A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information storage equal to 1,024 bytes, commonly used to measure small files and memory capacity. Understanding kilobytes helps you gauge file sizes and manage storage efficiently on your devices. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about data measurement units and their importance.
Table of Comparison
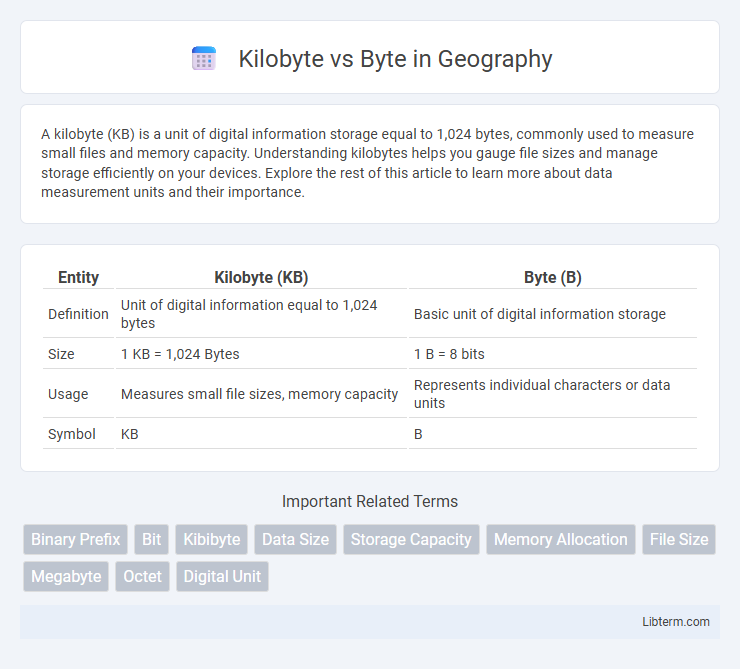
| Entity | Kilobyte (KB) | Byte (B) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unit of digital information equal to 1,024 bytes | Basic unit of digital information storage |
| Size | 1 KB = 1,024 Bytes | 1 B = 8 bits |
| Usage | Measures small file sizes, memory capacity | Represents individual characters or data units |
| Symbol | KB | B |
Understanding the Basics: Byte and Kilobyte
A byte consists of 8 bits and serves as the fundamental unit of digital information storage, representing a single character such as a letter or number. A kilobyte (KB) traditionally equals 1,024 bytes in binary systems commonly used in computing, though it is sometimes rounded to 1,000 bytes in decimal contexts for data measurement. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately interpreting file sizes, memory capacity, and data transfer rates in both software and hardware applications.
Definition of a Byte
A byte is a fundamental unit of digital information consisting of 8 bits, used to encode a single character such as a letter, number, or symbol in computing. Kilobyte (KB) represents 1,024 bytes in binary systems, commonly used to quantify storage capacity or data size. Understanding bytes is essential for measuring memory, file sizes, and data transfer rates accurately.
What is a Kilobyte?
A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information storage equal to 1,024 bytes in binary notation, commonly used in computing to measure data size. Unlike a byte, which represents one character of data, a kilobyte aggregates 1,024 bytes to quantify larger amounts of information. Kilobytes are essential for understanding file sizes and memory capacity in digital systems.
Byte vs Kilobyte: Key Differences
A byte consists of 8 bits and serves as the fundamental unit of digital information, while a kilobyte (KB) typically equals 1,024 bytes in computer science, representing larger data storage. The key difference lies in their scale, with bytes used for small data quantities and kilobytes accommodating more substantial information such as small text files or images. Understanding byte versus kilobyte is essential for accurately measuring digital data capacity and memory size in computing environments.
Conversion: Bytes to Kilobytes Explained
One kilobyte (KB) equals 1,024 bytes, based on the binary system commonly used in computing. To convert bytes to kilobytes, divide the number of bytes by 1,024 to obtain the precise digital storage amount. This binary conversion standard ensures accurate measurement and comparison across computer systems and applications.
Storage Capacity: Practical Examples
A kilobyte (KB) equals 1,024 bytes, making it the fundamental unit for measuring small storage capacities in digital systems. For practical context, a simple text file containing approximately 1,000 characters occupies roughly 1 KB, while a single byte stores just one character or symbol. Understanding the distinction between kilobytes and bytes is crucial when evaluating storage limits in devices like USB flash drives or early-generation computer memories.
Real-World Uses of Bytes and Kilobytes
Bytes represent the fundamental unit of digital information, crucial for storing individual characters such as letters or symbols in text files, while kilobytes (1,024 bytes) measure larger data like simple images or short documents. In real-world applications, web pages and email attachments often range from a few kilobytes to several megabytes, emphasizing the need for efficient kilobyte management in internet data transfer. Memory storage and file size calculations in software development rely heavily on distinguishing between bytes and kilobytes to optimize performance and resource allocation.
Importance of Knowing File Sizes
Understanding the difference between a kilobyte (KB) and a byte (B) is crucial for accurately assessing file sizes and managing digital storage. A kilobyte equals 1,024 bytes, meaning file size measurements can impact storage allocation and data transfer speeds significantly. Accurate knowledge of these units helps optimize device performance and ensures efficient use of bandwidth during file downloads and uploads.
Common Misconceptions: Byte vs Kilobyte
A byte consists of 8 bits and is the basic unit of digital information, while a kilobyte traditionally represents 1024 bytes in computing, though it is often confused with 1000 bytes in decimal systems. Common misconceptions arise when kilobyte is assumed to be exactly 1000 bytes, leading to errors in storage capacity and data transfer calculations. Clarifying that 1 KB equals 1024 bytes in binary measurement helps avoid misunderstandings in computer memory and file size representations.
Choosing the Right Unit: When to Use Byte or Kilobyte
Use bytes when representing small amounts of data like individual characters or file sizes under 1,000 bytes to ensure precise measurement. Kilobytes are more efficient for larger data sizes, such as documents, images, or software files ranging from 1,000 to 1,000,000 bytes, offering readability and convenience. Selecting the appropriate unit depends on the context and scale of data, where bytes suit fine granularity and kilobytes aid in simplifying larger values.
Kilobyte Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com