Ecotones are transitional zones between two distinct ecological communities where species from both environments coexist, creating areas of high biodiversity and unique interactions. These regions often display increased ecological activity and play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem health and resilience. Explore the rest of this article to understand how ecotones impact your local environment and global ecosystems.
Table of Comparison
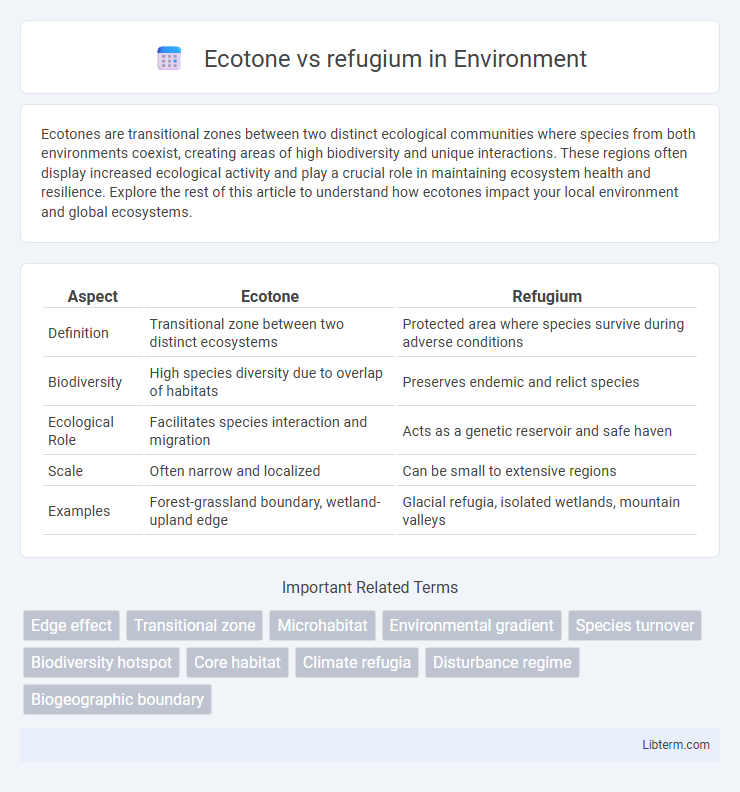
| Aspect | Ecotone | Refugium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transitional zone between two distinct ecosystems | Protected area where species survive during adverse conditions |
| Biodiversity | High species diversity due to overlap of habitats | Preserves endemic and relict species |
| Ecological Role | Facilitates species interaction and migration | Acts as a genetic reservoir and safe haven |
| Scale | Often narrow and localized | Can be small to extensive regions |
| Examples | Forest-grassland boundary, wetland-upland edge | Glacial refugia, isolated wetlands, mountain valleys |
Introduction to Ecotones and Refugia
Ecotones represent transitional zones between distinct ecological communities, characterized by high species diversity and unique environmental gradients. Refugia are areas that provide stable habitats enabling species survival during adverse climatic periods, often serving as genetic reservoirs. Both ecotones and refugia play critical roles in biodiversity conservation and ecosystem resilience by supporting species adaptation and persistence.
Defining Ecotone: Characteristics and Functions
An ecotone is a transitional zone where two distinct ecosystems or biomes meet and integrate, exhibiting characteristics from both adjacent environments and increased species diversity. This edge habitat often experiences greater biodiversity and ecological interactions due to the overlap of conditions and resources from the neighboring ecosystems. Ecotones function as critical areas for species migration, adaptation, and ecological stability, providing unique niches that support diverse wildlife populations.
Understanding Refugium: Key Features and Importance
Refugiums are specialized habitats that provide sanctuary for species during environmental stress, maintaining biodiversity and enabling population recovery. Unlike ecotones, refugiums act as stable environments, buffering against climate fluctuations and habitat loss by preserving rare or endangered species. Their role in conservation biology is crucial, as they support genetic diversity and serve as sources for recolonization in degraded ecosystems.
Ecological Significance of Ecotones
Ecotones are transition zones between two different ecological communities where species from both habitats coexist, often resulting in higher biodiversity and increased species interactions compared to the adjoining ecosystems. These areas serve as critical sites for ecological processes such as nutrient cycling, habitat connectivity, and gene flow, enhancing ecosystem resilience and adaptability. The ecological significance of ecotones lies in their role as hotspots for adaptation and evolution, providing unique microhabitats that support specialized species and ecological functions.
Biodiversity Hotspots: Ecotone vs Refugium
Ecotones and refugia are critical biodiversity hotspots that support distinct ecological functions; ecotones serve as transition zones between ecosystems, fostering species richness by merging habitats, while refugia act as safe havens for species during environmental stress and climate fluctuations. Both contribute uniquely to conservation strategies, with ecotones enhancing genetic exchange and species interactions, and refugia preserving vulnerable populations through adverse conditions. Understanding their roles supports targeted biodiversity management and ecosystem resilience in the face of global environmental change.
Roles in Species Adaptation and Survival
Ecotones provide transitional habitats that enhance species adaptation by promoting genetic diversity and facilitating migration between ecosystems, supporting survival under changing environmental conditions. Refugia serve as critical safe zones where species can persist during adverse climate periods, preserving biodiversity and enabling post-disturbance recolonization. Both ecotones and refugia play complementary roles in maintaining ecosystem resilience and species continuity amidst environmental stressors.
Impacts of Climate Change on Ecotones and Refugia
Climate change intensifies temperature fluctuations and alters precipitation patterns, disrupting ecotones where distinct ecosystems meet, leading to shifts in species composition and loss of biodiversity. Refugia serve as critical safe havens by providing stable microclimates and shelter from extreme climatic events, preserving genetic diversity during environmental upheaval. The degradation of ecotones and shrinking of refugia due to climate change threatens ecosystem resilience and complicates conservation efforts aimed at mitigating species extinction.
Human Influence on Ecotone and Refugium Dynamics
Human influence on ecotone and refugium dynamics significantly alters biodiversity patterns by fragmenting habitats and modifying environmental conditions. Urban development, agriculture, and pollution disrupt natural transitional zones (ecotones), reducing their connectivity and changing species composition, while refugia face increased risk from habitat loss and climate change-induced stress. Conservation strategies must integrate the impact of human activities on these critical ecological areas to maintain their role in supporting species resilience and evolutionary processes.
Conservation Strategies: Ecotones vs Refugia
Ecotones, characterized by the transitional zones between ecosystems, support high biodiversity and serve as natural corridors facilitating species migration and genetic exchange. Refugia are isolated habitats that provide safe havens for species during adverse environmental conditions, preserving genetic diversity and enabling species survival through climate fluctuations. Conservation strategies utilizing ecotones emphasize maintaining landscape connectivity, while refugia-focused approaches prioritize protecting stable, undisturbed habitats essential for long-term species persistence.
Future Research Directions in Ecotone and Refugium Studies
Future research directions in ecotone and refugium studies emphasize integrating high-resolution spatial data and advanced remote sensing technologies to map ecotones' dynamic boundaries and identify cryptic refugia. Investigations into climate change impacts and species' adaptive capacities within these transitional zones will enhance predictive models of biodiversity resilience. Emphasizing multi-disciplinary approaches, researchers aim to link ecological genetics with landscape ecology to understand organismal responses across shifting ecotones and refugia.
Ecotone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com