Drone monitoring offers unparalleled real-time data collection and aerial surveillance capabilities across various industries, enhancing efficiency and safety. By leveraging advanced sensors and high-resolution imaging, drones can capture detailed information from hard-to-reach areas, reducing human risk and operational costs. Discover how drone monitoring can transform your workflows and elevate your business by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
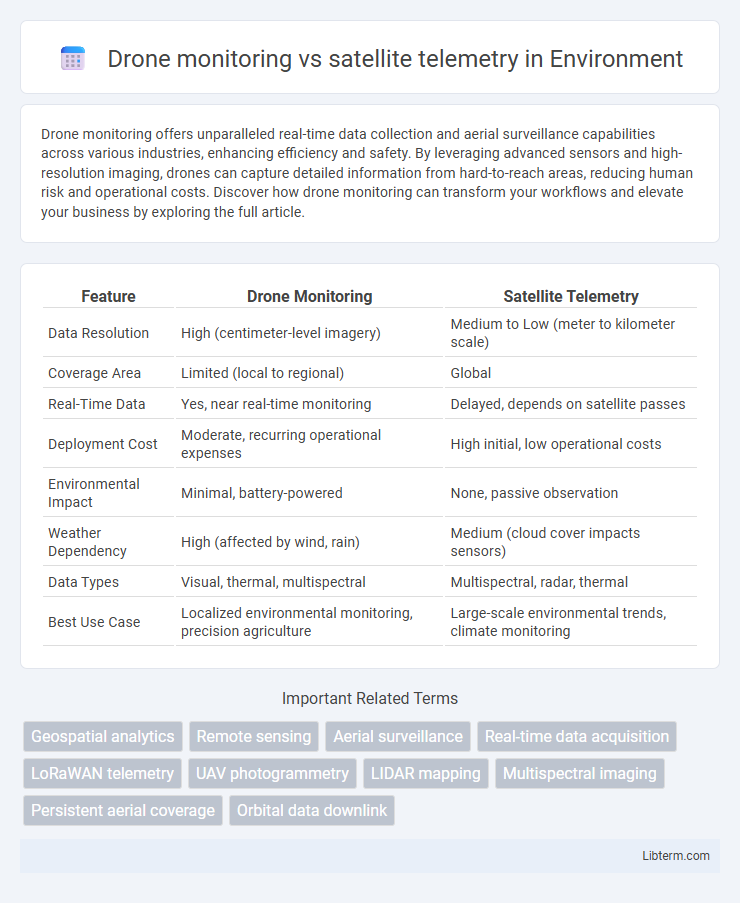
| Feature | Drone Monitoring | Satellite Telemetry |
|---|---|---|
| Data Resolution | High (centimeter-level imagery) | Medium to Low (meter to kilometer scale) |
| Coverage Area | Limited (local to regional) | Global |
| Real-Time Data | Yes, near real-time monitoring | Delayed, depends on satellite passes |
| Deployment Cost | Moderate, recurring operational expenses | High initial, low operational costs |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal, battery-powered | None, passive observation |
| Weather Dependency | High (affected by wind, rain) | Medium (cloud cover impacts sensors) |
| Data Types | Visual, thermal, multispectral | Multispectral, radar, thermal |
| Best Use Case | Localized environmental monitoring, precision agriculture | Large-scale environmental trends, climate monitoring |
Introduction to Drone Monitoring and Satellite Telemetry
Drone monitoring provides real-time, high-resolution data collection through remote piloted devices equipped with advanced sensors, enabling precise environmental and infrastructure assessments. Satellite telemetry offers extensive spatial coverage by transmitting data from orbiting satellites, facilitating continuous monitoring of Earth's surface, weather patterns, and global communications. Both technologies play crucial roles in data acquisition, yet drones excel in localized detail while satellite telemetry supports large-scale observation.
Core Technologies Behind Drones and Satellites
Drones leverage GPS modules, Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs), and real-time video transmission systems for precise aerial monitoring and immediate data relay. Satellites employ advanced telemetry sensors, radio frequency communication, and onboard processors to capture and transmit large-scale environmental and positional data globally. Both technologies rely on sophisticated signal processing and autonomous navigation algorithms to optimize data accuracy and operational efficiency.
Data Resolution: Ground-level vs. Space-based Observation
Drone monitoring provides high-resolution, ground-level data capturing fine details such as crop health, infrastructure conditions, or wildlife movements with centimeter-level accuracy. Satellite telemetry offers broader, space-based observation with lower spatial resolution, typically ranging from meters to kilometers, enabling large-area analysis over time but lacking granular detail. Combining both technologies enhances environmental monitoring by leveraging drones' precision and satellites' extensive coverage.
Coverage Area and Accessibility Comparison
Drone monitoring offers high-resolution, localized data within limited coverage areas typically spanning a few square kilometers, making it ideal for detailed, site-specific inspections. Satellite telemetry provides extensive coverage, reaching thousands of square kilometers to monitor large-scale phenomena such as weather patterns, environmental changes, and global communications. Accessibility is higher with drones due to flexible deployment and lower operational costs, whereas satellites require significant infrastructure and investment, limiting real-time interaction despite comprehensive geographic reach.
Real-Time Data Acquisition Capabilities
Drone monitoring provides superior real-time data acquisition capabilities compared to satellite telemetry due to its ability to capture high-resolution imagery and sensor data at low altitudes with minimal latency. Satellite telemetry, while effective for broad-area monitoring, often experiences delays and lower spatial resolution caused by orbital paths and atmospheric interference. The close proximity of drones to the target allows for immediate processing and rapid decision-making in dynamic environments.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Operational Expenses
Drone monitoring requires substantial initial investment in high-quality UAVs, sensors, and ground control systems, yet offers lower ongoing operational costs, including maintenance and data processing. Satellite telemetry demands significant expenditure on satellite development, launch, and ground station infrastructure, combined with high operational expenses for data transmission and satellite upkeep. Cost efficiency favors drones for localized, frequent monitoring, while satellite telemetry suits large-scale, less frequent data collection despite higher upfront and operational investments.
Flexibility and Mission Customization
Drone monitoring offers enhanced flexibility and mission customization by enabling real-time data collection at low altitudes with precise flight path adjustments tailored to specific objectives. Satellite telemetry provides broader coverage but operates on fixed schedules and orbits, limiting adaptability for dynamic or localized missions. The ability of drones to be rapidly deployed and reprogrammed in response to evolving conditions makes them ideal for targeted, flexible monitoring tasks.
Regulatory and Privacy Considerations
Drone monitoring offers granular data collection but faces stringent regulatory frameworks such as FAA Part 107 in the U.S., which limit flight areas and altitudes to protect privacy and ensure safety. Satellite telemetry operates under international space law and national regulations, often providing broader coverage with fewer privacy concerns due to lower spatial resolution. Both technologies require compliance with data protection laws like GDPR, emphasizing transparent data handling and user consent to mitigate privacy risks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Drone monitoring offers high-resolution, real-time data collection with minimal environmental disturbance, making it ideal for localized studies of ecosystems and wildlife habitats, while consuming less energy compared to satellite telemetry systems. Satellite telemetry provides extensive global coverage critical for long-term climate monitoring and tracking environmental changes across vast or inaccessible areas but involves significant carbon emissions during launch and operation phases. Combining drone monitoring's precision and satellite telemetry's broad scope enhances sustainability by optimizing data accuracy and reducing the overall environmental footprint of environmental monitoring efforts.
Future Trends: Integration and Advancement in Remote Sensing
Drone monitoring and satellite telemetry are increasingly integrated to enhance remote sensing capabilities, combining drones' high-resolution, low-altitude data with satellites' broad coverage and temporal consistency. Future trends emphasize advancements in AI-powered data processing and real-time analytics, enabling more precise environmental monitoring and disaster management. Enhanced connectivity between low Earth orbit satellites and autonomous drones will facilitate seamless data sharing, driving innovation in agriculture, urban planning, and climate change studies.
Drone monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com