Climatology studies long-term weather patterns and atmospheric conditions shaping Earth's diverse climates. Understanding these patterns helps predict environmental changes and their impact on ecosystems and human activities. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of climatology and its critical role in our world.
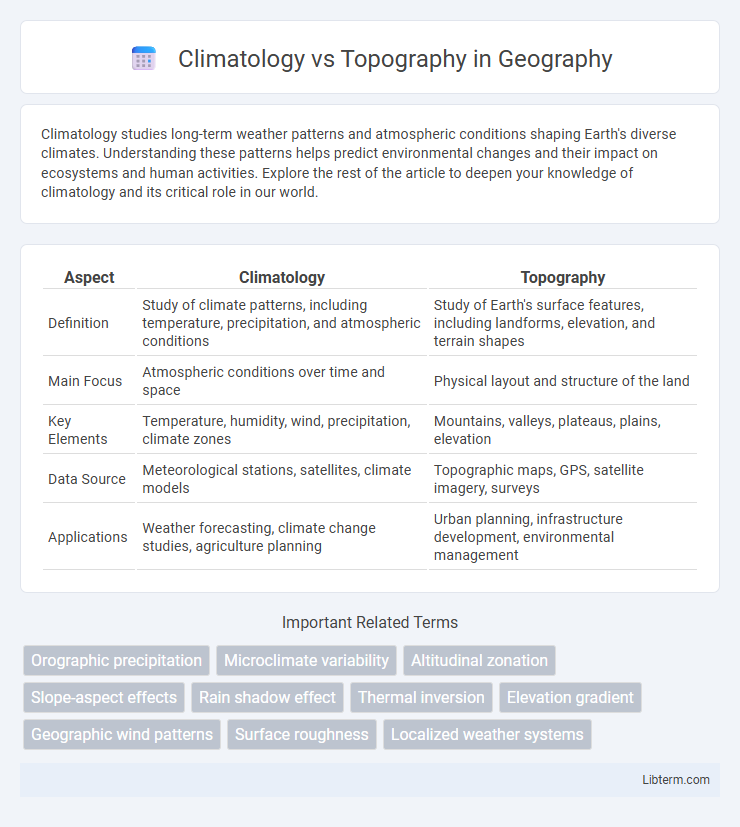
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Climatology | Topography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric conditions | Study of Earth's surface features, including landforms, elevation, and terrain shapes |
| Main Focus | Atmospheric conditions over time and space | Physical layout and structure of the land |
| Key Elements | Temperature, humidity, wind, precipitation, climate zones | Mountains, valleys, plateaus, plains, elevation |
| Data Source | Meteorological stations, satellites, climate models | Topographic maps, GPS, satellite imagery, surveys |
| Applications | Weather forecasting, climate change studies, agriculture planning | Urban planning, infrastructure development, environmental management |
Introduction to Climatology and Topography
Climatology studies the long-term patterns and variations in atmospheric conditions, emphasizing temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind on regional and global scales. Topography examines the Earth's surface features such as mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus, influencing climate patterns through elevation, slope, and orientation. Understanding the interplay between climatology and topography is essential for analyzing weather systems, climate zones, and environmental impacts.
Defining Climatology: The Study of Climate
Climatology is the scientific study of climate, analyzing long-term patterns of temperature, humidity, wind, and precipitation to understand atmospheric behavior over extended periods. It involves examining data from various regions to identify trends, climate variability, and changes driven by natural or anthropogenic factors. Unlike topography, which focuses on the physical features of the Earth's surface such as mountains and valleys, climatology centers on atmospheric phenomena and their impact on ecosystems and human activities.
Understanding Topography: Landforms and Terrain
Topography influences local climate patterns by shaping landforms such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus that affect wind flow, precipitation distribution, and temperature variations. Understanding terrain features is essential to predict microclimates and watershed behaviors in climatology studies. Detailed topographic analysis aids in modeling environmental conditions and assessing natural hazards linked to climatic factors.
Key Differences Between Climatology and Topography
Climatology studies atmospheric conditions and long-term weather patterns, whereas topography examines the physical features and elevation of the Earth's surface. Climatology analyzes temperature, precipitation, and wind trends over time, while topography focuses on mountains, valleys, and plains shaping the landscape. These distinct fields interact as topography influences climate patterns by affecting airflow and precipitation distribution.
How Topography Influences Climate Patterns
Topography significantly influences climate patterns by affecting temperature, precipitation, and wind flow. Mountain ranges cause orographic lift, leading to increased rainfall on windward slopes and creating rain shadows with dry conditions on leeward sides. Elevation changes result in cooler temperatures at higher altitudes, while valleys may trap cold air, contributing to microclimates.
The Role of Climatology in Environmental Planning
Climatology provides critical data on temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations that influence land use decisions and resource management in environmental planning. Understanding local and regional climate patterns helps planners anticipate risks such as flooding, droughts, and heatwaves, enabling the design of resilient infrastructure. Integrating climatology with topographical analysis ensures sustainable development by aligning construction practices with prevailing weather conditions and natural landscape features.
Topographical Factors Affecting Local Weather
Topography significantly influences local weather patterns through variations in elevation, slope orientation, and landforms such as mountains and valleys. Mountain ranges can block air masses, causing orographic precipitation on windward sides and rain shadows on leeward sides, while valleys often experience temperature inversions and localized wind patterns. Elevation changes typically lead to cooler temperatures and increased precipitation, shaping microclimates within a region.
Applications of Climatology and Topography in Geography
Climatology provides essential data on atmospheric patterns, temperature variations, and precipitation trends that inform agricultural planning, urban development, and disaster management in geography. Topography influences landform distribution, watershed delineation, and soil erosion processes, crucial for infrastructure design and environmental conservation efforts. Integrating climatological data with topographic analysis enhances geographic modeling, enabling precise predictions of climate impact on diverse terrains.
Case Studies: Climatology and Topography Interactions
Case studies reveal how climatology and topography intricately interact to shape local weather patterns and ecological systems. In the Pacific Northwest, mountain ranges induce orographic rainfall, creating distinct microclimates and influencing forest biodiversity. Similarly, the Himalayas affect monsoon circulation and temperature gradients, demonstrating topography's role in modifying regional climate dynamics.
Future Trends in Climatology and Topography Research
Future trends in climatology research emphasize advanced climate modeling techniques, integrating machine learning algorithms to improve prediction accuracy of extreme weather events and climate change impacts. Topography research increasingly utilizes high-resolution satellite imagery and LiDAR technology to map terrain changes, enabling better understanding of landscape evolution and its interaction with climatic factors. Interdisciplinary approaches combining climatology and topography data foster enhanced environmental monitoring and resource management strategies amid global climate challenges.
Climatology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com