Cosmopolitan cocktails blend vodka, triple sec, cranberry juice, and lime juice for a refreshing, tangy taste that's perfect for any occasion. This iconic drink, popularized in the 1990s, offers a balance of sweet and sour flavors that cater to both casual drinkers and cocktail enthusiasts. Discover how to make the perfect Cosmopolitan and impress your guests by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
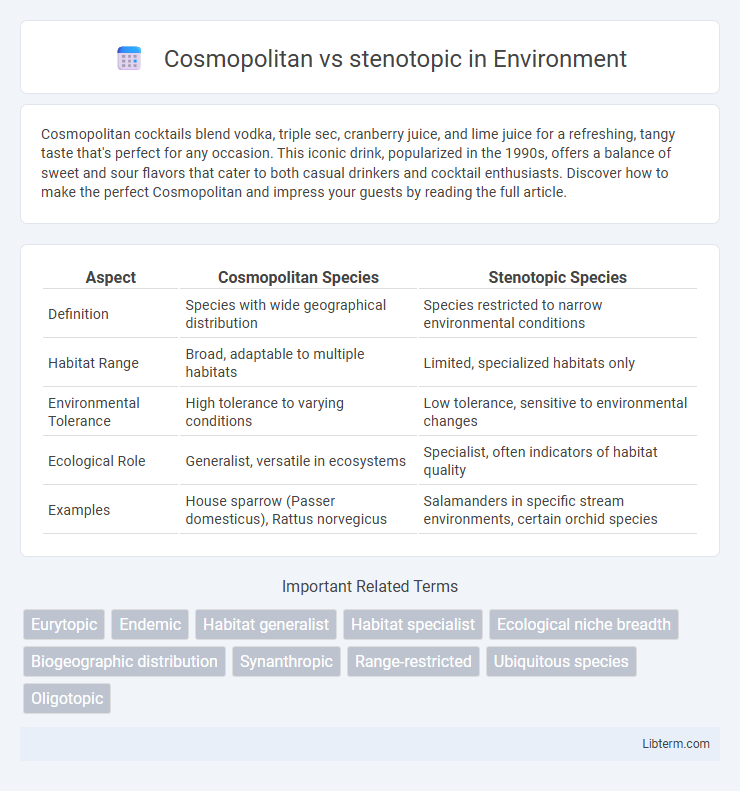
| Aspect | Cosmopolitan Species | Stenotopic Species |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Species with wide geographical distribution | Species restricted to narrow environmental conditions |
| Habitat Range | Broad, adaptable to multiple habitats | Limited, specialized habitats only |
| Environmental Tolerance | High tolerance to varying conditions | Low tolerance, sensitive to environmental changes |
| Ecological Role | Generalist, versatile in ecosystems | Specialist, often indicators of habitat quality |
| Examples | House sparrow (Passer domesticus), Rattus norvegicus | Salamanders in specific stream environments, certain orchid species |
Introduction to Cosmopolitan and Stenotopic Species
Cosmopolitan species exhibit a broad geographic distribution, thriving in diverse environmental conditions across multiple regions worldwide. Stenotopic species have a narrow ecological tolerance, confined to specific habitats with limited adaptability to environmental changes. Understanding the contrast between these species helps in studying biodiversity patterns and ecosystem resilience.
Defining Cosmopolitan Species
Cosmopolitan species are organisms found across a wide range of geographic areas, thriving in diverse environmental conditions, unlike stenotopic species that have narrow habitat preferences and limited distribution. These highly adaptable species exhibit broad ecological tolerance and a generalized niche, enabling them to colonize various ecosystems worldwide. Examples include the house sparrow (Passer domesticus) and the common pigeon (Columba livia), both demonstrating extensive dispersal and survival capabilities in urban and natural habitats globally.
Understanding Stenotopic Species
Stenotopic species exhibit a narrow ecological niche, thriving only in specific, stable habitats with limited environmental variation. Their restricted tolerance to changes in temperature, humidity, or soil composition contrasts sharply with cosmopolitan species, which adapt to a broad range of conditions and geographies. Understanding stenotopic species is critical for conservation efforts, as their specialized requirements make them more vulnerable to habitat loss and environmental disturbances.
Key Differences between Cosmopolitan and Stenotopic Species
Cosmopolitan species have a broad geographic distribution, thriving in diverse environmental conditions and various habitats worldwide, whereas stenotopic species are restricted to narrow ecological niches with specific environmental requirements. Adaptability to wide-ranging climates and resource availability characterizes cosmopolitan organisms, contrasting with stenotopic organisms that exhibit limited tolerance to environmental fluctuations. These differences influence biodiversity patterns, conservation strategies, and ecosystem resilience in varying habitats.
Geographic Distribution Patterns
Cosmopolitan species exhibit extensive geographic distribution, thriving in diverse habitats across multiple continents and climates, demonstrating high ecological adaptability. Stenotopic species, in contrast, occupy highly restricted geographic areas, limited to specific environmental conditions or microhabitats with narrow tolerance ranges. This stark difference in distribution patterns reflects the varying degrees of ecological specialization and dispersal capabilities between cosmopolitan and stenotopic organisms.
Ecological Adaptability and Habitat Range
Cosmopolitan species exhibit high ecological adaptability, thriving in diverse environmental conditions across wide geographical ranges. Stenotopic species have narrow habitat ranges, specialized to specific ecological niches with limited tolerance to environmental variability. The difference in habitat range highlights the adaptability of cosmopolitan species compared to the restricted niche specialization of stenotopic organisms.
Examples of Cosmopolitan Organisms
Cosmopolitan organisms such as the house sparrow (Passer domesticus), the Norway rat (Rattus norvegicus), and the common dandelion (Taraxacum officinale) thrive across diverse habitats and continents due to their high ecological tolerance. These species have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, from urban areas to rural ecosystems, demonstrating broad habitat plasticity. Their widespread distribution contrasts with stenotopic organisms, which are restricted to narrow ecological niches.
Notable Stenotopic Species
Notable stenotopic species exhibit a narrow range of environmental tolerance, thriving only in highly specific habitats such as Hydra oligactis, which is restricted to cold freshwater environments, and the desert-adapted scorpion Paruroctonus utahensis, surviving only in arid, saline soils. These species contrast sharply with cosmopolitan species that inhabit diverse ecological zones worldwide. Stenotopic organisms provide critical insights into habitat specialization and ecosystem sensitivity due to their limited distribution and high vulnerability to habitat disturbance.
Environmental Factors Influencing Distribution
Cosmopolitan species exhibit broad tolerance to diverse environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and habitat variability, enabling widespread geographic distribution across multiple ecosystems. In contrast, stenotopic species have narrow ecological niches, often restricted by specific parameters like pH, moisture, or temperature ranges, limiting their presence to specialized habitats. These environmental constraints directly influence species distribution patterns, with cosmopolitan organisms thriving in fluctuating conditions while stenotopic species depend on stable, particular environmental factors.
Conservation Implications and Biodiversity Considerations
Cosmopolitan species, characterized by their wide geographic distribution and ecological tolerance, often exhibit greater resilience to environmental changes, thereby posing distinct conservation challenges compared to stenotopic species, which are restricted to specific, often vulnerable habitats. The conservation of stenotopic species requires targeted habitat protection and management to preserve their specialized ecological niches, which are critical for maintaining regional biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Biodiversity strategies must balance the broad ecological roles of cosmopolitan species with the acute habitat dependence of stenotopic species to ensure comprehensive ecosystem conservation and sustainable species survival.
Cosmopolitan Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com