Immigrants contribute to cultural diversity and economic growth by bringing unique skills and perspectives to their new communities. Understanding the challenges they face, including language barriers and legal hurdles, is essential for fostering inclusion and support. Explore the rest of this article to learn how your community can benefit from and support immigrant integration.
Table of Comparison
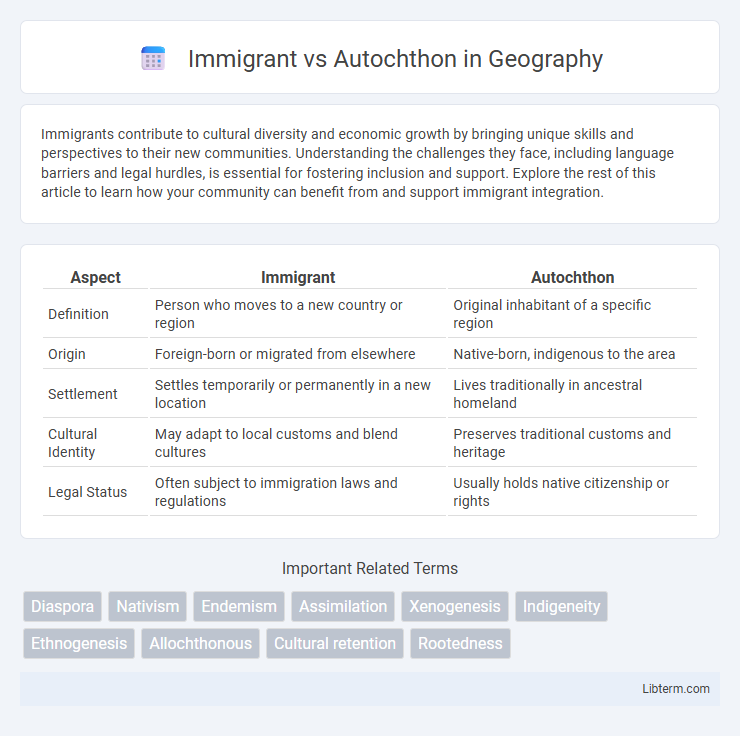
| Aspect | Immigrant | Autochthon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Person who moves to a new country or region | Original inhabitant of a specific region |
| Origin | Foreign-born or migrated from elsewhere | Native-born, indigenous to the area |
| Settlement | Settles temporarily or permanently in a new location | Lives traditionally in ancestral homeland |
| Cultural Identity | May adapt to local customs and blend cultures | Preserves traditional customs and heritage |
| Legal Status | Often subject to immigration laws and regulations | Usually holds native citizenship or rights |
Understanding Immigrants and Autochthons: Key Definitions
Immigrants are individuals who move from one country or region to settle permanently in another, often bringing diverse cultural backgrounds and experiences. Autochthons, or indigenous populations, are native inhabitants of a particular place with historical continuity and deep-rooted connection to their land. Understanding these key definitions is vital for analyzing social integration, cultural identity, and policy development in multicultural societies.
Historical Perspectives on Migration and Native Populations
Historical perspectives on migration reveal complex interactions between immigrants and autochthonous populations, highlighting shifts in cultural, social, and political dynamics over time. Immigrants often introduce new technologies, customs, and economic practices, while autochthons embody long-standing traditions and territorial claims, shaping identity and resource distribution. Understanding these historical contexts helps elucidate contemporary debates on integration, sovereignty, and cultural preservation.
Demographic Trends: Immigrants vs. Autochthons
Immigrant populations have surged in urban centers, contributing to demographic shifts that contrast with the stable birth rates of autochthonous groups. Immigrant communities often display younger age profiles and higher fertility rates, impacting population growth and age distribution differently compared to native-born populations. These trends influence workforce dynamics, social services demand, and cultural integration within regions dominated by either immigrant or autochthonous demographics.
Economic Contributions: Comparing Roles and Impacts
Immigrants significantly contribute to economic growth by filling essential labor shortages, fostering innovation, and stimulating entrepreneurship across diverse industries. Autochthons, or native-born populations, provide a stable workforce with localized knowledge that supports sustained economic development and social cohesion. Comparative analysis reveals that the integration of immigrants enhances productivity and market dynamism, while autochthons often maintain institutional continuity and cultural capital.
Social Integration and Cultural Exchange
Immigrants often enhance social integration by introducing diverse cultural practices, languages, and traditions that foster multicultural communities. Autochthons maintain indigenous customs and established social norms, which serve as a foundation for cultural continuity within a region. The dynamic interaction between immigrants and autochthons facilitates cultural exchange, promoting mutual understanding and enriching societal cohesion.
Challenges Faced by Immigrants and Autochthons
Immigrants often encounter challenges such as language barriers, cultural assimilation, and limited access to employment opportunities, which hinder social integration and economic stability. Autochthons face difficulties like protecting indigenous rights, preserving cultural heritage, and addressing socio-economic disparities exacerbated by demographic changes. Both groups struggle with identity conflicts and competition for resources, leading to tensions that require inclusive policies promoting mutual understanding and equal opportunities.
Policy Approaches: Supporting Diversity and Inclusion
Policies supporting diversity and inclusion balance immigrant integration with autochthonous community interests, promoting social cohesion and equal opportunities. Inclusive policies often emphasize multicultural education, anti-discrimination laws, and equitable access to services for both immigrants and native populations. Effective approaches involve community engagement programs that foster mutual understanding and respect while addressing potential tensions between immigrant groups and autochthonous residents.
Identity and Belonging: Navigating Differences
Immigrant and autochthon identities often intersect yet diverge in experiences of belonging, shaping individual and collective self-perception in profound ways. Immigrants navigate dual cultural frameworks, balancing heritage traditions with integration into new social environments, which impacts their sense of identity and inclusion. Autochthons maintain ancestral ties and territorial claims that reinforce a rooted identity, creating distinct boundaries that influence perceptions of belonging and social cohesion.
Common Stereotypes and Misconceptions
Common stereotypes portray immigrants as outsiders prone to economic burden and cultural disruption, while autochthons are often idealized as the original, authentic inhabitants safeguarding tradition. Misconceptions about immigrants include assumptions of unwillingness to integrate or contribute, ignoring evidence of diverse skill sets and community involvement. In contrast, autochthons may be inaccurately viewed as homogeneous groups resistant to change, overlooking internal diversity and evolving identities.
Fostering Cohesion: Building Bridges Between Communities
Fostering cohesion between immigrants and autochthons requires promoting intercultural dialogue and shared community projects that emphasize mutual understanding and respect. Community centers and local initiatives that encourage collaboration help bridge social gaps, reducing prejudices and building trust. Educational programs highlighting common values and diverse cultural contributions strengthen collective identity and social harmony.
Immigrant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com