Terpenes and alkaloids are two important classes of natural compounds found in plants, each with distinct chemical properties and biological effects. Terpenes contribute to the characteristic aromas and flavors of many herbs, while alkaloids often have potent pharmacological activities that can impact human health. Discover how these compounds influence your experience and wellbeing by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
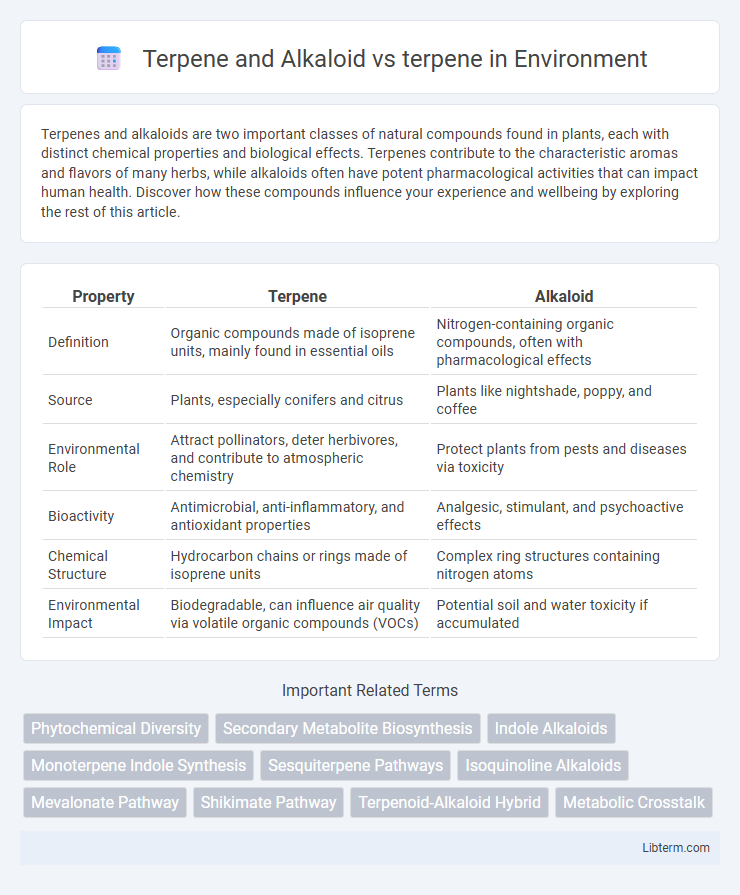
| Property | Terpene | Alkaloid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Organic compounds made of isoprene units, mainly found in essential oils | Nitrogen-containing organic compounds, often with pharmacological effects |
| Source | Plants, especially conifers and citrus | Plants like nightshade, poppy, and coffee |
| Environmental Role | Attract pollinators, deter herbivores, and contribute to atmospheric chemistry | Protect plants from pests and diseases via toxicity |
| Bioactivity | Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties | Analgesic, stimulant, and psychoactive effects |
| Chemical Structure | Hydrocarbon chains or rings made of isoprene units | Complex ring structures containing nitrogen atoms |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, can influence air quality via volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | Potential soil and water toxicity if accumulated |
Introduction to Terpenes and Alkaloids
Terpenes and alkaloids are two major classes of organic compounds found in plants, each with distinct chemical structures and biological roles. Terpenes, composed primarily of isoprene units, are responsible for the aromatic properties and essential oils in many plants, playing key roles in plant defense and pollinator attraction. Alkaloids, nitrogen-containing compounds, exhibit diverse pharmacological effects and are often used in medicine for their analgesic, stimulant, or toxic properties.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are a diverse class of organic compounds produced by plants, particularly conifers and cannabis, responsible for their distinct aromas and flavors. Unlike alkaloids, which often have physiological effects and medicinal properties, terpenes primarily serve as natural repellents and attractants in ecological interactions. They also contribute to the therapeutic potential of essential oils by modulating the effects of cannabinoids and enhancing aroma profiles.
What Are Alkaloids?
Alkaloids are naturally occurring organic compounds mainly found in plants, characterized by nitrogen atoms within their structures, which contribute to potent pharmacological effects. Unlike terpenes, which are hydrocarbons primarily responsible for plants' aroma and flavor, alkaloids exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including analgesic, stimulant, and toxic properties. Prominent examples of alkaloids include morphine, caffeine, and quinine, which play crucial roles in medicine and pharmacology.
Structural Differences: Terpenes vs Alkaloids
Terpenes are composed primarily of isoprene units arranged in various cyclic and acyclic structures, characterized by their hydrocarbon frameworks, whereas alkaloids contain nitrogen atoms incorporated into heterocyclic rings, often resulting in complex, nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The structural diversity of terpenes arises from multiple isoprene units (C5H8) linked in linear, branched, or cyclic forms, contrasting with alkaloids that typically feature nitrogen heterocycles such as pyridine, pyrrolidine, or indole rings. These structural differences influence their biosynthesis pathways, chemical properties, and biological activities, with terpenes derived mainly from the mevalonate or MEP pathway and alkaloids synthesized via amino acid precursors.
Functions of Terpenes in Nature
Terpenes are organic compounds primarily responsible for the aromatic qualities of many plants and play crucial roles in ecological interactions such as attracting pollinators and repelling herbivores. Unlike alkaloids, which often serve as chemical defenses through toxicity and pharmacological activity, terpenes function mainly in plant communication and protection by producing volatile scents and flavors. These compounds also contribute to plant resilience against environmental stress and microbial infections, making them essential in natural plant survival strategies.
Roles of Alkaloids in Plants and Animals
Alkaloids play critical roles in plants by acting as natural defense compounds against herbivores and pathogens, often exhibiting toxic, bitter, or deterrent properties that protect plant tissues. In animals, alkaloids can influence physiological processes such as nerve signaling and muscle contraction, with many alkaloids being used pharmaceutically for their analgesic, stimulant, or sedative effects. Unlike terpenes, which primarily contribute to aroma and plant interactions with the environment, alkaloids have more pronounced bioactive effects that directly affect animal and insect behavior and survival.
Therapeutic Benefits: Terpenes vs Alkaloids
Terpenes exhibit anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic properties that support pain relief and stress reduction, commonly found in essential oils and cannabis. Alkaloids, such as morphine and quinine, provide potent therapeutic effects including analgesia, antimalarial activity, and central nervous system stimulation. While terpenes modulate mood and inflammation through aromatic compounds, alkaloids directly interact with neurotransmitter receptors to offer strong pharmacological actions.
Applications in Medicine and Industry
Terpenes exhibit significant applications in medicine as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer agents, while alkaloids are primarily utilized for their potent pharmacological effects, including analgesic, antimalarial, and antitumor properties. In industry, terpenes serve as key components in fragrances, flavorings, and bio-based solvents, contrasting with alkaloids, which are less common industrially but essential in pharmaceutical drug synthesis. The distinct bioactivities and chemical structures of terpenes and alkaloids define their complementary roles in therapeutic development and commercial production.
Safety, Toxicity, and Side Effects
Terpenes and alkaloids are bioactive compounds with distinct safety profiles, where terpenes generally exhibit lower toxicity and fewer side effects, often used for their aromatic and therapeutic properties in aromatherapy and herbal medicine. Alkaloids, found in plants like poppies and nightshade, can have potent pharmacological effects but carry higher risks of toxicity and adverse side effects, necessitating cautious dosage and medical supervision. Safety concerns with alkaloids include potential neurotoxicity and dependency, whereas terpenes' side effects are typically mild, such as skin irritation or allergic reactions.
Comparative Analysis: Terpene and Alkaloid vs Terpene
Terpenes and alkaloids differ significantly in chemical structure and biological roles, with terpenes being hydrocarbon-based compounds responsible for aromatic properties in plants, while alkaloids are nitrogen-containing molecules often associated with pharmacological effects. Terpenes primarily function as attractants or repellents in plant ecology, whereas alkaloids frequently serve defensive roles against herbivores and pathogens. Comparative analysis reveals terpenes' volatility and role in fragrance and flavor contrast with alkaloids' diverse bioactive profiles, including analgesic and psychoactive properties.
Terpene and Alkaloid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com