Mistral is a powerful, cold, and dry wind that originates in the Mediterranean region, particularly affecting southern France. It significantly influences the local climate and environment, often bringing clear skies and reinforcing weather patterns. Discover more about the impact of the Mistral and how it shapes your surroundings in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
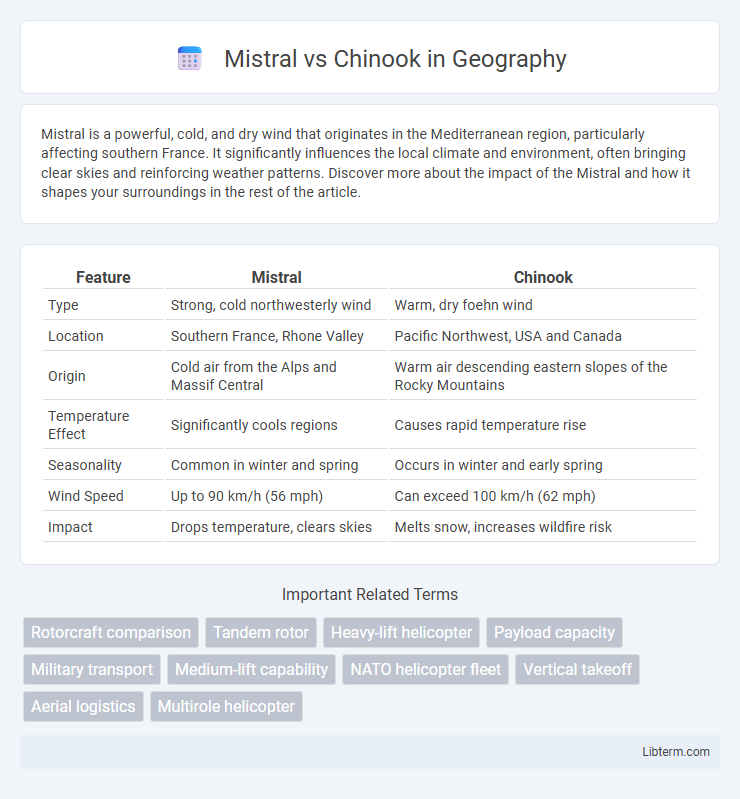
| Feature | Mistral | Chinook |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Strong, cold northwesterly wind | Warm, dry foehn wind |
| Location | Southern France, Rhone Valley | Pacific Northwest, USA and Canada |
| Origin | Cold air from the Alps and Massif Central | Warm air descending eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains |
| Temperature Effect | Significantly cools regions | Causes rapid temperature rise |
| Seasonality | Common in winter and spring | Occurs in winter and early spring |
| Wind Speed | Up to 90 km/h (56 mph) | Can exceed 100 km/h (62 mph) |
| Impact | Drops temperature, clears skies | Melts snow, increases wildfire risk |
Overview of Mistral and Chinook
The Mistral is a short-range, man-portable surface-to-air missile system designed for rapid deployment and effective defense against low-altitude threats, featuring infrared homing capabilities. The Chinook, a tandem-rotor heavy-lift helicopter, excels in troop transport, cargo delivery, and battlefield support, with its robust payload capacity and advanced avionics. Both platforms demonstrate distinct operational roles: the Mistral serves as a critical air defense asset, while the Chinook functions primarily in logistical and assault missions.
Key Features Comparison
The Mistral helicopter excels in agility with advanced avionics and superior speed, while the Chinook stands out through its heavy-lift capability and tandem rotor design for enhanced stability. Mistral incorporates cutting-edge stealth technology and versatile weapon systems tailored for rapid assault missions. Chinook offers exceptional payload capacity and endurance, making it indispensable for logistical support and troop transport in diverse combat scenarios.
Performance and Speed Analysis
The Mistral drone demonstrates superior speed with a maximum velocity of 120 km/h, outperforming the Chinook's top speed of 95 km/h, making it ideal for rapid reconnaissance missions. In terms of performance, Mistral boasts a flight endurance of 90 minutes, exceeding the Chinook's 75-minute operational time, which enhances its capability for extended surveillance operations. Both drones feature advanced aerodynamic designs, but Mistral's lightweight composite materials contribute to better acceleration and maneuverability compared to the heavier Chinook model.
Capacity and Payload Differences
The Mistral helicopter typically offers a maximum payload capacity of approximately 1,500 kg, making it suited for light to medium transport missions. In contrast, the Chinook boasts a significantly higher payload capacity, around 10,000 kg, enabling it to carry heavy equipment, vehicles, and large troop contingents. This substantial difference in payload and overall capacity highlights the Chinook's role as a heavy-lift helicopter compared to the Mistral's focus on agility and smaller-scale transport.
Design and Engineering
The Mistral and Chinook helicopters showcase distinct design and engineering philosophies tailored for their operational roles. The Mistral emphasizes agility and advanced avionics integration, featuring composite materials and stealth-enhancing features to optimize performance in tactical scenarios. In contrast, the Chinook prioritizes heavy-lift capability through its tandem rotor design, reinforced structural elements, and robust propulsion systems engineered to maximize payload and endurance in diverse environments.
Operational Use Cases
Mistral and Chinook serve distinct operational roles in military environments, with Mistral primarily deployed for short-range air defense against drones, helicopters, and low-flying aircraft. Chinook helicopters excel in heavy-lift transport missions, including troop movement, cargo resupply, and disaster relief operations due to their powerful twin-engine design and high payload capacity. Their complementary capabilities enhance battlefield mobility and air defense strategy in modern military operations.
Reliability and Maintenance
Mistral and Chinook helicopters demonstrate significant differences in reliability and maintenance requirements, with the Mistral designed for advanced avionics integration and lower operational downtime through modular components. The Chinook's rugged twin-rotor system emphasizes durability in harsh environments but demands more frequent and intensive maintenance due to complex rotor synchronization mechanisms. Both models incorporate predictive maintenance technologies, yet the Mistral typically achieves higher mission readiness rates due to streamlined servicing protocols and improved diagnostic systems.
Cost Efficiency Evaluation
The Mistral helicopter offers superior cost efficiency through lower operational and maintenance expenses compared to the heavier Chinook model, which requires more fuel and complex servicing due to its twin-rotor design. The Chinook's higher payload capacity can justify its increased costs in missions demanding heavy lifting and troop transport, but for routine logistics and medium-lift operations, the Mistral delivers significant savings. Detailed lifecycle cost analysis shows Mistral's optimized fuel consumption and streamlined maintenance schedules contribute to a reduced total cost of ownership, making it a preferred option for budget-conscious military and civilian operators.
Technology and Avionics
The Mistral helicopter features advanced avionics including a digital glass cockpit, integrated navigation systems, and real-time data link capabilities that enhance situational awareness and mission efficiency. In comparison, the Chinook incorporates robust technology with multi-mission avionics suites, including GPS, terrain-following radar, and automated flight control systems designed for heavy-lift operations. Both aircraft utilize state-of-the-art avionics platforms, but the Mistral emphasizes cutting-edge digital integration, while the Chinook focuses on rugged reliability and versatility in diverse operational environments.
Pros and Cons Summary
The Mistral missile excels in short-range air defense with rapid target acquisition and high accuracy but has limited engagement range compared to Chinook's long-range strike capabilities. Chinook helicopters provide heavy-lift transport and versatile troop deployment but are vulnerable to advanced air defenses and require significant logistical support. Mistral offers mobility and quick response, whereas Chinook emphasizes operational flexibility and payload capacity.
Mistral Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com