Snow melt plays a crucial role in replenishing freshwater resources and maintaining ecosystem balance by slowly releasing water into rivers and soil. Understanding the timing and rate of snow melt helps predict flood risks and manage water supplies effectively. Discover how snow melt impacts your environment and what factors influence this natural process in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
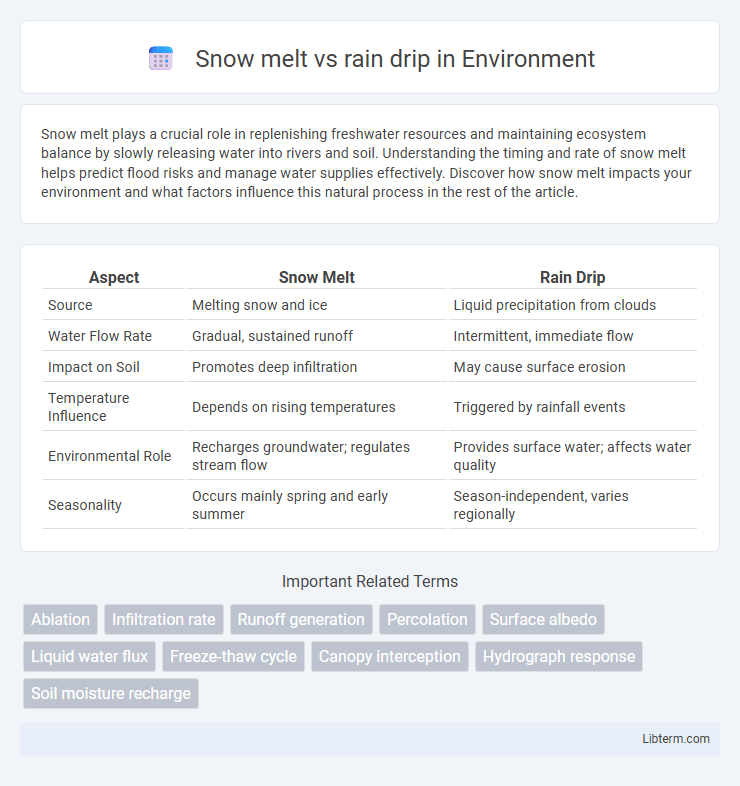
| Aspect | Snow Melt | Rain Drip |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Melting snow and ice | Liquid precipitation from clouds |
| Water Flow Rate | Gradual, sustained runoff | Intermittent, immediate flow |
| Impact on Soil | Promotes deep infiltration | May cause surface erosion |
| Temperature Influence | Depends on rising temperatures | Triggered by rainfall events |
| Environmental Role | Recharges groundwater; regulates stream flow | Provides surface water; affects water quality |
| Seasonality | Occurs mainly spring and early summer | Season-independent, varies regionally |
Understanding Snow Melt and Rain Drip
Snow melt occurs when accumulated snow absorbs enough heat to transition into liquid water, influenced by temperature, solar radiation, and surface conditions. Rain drip refers to water droplets falling from surfaces like tree leaves or rooftops after rainfall, shaping localized moisture distribution. Differentiating between snow melt and rain drip is vital for hydrological studies, as each affects groundwater recharge and surface runoff distinctly.
Key Differences in Water Sources
Snow melt originates from frozen precipitation accumulating on surfaces and gradually turning into liquid water as temperatures rise, whereas rain drip results directly from liquid precipitation falling through the atmosphere. The key difference lies in the phase change process involved in snow melt, which can influence the timing and volume of water runoff compared to rain drip. Snow melt often provides a sustained release of water over time, while rain drip typically leads to immediate surface moisture input.
Seasonal Patterns: Snow Melt vs Rain Drip
Snow melt typically occurs during spring when rising temperatures cause accumulated snow to thaw gradually, resulting in a steady and prolonged water release that recharges groundwater and sustains stream flow. Rain drip, by contrast, happens whenever precipitation falls as rain, often leading to immediate but shorter-term water input that can cause quicker surface runoff and localized soil saturation. Seasonal patterns differ as snow melt contributes to base flow increase during transition seasons, while rain drip varies with rainfall events, influencing hydrological cycles more sporadically.
Impact on Soil Moisture
Snow melt provides a slow, sustained release of water that deeply infiltrates the soil, enhancing soil moisture retention and supporting plant roots during dry periods. In contrast, rain drip delivers more immediate but often shallower water absorption, which can lead to quicker runoff and less effective soil moisture replenishment. The gradual infiltration from snow melt contributes to improved groundwater recharge and stable soil moisture levels crucial for ecosystem health.
Effects on Water Table and Groundwater Recharge
Snowmelt provides a gradual, sustained infiltration that enhances groundwater recharge by allowing water to percolate deeply into aquifers, leading to a steady rise in the water table. In contrast, rain drip often results in rapid surface runoff, reducing infiltration rates and limiting groundwater replenishment, especially during intense or short-duration storms. This difference in hydrological dynamics significantly influences water availability, aquifer storage capacity, and the timing of groundwater flow in watershed ecosystems.
Influence on Agriculture and Crops
Snow melt provides a reliable, slow-release water source that gradually infiltrates soil, replenishing groundwater and supporting crop growth during early spring. Rain drip offers more immediate moisture but can lead to soil erosion or nutrient runoff if heavy, affecting crop health and soil fertility. Understanding the balance between snow melt and rain drip is crucial for optimizing irrigation strategies and ensuring consistent agricultural yield.
Role in Urban Drainage Systems
Snow melt generates a steady and prolonged flow of water that urban drainage systems must efficiently channel to prevent flooding and ice formation. Rain drip creates intermittent, often concentrated runoff that can overwhelm localized drainage capacity during heavy precipitation events. Effective urban drainage design incorporates features like permeable pavements and retention basins to manage both slow snow melt and rapid rain drip, reducing water accumulation and infrastructure strain.
Environmental Impacts and Ecosystem Responses
Snowmelt delivers a sustained release of cold, oxygen-rich water into ecosystems, supporting aquatic life and replenishing groundwater but can contribute to soil erosion and nutrient runoff if excessive. Rain drip provides more immediate but intermittent moisture inputs, favoring surface-level vegetation growth and reducing soil saturation risks, yet may lead to variability in water availability for wildlife. Both processes influence hydrological cycles, with snowmelt driving seasonal water pulses and rain drip modulating short-term ecosystem responses.
Climate Change Implications
Snow melt accelerates water runoff, leading to earlier peak streamflows and reduced groundwater recharge compared to consistent rain drip, disrupting freshwater availability. Rain drip maintains gradual soil infiltration and supports stable ecosystems, whereas climate change intensifies snow melt patterns, increasing flood risks and altering hydrological cycles. These shifts challenge water resource management and biodiversity conservation in regions dependent on snowpack dynamics.
Strategies for Managing Snow Melt and Rain Drip
Effective strategies for managing snow melt and rain drip include installing heated gutters and downspouts to prevent ice dams and ensure proper water flow. Utilizing permeable pavements and strategic landscaping enhances water absorption and reduces runoff during heavy precipitation events. Incorporating snow melt sensors and automated drainage systems optimizes timely water removal, minimizing structural damage and soil erosion.
Snow melt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com