Estuarine deltas form where river sediments accumulate as fresh water meets tidal salt water, creating nutrient-rich and dynamic ecosystems. These areas support diverse wildlife and act as natural buffers against storms and erosion, making them vital for environmental health and human communities. Discover how your local estuarine delta influences biodiversity and coastal resilience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
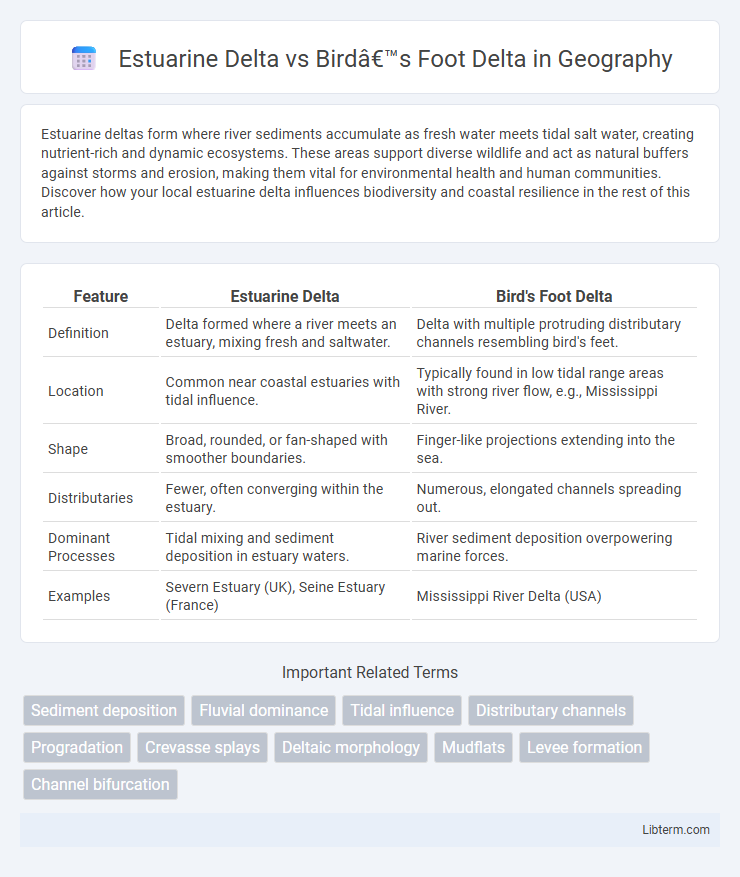
| Feature | Estuarine Delta | Bird's Foot Delta |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delta formed where a river meets an estuary, mixing fresh and saltwater. | Delta with multiple protruding distributary channels resembling bird's feet. |
| Location | Common near coastal estuaries with tidal influence. | Typically found in low tidal range areas with strong river flow, e.g., Mississippi River. |
| Shape | Broad, rounded, or fan-shaped with smoother boundaries. | Finger-like projections extending into the sea. |
| Distributaries | Fewer, often converging within the estuary. | Numerous, elongated channels spreading out. |
| Dominant Processes | Tidal mixing and sediment deposition in estuary waters. | River sediment deposition overpowering marine forces. |
| Examples | Severn Estuary (UK), Seine Estuary (France) | Mississippi River Delta (USA) |
Introduction to Delta Types
Estuarine deltas form where river sediment deposits mix with tidal influences, creating a mix of freshwater and saltwater ecosystems characterized by broad, fan-shaped landforms. Bird's Foot deltas develop in regions with strong river discharge and weak wave or tidal actions, resulting in elongated, finger-like projections into the sea, famously seen in the Mississippi River Delta. The primary distinction lies in sediment distribution and hydrodynamic forces, influencing delta morphology and ecological patterns.
Defining Estuarine Deltas
Estuarine deltas form where river sediments accumulate at the mouth of an estuary, creating a unique interface between freshwater and marine environments characterized by tidal action and sediment deposition. Unlike bird's foot deltas, which have finger-like distributary channels extending into the sea, estuarine deltas exhibit more complex sediment patterns influenced by both tidal currents and river discharge. The defining feature of estuarine deltas is their location within estuaries, where mixing of saline and freshwater significantly influences sediment distribution and delta morphology.
Characteristics of Bird’s Foot Deltas
Bird's Foot Deltas are characterized by their elongated distributary channels that extend into the body of water, resembling the shape of a bird's foot. These deltas form primarily in regions with strong river sediment supply and weak wave or tidal action, allowing sediments to build outwards. The Mississippi River Delta is a classic example, showcasing multiple protruding channels and extensive wetland areas.
Formation Processes: Estuarine vs Bird’s Foot
Estuarine deltas form where river systems meet tidal waters, characterized by combined fluvial and marine processes that create a mixing zone of fresh and saltwater, leading to sediment deposition influenced by tidal currents. Bird's Foot deltas develop primarily through continuous sediment supply from rivers pushing distributaries outward into a standing water body, resulting in distinctive elongated lobes shaped by riverine sedimentation overpowering wave and tidal influences. The key difference in formation lies in estuarine deltas' sediment distribution moderated by tidal dynamics versus the Bird's Foot delta's progradation driven by dominant fluvial sediment deposition.
Geographic Examples of Each Delta Type
The Mississippi River Delta in Louisiana exemplifies a Bird's Foot Delta, characterized by its protruding distributary channels extending into the Gulf of Mexico. In contrast, the Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt Delta in the Netherlands represents an Estuarine Delta, where multiple river channels spread out over a larger estuary before entering the North Sea. These geographic examples highlight distinct delta formations influenced by sediment deposition and tidal interactions.
Sediment Deposition Patterns
Estuarine deltas exhibit sediment deposition primarily influenced by tidal currents and river flows, creating a more concave shape with sediments settling evenly across the delta plain and intertidal zones. Bird's foot deltas are characterized by elongated distributary channels that extend into the basin, where sediment deposition occurs predominantly at the channel mouths, forming finger-like projections due to strong river discharge overpowering marine processes. These contrasting sediment patterns reflect differences in hydrodynamic forces, with estuarine deltas showing more diffused sediment spread and bird's foot deltas displaying channel-dominated sediment buildup.
Ecological Significance and Biodiversity
Estuarine deltas support diverse ecosystems by mixing freshwater and saltwater, creating nutrient-rich habitats that sustain various fish, bird, and plant species. Bird's Foot deltas, exemplified by the Mississippi River Delta, feature freshwater channels extending into marine environments, fostering distinct wetland ecosystems critical for migratory birds and aquatic biodiversity. Both delta types serve as vital nurseries for marine life, act as natural water filters, and support economically important fisheries.
Human Impact and Land Use
Estuarine deltas often face significant human impact through urbanization and industrial development, leading to habitat loss, water pollution, and altered sediment flow. Bird's Foot deltas, like the Mississippi River Delta, experience extensive land use changes including agriculture and oil extraction, which contribute to subsidence, wetland degradation, and increased vulnerability to sea-level rise. Both delta types require targeted management strategies to balance economic activities with ecosystem preservation and mitigate negative effects from dredging, levee construction, and land reclamation.
Environmental Challenges and Threats
Estuarine deltas, characterized by their rich biodiversity and nutrient-rich waters, face environmental challenges such as pollution from upstream agricultural runoff and urban waste, leading to habitat degradation and loss of aquatic species. Bird's Foot deltas, like the Mississippi River Delta, confront significant threats from sediment deprivation due to upstream damming, subsidence, and sea-level rise, resulting in land loss and increased vulnerability to storm surges. Both delta types experience challenges from climate change impacts, including altered hydrology and increased salinity intrusion, threatening the ecological balance and local livelihoods.
Summary: Key Differences and Similarities
Estuarine deltas form where river water mixes with seawater in estuaries, creating rich ecosystems with diverse sediments and tidal influences, while Bird's Foot deltas like the Mississippi feature protruding distributary channels resembling a bird's foot due to sediment deposition in calm waters. Both deltas serve as critical habitats and support extensive biodiversity, but estuarine deltas are shaped by tidal dynamics, whereas Bird's Foot deltas primarily develop from river sediment accumulation. The differences in formation processes affect their morphology, sediment distribution, and ecological functions.
Estuarine Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com