water quality, providing habitat for diverse wildlife, and stabilizing stream banks through root systems that prevent erosion. Unlike the littoral zone, which refers to the nearshore area of a lake or ocean influenced primarily by wave action and light penetration, the riparian zone is defined by its proximity to running water and its dynamic hydrological processes.
Characteristics of the Littoral Zone
The littoral zone, found along the shorelines of lakes, ponds, and oceans, is characterized by shallow waters where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, promoting abundant aquatic plant growth and supporting diverse aquatic life. This zone is marked by fluctuating water levels and is home to various species of algae, invertebrates, and fish that rely on the rich habitat for spawning and feeding. The nutrient-rich sediment and high oxygen availability make the littoral zone a critical area for maintaining ecosystem productivity and biodiversity.
Key Differences Between Riparian and Littoral Zones
Riparian zones are land areas directly adjacent to rivers and streams, characterized by vegetation that stabilizes banks and supports aquatic ecosystems, while littoral zones refer to the shallow water areas near shorelines of lakes and ponds, rich in aquatic plants and providing habitat for diverse fish and invertebrates. Riparian zones primarily influence water quality and sediment control through terrestrial-aquatic interactions, whereas littoral zones focus on light penetration and nutrient cycling within the water column. Both zones are crucial for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance but differ fundamentally in their location, ecological functions, and dominant vegetation types.
Ecological Functions of Riparian Zones
Riparian zones regulate water quality by filtering sediments, nutrients, and pollutants before they enter aquatic ecosystems, enhancing overall habitat health. These areas provide critical habitat and migration corridors for diverse wildlife, supporting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Riparian vegetation stabilizes stream banks, reducing erosion and maintaining the physical structure essential for aquatic life sustainability.
Ecological Importance of Littoral Zones
Littoral zones, the nearshore areas of lakes and oceans where sunlight penetrates to the sediment allowing aquatic plants to grow, serve as critical habitats supporting high biodiversity and complex food webs. These zones facilitate nutrient cycling and provide spawning grounds, shelter, and feeding areas for numerous fish species and invertebrates, contributing substantially to ecosystem productivity. Riparian zones, by contrast, are terrestrial-aquatic interfaces along stream and river banks, primarily influencing water quality through sediment filtration and bank stabilization rather than directly supporting aquatic biodiversity like the littoral zones.
Common Flora and Fauna in Riparian Zones
Riparian zones are characterized by diverse vegetation including willows, cottonwoods, and alders, which provide crucial habitat for bird species such as kingfishers, herons, and warblers. Aquatic and semi-aquatic fauna like beavers, frogs, and various fish species thrive in these moist environments, relying on the vegetation for shelter and food. This biodiversity contrasts with littoral zones, which are typically dominated by submerged and emergent aquatic plants and support different communities adapted to shallow water conditions.
Typical Plant and Animal Life in Littoral Zones
Littoral zones host diverse aquatic plants such as cattails, water lilies, and submerged macrophytes that thrive in shallow waters with abundant sunlight. These zones support various animals including amphibians like frogs, fish species such as bass and perch, and numerous invertebrates like snails and insect larvae. In contrast, riparian zones, located along riverbanks, primarily feature terrestrial and semi-aquatic vegetation like willows and cottonwoods, supporting mammals and birds adapted to fluctuating water levels.
Human Impacts on Riparian and Littoral Environments
Human activities such as urban development, agriculture, and deforestation significantly degrade riparian zones by increasing sedimentation, nutrient runoff, and habitat fragmentation, which alters water quality and disrupts aquatic ecosystems. Littoral zones face pressures from shoreline modification, pollution, and invasive species introduction that reduce biodiversity and impair the natural filtration functions critical to maintaining water clarity. Effective management strategies targeting riparian buffers and littoral habitat restoration are essential to mitigate these impacts and preserve ecosystem services.
Conservation Strategies for Riparian and Littoral Zones
Conservation strategies for riparian zones emphasize restoring native vegetation to stabilize stream banks, improve water quality, and provide habitat connectivity for aquatic and terrestrial species. Littoral zone conservation focuses on managing shoreline development and controlling invasive aquatic plants to maintain biodiversity and protect fish spawning areas. Both zones require integrated water regulation practices and community engagement to enhance ecosystem resilience and support sustainable land and water use.
Riparian zone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com