Steam sterilization uses high-temperature steam under pressure to eliminate microorganisms on medical equipment and supplies. This method is recognized for its efficiency, safety, and ability to penetrate complex instruments, ensuring thorough sterilization. Discover how steam sterilization can protect your health and improve sterilization processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
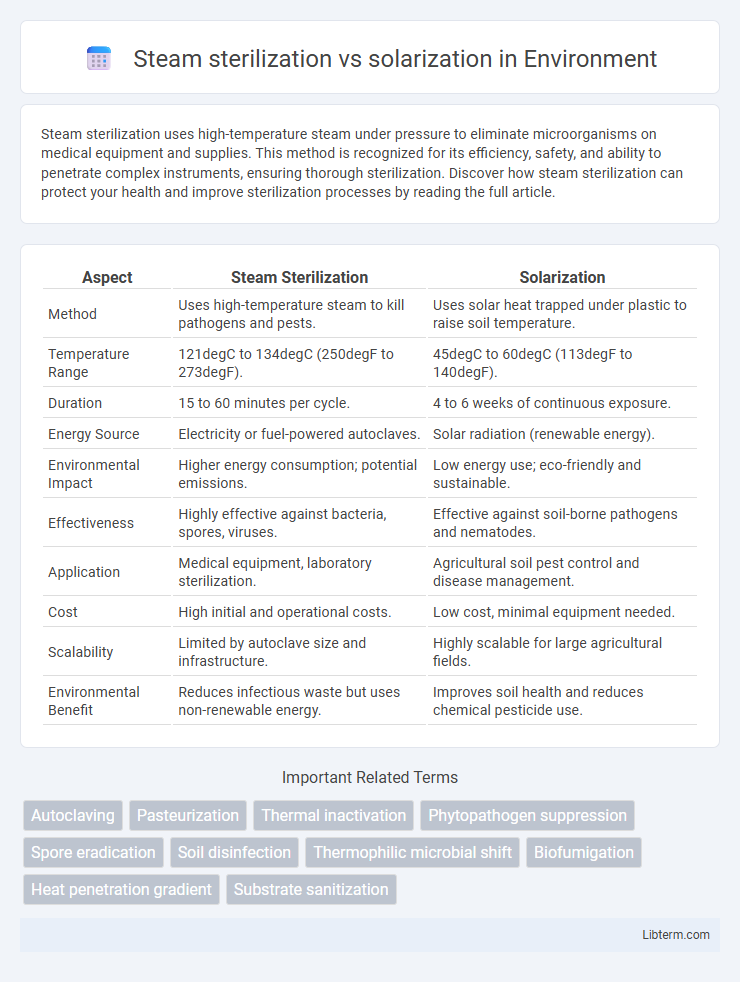
| Aspect | Steam Sterilization | Solarization |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Uses high-temperature steam to kill pathogens and pests. | Uses solar heat trapped under plastic to raise soil temperature. |
| Temperature Range | 121degC to 134degC (250degF to 273degF). | 45degC to 60degC (113degF to 140degF). |
| Duration | 15 to 60 minutes per cycle. | 4 to 6 weeks of continuous exposure. |
| Energy Source | Electricity or fuel-powered autoclaves. | Solar radiation (renewable energy). |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy consumption; potential emissions. | Low energy use; eco-friendly and sustainable. |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective against bacteria, spores, viruses. | Effective against soil-borne pathogens and nematodes. |
| Application | Medical equipment, laboratory sterilization. | Agricultural soil pest control and disease management. |
| Cost | High initial and operational costs. | Low cost, minimal equipment needed. |
| Scalability | Limited by autoclave size and infrastructure. | Highly scalable for large agricultural fields. |
| Environmental Benefit | Reduces infectious waste but uses non-renewable energy. | Improves soil health and reduces chemical pesticide use. |
Introduction to Soil Disinfection Methods
Soil disinfection methods such as steam sterilization and solarization are critical for controlling soil-borne pathogens and enhancing crop yield. Steam sterilization employs high-temperature steam (above 100degC) to eradicate pests, fungi, and weed seeds rapidly, ensuring thorough soil sanitization. Solarization utilizes solar energy by covering moist soil with transparent plastic sheets, raising soil temperatures to 45-60degC over several weeks, which suppresses pathogens through prolonged heat exposure.
What is Steam Sterilization?
Steam sterilization is a method that uses saturated steam under pressure to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including bacteria, viruses, spores, and fungi, from medical instruments, laboratory tools, and soil in agriculture. This process typically occurs at temperatures of 121-134degC for a specified duration, ensuring effective sterilization through moist heat penetration. Steam sterilization is widely regarded as a reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly technique compared to solarization, which relies on solar heat to reduce soil pathogens but lacks the consistent and thorough microbial kill rate of steam.
Understanding Solarization
Solarization uses solar energy to increase soil temperature, effectively controlling soilborne pathogens, weeds, and pests by trapping heat under a transparent plastic cover. This eco-friendly method promotes beneficial microbial activity and improves soil structure without chemical inputs, making it suitable for sustainable agriculture. Steam sterilization, in contrast, relies on high-temperature steam to rapidly eliminate soil contaminants, offering faster results but with higher energy consumption and cost.
Key Differences Between Steam Sterilization and Solarization
Steam sterilization uses high-temperature saturated steam at 121-134degC under pressure to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including spores, within minutes, ensuring complete sterilization. Solarization relies on trapping solar radiation to raise soil temperatures to 45-60degC over several weeks, reducing soil-borne pathogens but not achieving complete sterilization. The primary differences lie in temperature efficacy, application time, and the ability to sterilize, with steam offering rapid, thorough sterilization and solarization providing a slower, partial disinfection method ideal for field soil treatment.
Effectiveness Against Soilborne Pathogens
Steam sterilization achieves near-complete eradication of soilborne pathogens by heating soil to temperatures above 80degC, effectively killing fungi, bacteria, nematodes, and weed seeds within hours. Solarization relies on the sun's thermal energy to raise soil temperatures to 45-55degC over several weeks, significantly reducing but not eliminating many soilborne pathogens, particularly in regions with intense sunlight. While steam sterilization offers rapid and consistent pathogen control, solarization provides an energy-efficient, environmentally friendly alternative with moderate effectiveness dependent on climate conditions.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Steam sterilization consumes significant amounts of energy and water, leading to a higher carbon footprint compared to solarization, which relies on natural sunlight and minimal resource input. Solarization uses solar radiation to increase soil temperature, effectively reducing pathogens without emissions or chemical residues, promoting sustainable soil health. While steam sterilization offers rapid results, solarization is more environmentally friendly, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources.
Cost and Resource Requirements
Steam sterilization requires significant energy consumption and specialized equipment, leading to higher initial and operational costs compared to solarization. Solarization utilizes natural solar energy, making it a low-cost and environmentally friendly method with minimal resource inputs, but its effectiveness depends on favorable climatic conditions and prolonged exposure time. Cost-efficiency evaluations favor solarization in regions with abundant sunlight, while steam sterilization is preferred in controlled environments where rapid and consistent sterilization is essential.
Suitability for Different Crops and Environments
Steam sterilization is highly effective for a wide range of crops, especially in controlled greenhouse environments, by eliminating soil-borne pathogens and pests with consistent heat application. Solarization suits warm, sunny climates and is ideal for field crops, leveraging solar energy to raise soil temperatures and suppress harmful organisms naturally. Crop suitability depends on factors like soil type and climate; steam sterilization is preferred for high-value, sensitive crops, while solarization fits organic farming practices in regions with intense sunlight.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Steam sterilization offers rapid and effective elimination of soil-borne pathogens through high-temperature steam, ensuring deep penetration and thorough sterilization. However, it requires specialized equipment, high energy consumption, and can disrupt soil beneficial microbes. Solarization is an eco-friendly, low-cost method that uses solar heat to reduce soil pathogens and weeds but depends on climatic conditions, requires longer exposure time, and may not achieve the same sterilization depth as steam.
Choosing the Right Soil Disinfection Technique
Steam sterilization offers rapid and thorough soil pathogen elimination by applying high temperatures, making it ideal for intensive agriculture and greenhouse environments. Solarization harnesses solar energy to raise soil temperatures over several weeks, effectively reducing pests and weeds with minimal environmental impact, suitable for warm climates. Selecting the appropriate technique depends on factors such as soil type, crop sensitivity, cost, and environmental considerations, with steam sterilization favored for immediate results and solarization chosen for sustainable, low-cost management.
Steam sterilization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com