Rapid urbanization transforms landscapes, driving economic growth while straining infrastructure and natural resources. Understanding the impact on housing, transportation, and public services is essential for sustainable city planning. Explore the rest of this article to learn how urbanization shapes your environment and future.
Table of Comparison
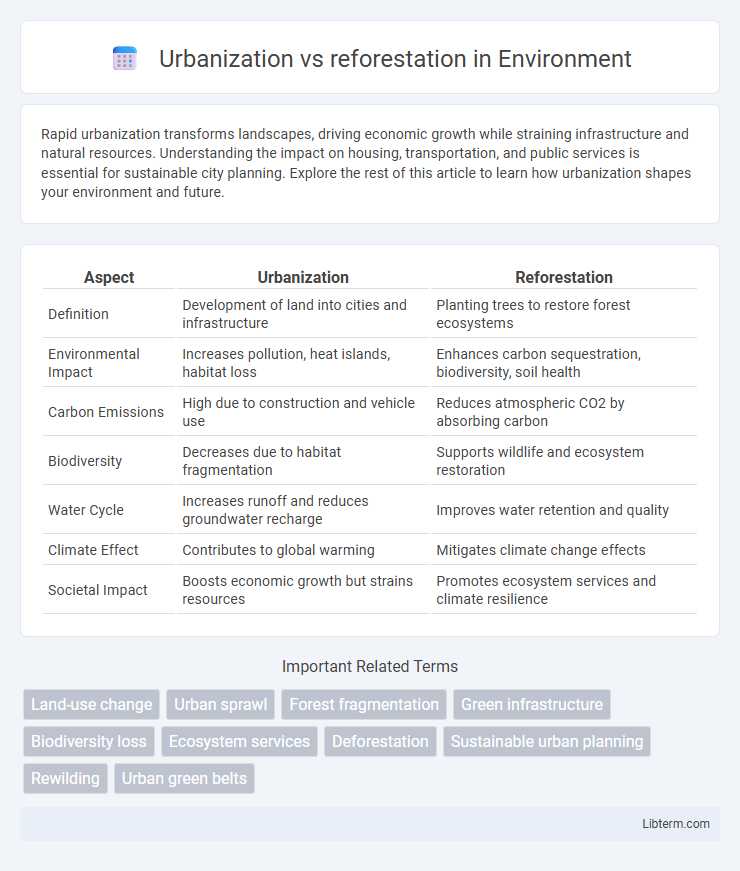
| Aspect | Urbanization | Reforestation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Development of land into cities and infrastructure | Planting trees to restore forest ecosystems |
| Environmental Impact | Increases pollution, heat islands, habitat loss | Enhances carbon sequestration, biodiversity, soil health |
| Carbon Emissions | High due to construction and vehicle use | Reduces atmospheric CO2 by absorbing carbon |
| Biodiversity | Decreases due to habitat fragmentation | Supports wildlife and ecosystem restoration |
| Water Cycle | Increases runoff and reduces groundwater recharge | Improves water retention and quality |
| Climate Effect | Contributes to global warming | Mitigates climate change effects |
| Societal Impact | Boosts economic growth but strains resources | Promotes ecosystem services and climate resilience |
Understanding Urbanization: Trends and Impacts
Urbanization drives significant land-use changes, with over 56% of the global population residing in cities as of 2023, contributing to habitat loss and increased carbon emissions. This rapid expansion often reduces green spaces, exacerbating urban heat islands and biodiversity decline. Understanding these trends is critical to balancing urban growth with reforestation efforts that enhance ecosystem services and carbon sequestration.
The Importance of Reforestation in Modern Cities
Reforestation in modern cities plays a critical role in mitigating the environmental impacts of rapid urbanization by improving air quality, reducing urban heat islands, and enhancing biodiversity. Green spaces created through urban reforestation contribute to carbon sequestration and improve mental health for city residents. Integrating reforestation initiatives within urban planning supports sustainable city development and resilience against climate change.
Urban Expansion: Challenges for Natural Ecosystems
Urban expansion leads to habitat fragmentation, reducing biodiversity and disrupting ecosystem services essential for air and water quality. Increased impervious surfaces from urbanization exacerbate runoff and pollution, hindering natural hydrological cycles critical for forest health. Balancing urban growth with reforestation initiatives is vital to maintaining ecological resilience and mitigating climate change impacts in rapidly developing areas.
Environmental Consequences of Rapid Urbanization
Rapid urbanization leads to significant environmental consequences such as increased air and water pollution, loss of biodiversity, and elevated greenhouse gas emissions. The replacement of natural landscapes with concrete surfaces disrupts ecosystems, reduces carbon sequestration, and exacerbates heat island effects. In contrast, reforestation efforts help mitigate these impacts by restoring habitats, improving air quality, and enhancing carbon storage capacity.
Reforestation as a Countermeasure to Urban Sprawl
Reforestation mitigates the environmental impact of urban sprawl by restoring natural habitats, improving air quality, and enhancing biodiversity in expanding metropolitan areas. Strategic tree planting and forest restoration projects serve as natural carbon sinks, offsetting emissions generated by increased urban development. Integrating reforestation into urban planning supports sustainable growth while maintaining ecosystem services and reducing the heat island effect.
Socio-Economic Effects of Urbanization vs Reforestation
Urbanization drives economic growth by creating job opportunities, enhancing infrastructure, and increasing access to services, but it often leads to social disparities, overcrowding, and strain on resources. Reforestation fosters environmental sustainability, supports rural economies through timber and non-timber products, and improves public health by enhancing air quality and providing recreational spaces. Balancing urban development with reforestation initiatives can mitigate socio-economic challenges while promoting long-term ecological and community well-being.
Urban Green Spaces: Bridging Development and Nature
Urban green spaces serve as vital ecological corridors that mitigate the environmental impacts of urbanization by enhancing air quality, reducing urban heat islands, and supporting biodiversity within cities. Reforestation efforts complement these spaces by restoring native habitats and increasing carbon sequestration, creating a balanced approach to sustainable urban development. Integrating urban green spaces with reforestation initiatives fosters resilient, health-promoting environments that bridge the gap between rapid urban expansion and nature conservation.
Biodiversity Loss: Urbanization’s Toll vs Reforestation’s Gains
Urbanization accelerates habitat destruction, causing significant biodiversity loss by fragmenting ecosystems and displacing native species. In contrast, reforestation restores habitats, enhancing species richness and promoting ecological balance. Effective reforestation initiatives can mitigate the impacts of urban expansion by creating green corridors and supporting the recovery of endangered flora and fauna.
Sustainable Urban Planning: Integrating Trees into Cities
Sustainable urban planning incorporates reforestation principles by integrating trees and green spaces into city landscapes, improving air quality and reducing urban heat islands. Effective strategies include planting native tree species along streets, in parks, and on rooftops to promote biodiversity and carbon sequestration. Urban forestry not only enhances aesthetic value but also supports climate resilience and residents' well-being, balancing urbanization with ecological sustainability.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Urban Growth and Forest Restoration
Future perspectives on balancing urban growth and forest restoration emphasize integrating green infrastructure into city planning to promote sustainable urbanization while preserving biodiversity. Advances in technology and policy support the development of urban forests, green roofs, and vertical gardens to mitigate the environmental impact of expanding metropolitan areas. Collaborative efforts between governments, urban planners, and environmental organizations aim to create resilient cities that harmonize economic development with forest ecosystem restoration.
Urbanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com