The littoral zone is the coastal area where land meets the sea, characterized by dynamic interactions between marine and terrestrial ecosystems. This zone supports diverse species and plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling, habitat provision, and shoreline protection. Explore the rest of the article to understand the ecological importance and challenges facing your local littoral zones.
Table of Comparison
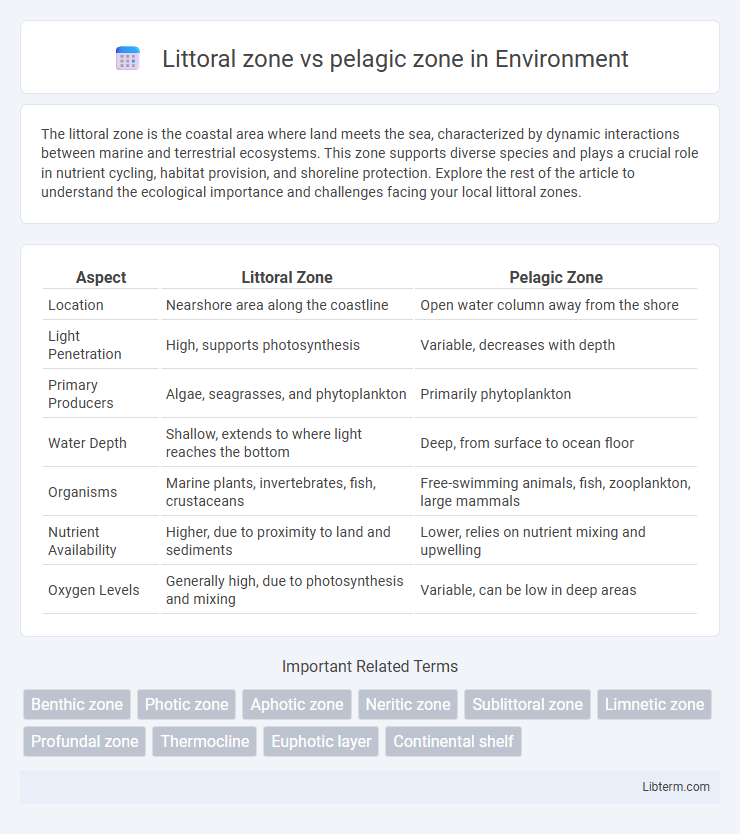
| Aspect | Littoral Zone | Pelagic Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Nearshore area along the coastline | Open water column away from the shore |
| Light Penetration | High, supports photosynthesis | Variable, decreases with depth |
| Primary Producers | Algae, seagrasses, and phytoplankton | Primarily phytoplankton |
| Water Depth | Shallow, extends to where light reaches the bottom | Deep, from surface to ocean floor |
| Organisms | Marine plants, invertebrates, fish, crustaceans | Free-swimming animals, fish, zooplankton, large mammals |
| Nutrient Availability | Higher, due to proximity to land and sediments | Lower, relies on nutrient mixing and upwelling |
| Oxygen Levels | Generally high, due to photosynthesis and mixing | Variable, can be low in deep areas |
Introduction to Aquatic Zones
The littoral zone is the nearshore area of a water body where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, supporting diverse plant life and providing habitat for numerous aquatic species. In contrast, the pelagic zone refers to the open water region away from the shore, extending from the surface to the deep ocean or lake depths, characterized by free-swimming organisms and limited vegetation. Both zones play critical roles in aquatic ecosystems by sustaining distinct communities and contributing to overall biodiversity.
Defining the Littoral Zone
The littoral zone is the nearshore area of a body of water where sunlight penetrates to the sediment, allowing aquatic plants to root and thrive, distinguishing it from the open water pelagic zone. Characterized by shallow depths and abundant nutrients, the littoral zone supports diverse ecosystems including algae, invertebrates, and fish species that depend on vegetation and substrate for shelter and breeding. In contrast, the pelagic zone refers to deeper, open water away from the shore, where light availability decreases and aquatic life adapts to a more open environment without the structural habitat provided by the littoral zone.
Understanding the Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone encompasses the open ocean waters away from the coast and sea floor, characterized by its vast and deep environment where sunlight penetration varies from surface to deeper layers. It supports a diverse range of organisms including plankton, fish, and marine mammals adapted to varying light, pressure, and temperature conditions. Unlike the littoral zone, which lies near shorelines and supports abundant plant growth, the pelagic zone is dominated by free-swimming species and plays a critical role in global carbon cycling and oceanic food webs.
Key Differences Between Littoral and Pelagic Zones
The littoral zone refers to the nearshore area of a body of water where sunlight penetrates to the bottom, supporting abundant aquatic plant life and diverse animal species. In contrast, the pelagic zone encompasses the open water column away from the shore, characterized by limited light penetration and organisms adapted for free swimming or floating. Key differences include light availability, habitat structure, and biodiversity, with the littoral zone hosting rooted vegetation and higher biological productivity compared to the largely planktonic and nektonic life forms of the pelagic zone.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
The littoral zone is the nearshore area where sunlight penetrates to the sediment, allowing rooted aquatic plants to thrive, characterized by shallow depths, variable temperatures, and high nutrient availability. In contrast, the pelagic zone refers to the open water column beyond the littoral zone, featuring deeper waters with lower nutrient concentrations, stable temperatures, and diminished light penetration as depth increases. Physical characteristics of the littoral zone promote diverse benthic habitats, while the pelagic zone supports free-swimming organisms adapted to a more uniform aquatic environment.
Biological Diversity in Each Zone
The littoral zone, characterized by shallow waters and abundant sunlight, supports diverse aquatic plants, algae, invertebrates, and fish species that rely on complex habitats like submerged vegetation and rocky substrates. In contrast, the pelagic zone, encompassing open water away from the shore, hosts plankton, large pelagic fish, marine mammals, and migratory species adapted to a vast, nutrient-variable environment with fewer structural habitats. Biological diversity in the littoral zone tends to be higher due to habitat complexity, while the pelagic zone features specialized species adapted to wide-ranging depths and open-water food webs.
Ecological Roles and Functions
The littoral zone, characterized by shallow waters near shorelines, supports diverse aquatic plants and serves as a crucial breeding and feeding habitat for fish, amphibians, and invertebrates, enhancing nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. In contrast, the pelagic zone comprises the open water column away from the shore, dominated by plankton, nekton, and free-swimming organisms, playing a vital role in primary production and serving as a conduit for energy transfer through marine food webs. Both zones contribute to ecosystem stability but differ significantly in biotic composition and ecological processes, with the littoral zone focusing on benthic interactions and the pelagic zone emphasizing pelagic trophic dynamics.
Adaptations of Organisms in Both Zones
Organisms in the littoral zone exhibit adaptations such as strong attachment mechanisms, like holdfasts or suction discs, to withstand wave action and fluctuating water levels, while many possess tolerance to varying salinity and temperature. In contrast, pelagic zone species demonstrate adaptations for buoyancy control, including swim bladders in fish or oil-filled bodies in zooplankton, along with streamlined shapes for efficient swimming and enhanced sensory organs to detect prey in open water. Both zones support diverse respiratory and feeding adaptations, with littoral organisms often filter-feeding or grazing on benthic algae, and pelagic organisms relying on predation or plankton consumption.
Human Impacts on Littoral and Pelagic Zones
Human activities significantly impact littoral zones through coastal development, pollution, and habitat destruction, leading to loss of biodiversity and altered water quality. In pelagic zones, overfishing, marine debris, and chemical contaminants disrupt food webs and decrease fish populations. Both zones suffer from climate change effects, including ocean acidification and temperature rise, which further threaten aquatic ecosystems.
Conservation Strategies for Aquatic Zones
Conservation strategies for the littoral zone emphasize habitat restoration, controlling nutrient runoff, and protecting aquatic vegetation vital for biodiversity and shoreline stabilization. In the pelagic zone, efforts focus on sustainable fishing practices, monitoring water quality, and mitigating pollution to preserve open-water ecosystems and pelagic species diversity. Both zones benefit from integrated management approaches combining scientific monitoring, community engagement, and regulatory frameworks.
Littoral zone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com