Saline mine drainage occurs when water interacts with exposed salts and minerals in mining sites, leading to elevated salinity levels in local waterways. This process can severely impact aquatic ecosystems and water quality, posing challenges for environmental management. Explore the rest of this article to understand the causes, effects, and solutions for managing saline mine drainage effectively.
Table of Comparison
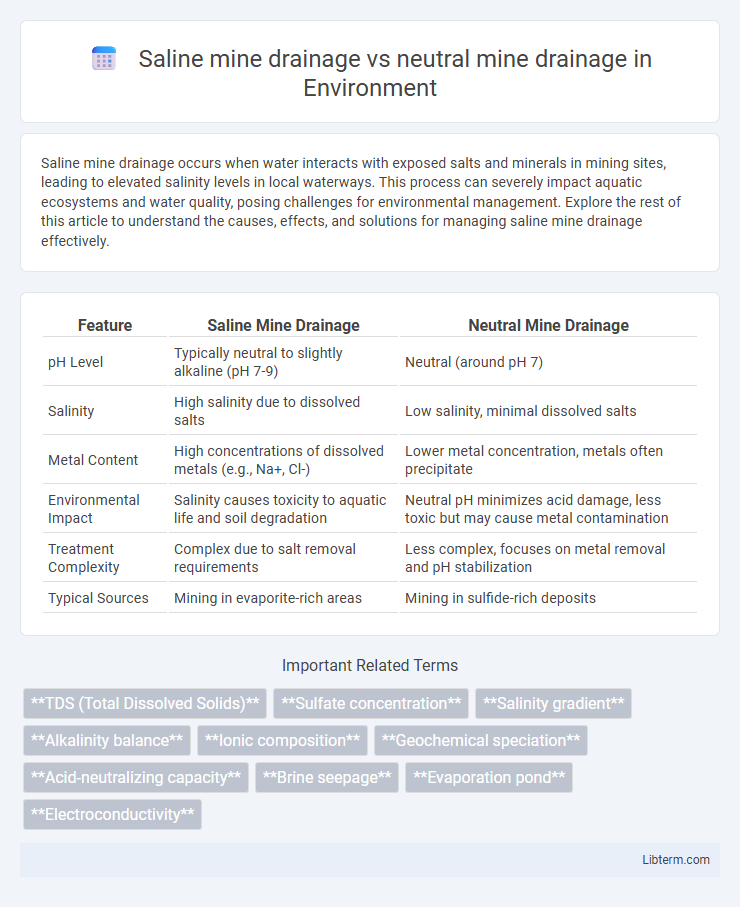
| Feature | Saline Mine Drainage | Neutral Mine Drainage |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | Typically neutral to slightly alkaline (pH 7-9) | Neutral (around pH 7) |
| Salinity | High salinity due to dissolved salts | Low salinity, minimal dissolved salts |
| Metal Content | High concentrations of dissolved metals (e.g., Na+, Cl-) | Lower metal concentration, metals often precipitate |
| Environmental Impact | Salinity causes toxicity to aquatic life and soil degradation | Neutral pH minimizes acid damage, less toxic but may cause metal contamination |
| Treatment Complexity | Complex due to salt removal requirements | Less complex, focuses on metal removal and pH stabilization |
| Typical Sources | Mining in evaporite-rich areas | Mining in sulfide-rich deposits |
Introduction to Mine Drainage Types
Saline mine drainage contains high concentrations of dissolved salts, often resulting from mining in coastal or evaporite-rich regions, leading to elevated salinity levels that impact water quality and aquatic life. Neutral mine drainage typically occurs when mine runoff maintains a near-neutral pH, caused by the presence of buffering minerals such as carbonates, resulting in fewer acidic impacts compared to acid mine drainage. Understanding these distinct mine drainage types is crucial for designing effective treatment strategies and mitigating environmental risks associated with mining operations.
Defining Saline Mine Drainage
Saline mine drainage (SMD) is characterized by elevated concentrations of dissolved salts, primarily sodium, chloride, sulfate, and magnesium, resulting from mining activities in areas with abundant evaporite minerals. Unlike neutral mine drainage, which typically maintains a near-neutral pH and contains low salt content, SMD presents distinct challenges in water treatment due to its high salinity and ionic strength. Understanding the chemical composition and environmental impact of SMD is crucial for effective management and remediation strategies in mining regions with saline geology.
Understanding Neutral Mine Drainage
Neutral mine drainage occurs when water interacts with sulfide minerals but maintains a near-neutral pH, typically between 6 and 8, resulting in less acidic conditions than saline mine drainage. This type of drainage often contains dissolved metals like iron and manganese but causes lower environmental harm due to reduced metal solubility and precipitation. Understanding the chemistry and behavior of neutral mine drainage is essential for effective remediation strategies and minimizing ecological impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
Sources of Salinity in Mine Waters
Saline mine drainage primarily originates from the dissolution of evaporite minerals such as halite and gypsum during mining activities, releasing high concentrations of sodium, chloride, sulfate, and other ions into surrounding waters. In contrast, neutral mine drainage typically involves oxidation of sulfide minerals like pyrite that generate sulfate and iron but maintain near-neutral pH without significant salinity increase. These sources of salinity in mine waters critically influence treatment strategies and environmental impacts due to their differing chemical compositions and loading characteristics.
Chemical Characteristics: Saline vs Neutral Drainage
Saline mine drainage typically exhibits high concentrations of dissolved salts such as sodium, chloride, and sulfate, resulting in elevated electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids, while neutral mine drainage maintains near-neutral pH levels with lower salinity and reduced ionic strength. The chemical profile of saline drainage often includes elevated levels of metals like iron, manganese, and heavy metals complexed with chloride ions, whereas neutral mine drainage favors metal precipitation due to neutral pH, limiting metal mobility. These distinct chemical characteristics influence the treatment strategies and environmental impact assessments for each type of mine drainage.
Environmental Impacts of Saline Mine Drainage
Saline mine drainage releases high concentrations of dissolved salts, such as sulfates and chlorides, into surrounding water bodies, which can lead to increased water salinity and harm aquatic ecosystems by disrupting osmoregulation in freshwater species. Unlike neutral mine drainage, which primarily affects pH levels, saline drainage poses long-term threats to soil quality and vegetation through salt accumulation and reduced soil permeability. The persistence of saline contaminants in groundwater and surface waters also complicates remediation efforts and limits the availability of freshwater resources for human and agricultural use.
Effects of Neutral Mine Drainage on Ecosystems
Neutral mine drainage typically exhibits a pH close to neutral (6-8), contrasting with acidic conditions in saline mine drainage, resulting in less metal solubility and toxicity. This neutral pH environment allows for higher biodiversity and supports more complex aquatic ecosystems, although elevated concentrations of metals like iron, manganese, and sulfate can still pose risks to sensitive species. The presence of neutral mine drainage can lead to bioaccumulation of contaminants in food webs, potentially disrupting reproductive cycles and reducing species richness over time.
Treatment Methods for Saline Mine Drainage
Saline mine drainage requires treatment methods that address high concentrations of dissolved salts, typically involving advanced membrane filtration such as reverse osmosis or nanofiltration to effectively remove ions like chloride and sulfate. Biological treatment methods, including halophilic bacteria, can also be utilized to degrade organic contaminants in saline conditions. Chemical precipitation combined with constructed wetlands designed for saline environments enhances removal efficiency, enabling environmentally compliant discharge.
Management Strategies for Neutral Mine Drainage
Management strategies for neutral mine drainage primarily involve chemical precipitation, biological treatment, and constructed wetlands to remove heavy metals and control pH levels. Implementing lime dosing and aeration enhances metal hydroxide precipitation, while sulfate-reducing bioreactors promote metal immobilization in anaerobic conditions. Monitoring and adaptive management ensure effective treatment, mitigating environmental impacts associated with neutral mine drainage.
Comparative Analysis: Saline versus Neutral Mine Drainage
Saline mine drainage contains high concentrations of dissolved salts, primarily sodium, chloride, and sulfate ions, leading to elevated electrical conductivity and potential toxicity to aquatic ecosystems. Neutral mine drainage typically exhibits near-neutral pH levels and lower salinity, resulting in reduced metal solubility and less impact on water quality compared to saline drainage. Comparative analysis reveals that saline mine drainage poses greater challenges for treatment and environmental management due to its increased salinity and complex ion composition, whereas neutral mine drainage treatment focuses on metal precipitation and pH stabilization.
Saline mine drainage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com