Bit is a fundamental unit of digital information, representing a binary state of either 0 or 1, crucial for computing processes and data storage. Understanding how bits function can enhance your grasp of how computers encode, process, and transmit data efficiently. Dive into the rest of the article to explore the role of bits in modern technology and their impact on your digital experience.
Table of Comparison
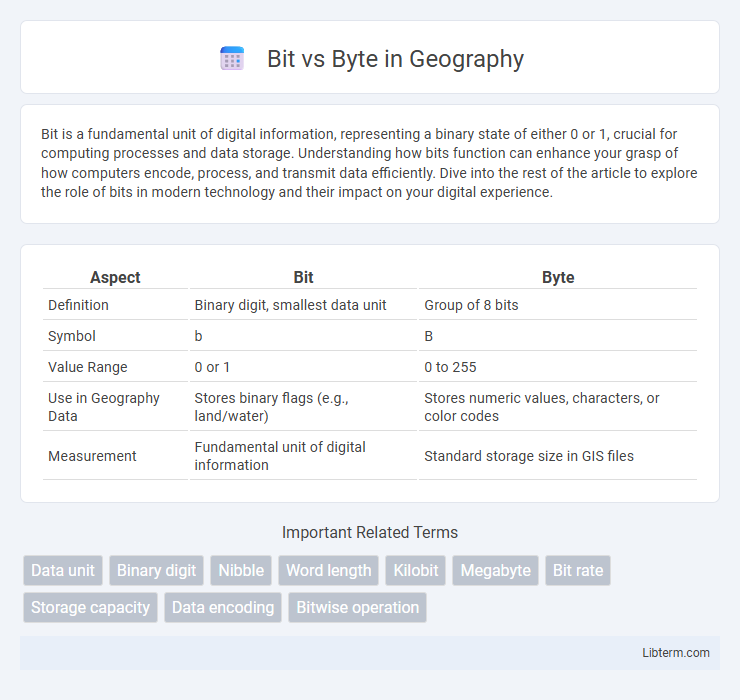
| Aspect | Bit | Byte |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Binary digit, smallest data unit | Group of 8 bits |
| Symbol | b | B |
| Value Range | 0 or 1 | 0 to 255 |
| Use in Geography Data | Stores binary flags (e.g., land/water) | Stores numeric values, characters, or color codes |
| Measurement | Fundamental unit of digital information | Standard storage size in GIS files |
Understanding Bits: The Smallest Unit of Data
A bit, short for binary digit, represents the smallest unit of data in computing and can have a value of either 0 or 1, reflecting the binary nature of digital systems. Bits serve as the foundational building blocks for all digital data, encoding everything from simple binary code to complex multimedia files. Understanding bits is crucial for grasping how computers process, store, and transmit information efficiently at the most fundamental level.
What is a Byte? Definition and Structure
A byte is a fundamental unit of digital information in computing, typically consisting of 8 bits, each bit representing a binary value of 0 or 1. Bytes serve as the basic addressable element in many computer architectures, enabling the encoding of a single character, such as a letter or number, in systems that use ASCII or Unicode encoding standards. The structure of a byte allows for 256 possible combinations, facilitating data storage, processing, and transmission in computers and digital devices.
Bit vs Byte: Key Differences Explained
A bit is the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a binary value of 0 or 1, while a byte consists of 8 bits, allowing it to store more complex information such as a single character. Bytes are used to measure data storage and memory capacity, typically expressed in kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), or gigabytes (GB), whereas bits are commonly used to measure data transfer speeds in bits per second (bps). Understanding the key differences between bits and bytes is essential for interpreting computer specifications, networking speeds, and storage capacities accurately.
Binary System: The Foundation of Bits and Bytes
The binary system, based on two symbols 0 and 1, forms the foundation of bits and bytes in digital computing. A bit, short for binary digit, represents the smallest unit of data capable of holding one binary value, either 0 or 1. Bytes consist of 8 bits and serve as the fundamental unit for encoding and processing complex data in computer systems.
The Evolution of Digital Storage Units
Digital storage units have evolved from the fundamental bit, representing a single binary value, to the more complex byte, consisting of eight bits that form the basis for encoding characters and data. As computing technology advanced, larger units like kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes emerged to accommodate increasing data storage demands in digital devices. This evolution reflects the continuous growth in data complexity and processing power, driving the expansion from simple bits to comprehensive byte-based systems for efficient information management.
Common Uses of Bits and Bytes in Technology
Bits are commonly used to measure data transfer speeds and network bandwidth, such as Mbps (megabits per second) in internet connections. Bytes, consisting of 8 bits, are standard units for file sizes, memory capacity, and storage devices, with kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), and gigabytes (GB) frequently referenced. Understanding the distinction between bits and bytes is essential for interpreting technical specifications in computing and telecommunications accurately.
Data Measurement Prefixes: Kilobits, Kilobytes, and Beyond
Kilobits (Kb) and Kilobytes (KB) represent distinct data measurement units where 1 Kilobit equals 1,000 bits, and 1 Kilobyte equals 1,024 bytes, reflecting binary base differences. Data measurement prefixes progress through Megabits (Mb), Megabytes (MB), Gigabits (Gb), Gigabytes (GB), Terabits (Tb), and Terabytes (TB), each representing multiples of 1,000 or 1,024 depending on decimal or binary standards. Understanding whether a prefix is decimal-based (SI units) or binary-based (IEC units) is crucial for accurate interpretation of storage capacity and data transfer rates in digital communication.
File Size Representation: Why Bits and Bytes Matter
File size representation relies on bytes rather than bits because one byte equals eight bits, making bytes a more practical unit for measuring digital data. Bits, representing binary digits, are fundamental to data encoding, but bytes provide a standardized size reference crucial for storage and memory capacity. Understanding the distinction between bits and bytes is essential for comprehending file sizes, data transfer rates, and computer memory allocation.
Avoiding Confusion: Best Practices for Using Bits and Bytes
To avoid confusion between bits and bytes, clearly specify units using standardized abbreviations: "bit" (b) and "byte" (B), where 1 byte equals 8 bits. Use consistent notation in documentation and avoid mixing the two in data rates and storage sizes without clarification. Implement clear labeling in interfaces and explanations, emphasizing the difference in scale and context to ensure accurate communication of digital information.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bits and Bytes
A bit is the smallest unit of data in computing, representing a binary value of either 0 or 1, while a byte consists of 8 bits and is used to encode a single character of text. Frequently asked questions often address the difference in storage capacity, where bytes measure file sizes and bits are used in data transmission rates like internet speed. Understanding the conversion between bits and bytes is essential, as 1 byte equals 8 bits, impacting how data is stored, processed, and communicated digitally.
Bit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com