A tidal bore is a natural phenomenon where a strong tide pushes up a river or narrow bay, creating a wave that travels against the current, unlike a typical ocean tidal wave generated by seismic activity. These powerful waves can vary in size and speed, often attracting surfers and scientists due to their unique behavior and impact on local ecosystems. Discover how tidal bores differ from tidal waves and what makes this extraordinary event so fascinating by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
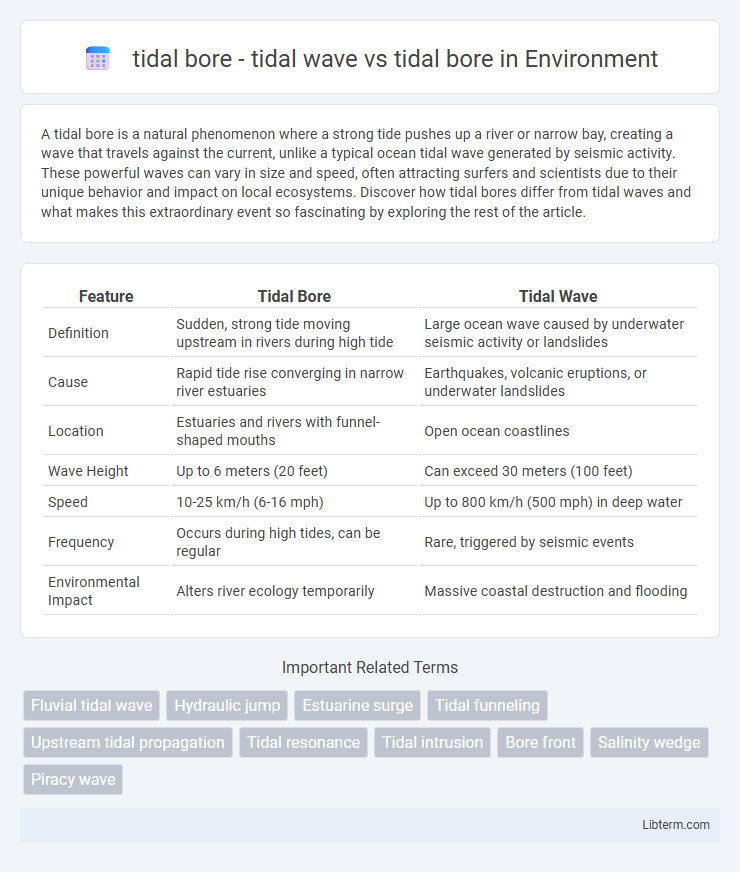
| Feature | Tidal Bore | Tidal Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden, strong tide moving upstream in rivers during high tide | Large ocean wave caused by underwater seismic activity or landslides |
| Cause | Rapid tide rise converging in narrow river estuaries | Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or underwater landslides |
| Location | Estuaries and rivers with funnel-shaped mouths | Open ocean coastlines |
| Wave Height | Up to 6 meters (20 feet) | Can exceed 30 meters (100 feet) |
| Speed | 10-25 km/h (6-16 mph) | Up to 800 km/h (500 mph) in deep water |
| Frequency | Occurs during high tides, can be regular | Rare, triggered by seismic events |
| Environmental Impact | Alters river ecology temporarily | Massive coastal destruction and flooding |
Understanding Tidal Phenomena: Tidal Bores vs. Tidal Waves
Tidal bores are unique tidal phenomena where incoming tides travel against the river current, creating a visible wave that moves upstream, often seen in specific estuaries like the Qiantang River in China. Tidal waves, commonly confused with tsunamis, are large oceanic waves caused by underwater seismic activity and are unrelated to tidal forces. Understanding the difference between tidal bores and tidal waves is essential for coastal management and predicting their distinct environmental impacts.
What Is a Tidal Bore?
A tidal bore is a natural phenomenon where the leading edge of an incoming tide forms a large wave that travels upstream against the river's current. Unlike a typical tidal wave caused by seismic activity, a tidal bore occurs in specific river conditions with a substantial tidal range and narrowing river channels. This wave can reach speeds of up to 25 mph and heights of several feet, creating unique surfing opportunities and impacting river ecosystems.
How Do Tidal Bores Form?
Tidal bores form when incoming tides funnel into narrow, shallow river mouths or estuaries, causing a sudden and strong surge of water to travel upstream against the current. Unlike tidal waves, which are large oceanic wave disturbances often caused by seismic activity, tidal bores result from the specific topography and tidal range leading to the formation of a wave front moving against the river flow. Key factors include a large tidal range exceeding 6 meters and a converging river channel that amplifies the incoming tide into a visible bore.
Key Characteristics of Tidal Bores
Tidal bores are powerful, fast-moving waves that travel upstream in a river or narrow bay as the incoming tide forces seawater against the river current, distinct from typical tidal waves caused by tectonic activity. Key characteristics of tidal bores include their ability to form a breaking wave or series of waves, strong turbulence, and significant height that can range from a few inches to several meters, often accompanied by a loud roar. These unique dynamics create a sudden surge of water that contrasts with the gradual rise and fall of normal tides or the destructive nature of tsunami tidal waves.
What Is a Tidal Wave?
A tidal wave is a misnomer often used to describe a tsunami, which is a series of ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, not tidal forces. Unlike tidal bores, which occur when the incoming tide forms a wave that travels upstream in a river or narrow bay, tidal waves are unrelated to the regular rise and fall of sea level. Tidal waves involve massive energy displacements across the ocean floor, whereas tidal bores result from the funneling effect of tidal water meeting river currents.
Differences Between Tidal Bores and Tidal Waves
Tidal bores are powerful surges of seawater traveling upstream in narrow rivers or estuaries during high tide, characterized by a wavefront moving against the river's current. Tidal waves, often confused with tsunamis, refer to large, oceanic waves typically caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, not by tidal forces. The key difference lies in origin: tidal bores result from tidal action in confined river channels, while tidal waves stem from seismic activity in the ocean.
Famous Tidal Bores Around the World
Famous tidal bores such as the Qiantang River in China, the Severn Bore in the UK, and the Amazon River's Pororoca demonstrate the unique phenomenon where the incoming tide creates a powerful, fast-moving wave that travels upstream. Unlike tidal waves, which are often mistaken for tsunamis caused by seismic activity, tidal bores occur regularly due to specific tidal and river conditions. These iconic tidal bores attract surfers and scientists alike, showcasing nature's dynamic interactions between ocean tides and river systems globally.
Ecological and Environmental Impacts of Tidal Bores
Tidal bores are powerful surges of seawater traveling upriver during high tides, significantly impacting river ecosystems by altering sediment distribution and nutrient flows. Unlike tidal waves, which are large oceanic waves typically caused by seismic activity, tidal bores contribute to maintaining estuarine habitats and supporting diverse aquatic species by creating unique tidal environments. The fluctuating salinity and oxygen levels caused by tidal bores promote biodiversity but can also disrupt freshwater species and lead to increased erosion along riverbanks.
Human Interactions and Activities Related to Tidal Bores
Tidal bores are unique natural phenomena where strong tidal currents push upriver against the current, creating a wave that attracts surfers and adventure seekers worldwide, especially in places like the Qiantang River in China and the Severn River in the UK. Local communities capitalize on these events through tourism, offering guided tours and festivals that celebrate the bore's cultural significance. However, human activities such as dam construction and riverbank development can disrupt the natural flow and frequency of tidal bores, impacting both ecosystems and traditional livelihoods dependent on these waves.
Safety Tips and Precautions Around Tidal Bores and Tidal Waves
Tidal bores, powerful surges of rising water traveling upstream in narrow rivers, demand caution due to unpredictable currents and strong waves that can easily sweep people away. Tidal waves, often confused with tsunamis, are large ocean waves caused by underwater disturbances and require immediate evacuation from coastal areas to avoid drowning and structural hazards. Safety tips include staying informed about local tidal schedules, avoiding riverbanks and shorelines during peak tidal bore or tsunami alerts, and following guidance from local authorities to minimize risk.
tidal bore - tidal wave Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com