Rift is a groundbreaking virtual reality headset that offers immersive experiences through advanced tracking and high-resolution displays. Designed to deliver seamless interaction within digital environments, Rift enhances gaming and creative applications significantly. Dive deeper into this article to explore how Rift can transform your virtual adventures.
Table of Comparison
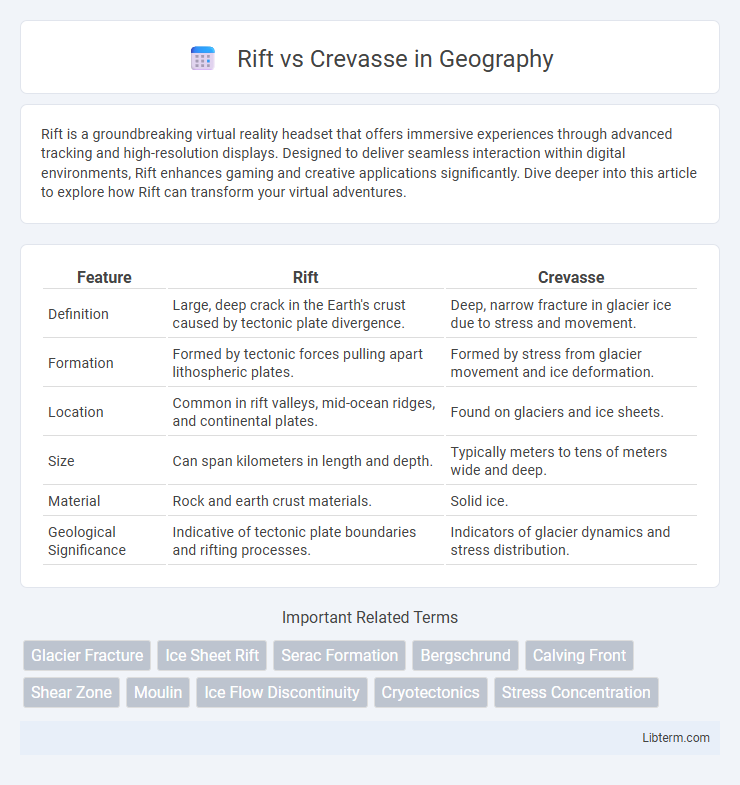
| Feature | Rift | Crevasse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, deep crack in the Earth's crust caused by tectonic plate divergence. | Deep, narrow fracture in glacier ice due to stress and movement. |
| Formation | Formed by tectonic forces pulling apart lithospheric plates. | Formed by stress from glacier movement and ice deformation. |
| Location | Common in rift valleys, mid-ocean ridges, and continental plates. | Found on glaciers and ice sheets. |
| Size | Can span kilometers in length and depth. | Typically meters to tens of meters wide and deep. |
| Material | Rock and earth crust materials. | Solid ice. |
| Geological Significance | Indicative of tectonic plate boundaries and rifting processes. | Indicators of glacier dynamics and stress distribution. |
Understanding Rifts and Crevasses: Definitions
Rifts are large cracks or fractures in the Earth's crust formed by tectonic forces causing the land to pull apart, often occurring near divergent plate boundaries. Crevasses are deep, narrow openings or fissures found primarily in glacier ice, resulting from the stresses of ice movement and deformation. Understanding the distinctions between rifts and crevasses is essential for studying geological processes and glacier dynamics.
Geological Formation Processes
Rifts form through tensional forces that pull apart the Earth's lithosphere, creating elongated valleys or basins often associated with divergent tectonic plate boundaries. Crevasses develop on glaciers as deep cracks resulting from the differential stress and strain caused by the ice flow over uneven terrain. While rifts involve crustal deformation on a continental or oceanic scale, crevasses are localized fractures primarily influenced by ice dynamics and stress distribution.
Location and Environment: Where They Occur
Rifts commonly occur along divergent tectonic plate boundaries, such as the East African Rift Valley, where the Earth's crust is pulling apart. Crevasses form primarily on glaciers and ice sheets, appearing in regions like Antarctica and Greenland due to stress and movement within the ice. The key environmental difference is that rifts are geological features on solid rock formations, whereas crevasses develop within moving ice masses.
Physical Characteristics and Appearance
A rift is a large, linear crack or fracture in the earth's surface formed by tectonic forces, often characterized by steep walls and considerable depth, typically found in rift valleys or oceanic plates. A crevasse is a deep, narrow opening or fissure within a glacier or ice sheet, often jagged and irregular, caused by the movement and stress of the ice. Unlike rifts, crevasses are temporary features formed in ice rather than solid rock and can vary greatly in width and length depending on the glacier's activity.
Causes Behind Rift and Crevasse Formation
Rifts form primarily due to tectonic plate divergence, where the stretching and thinning of the Earth's crust create elongated fractures often found at mid-ocean ridges or continental rift zones. Crevasses result from stress within glacial ice, caused by differential movement and tension as glaciers flow over uneven terrain or around obstacles. Both rifts and crevasses reflect the response of Earth's materials to stress but occur in fundamentally different geological and environmental contexts.
Dangers and Hazards Associated
Rifts and crevasses pose significant dangers due to their hidden depth and unstable edges, often leading to sudden falls that can cause severe injury or death. Both formations present hazards such as ice collapse, hypothermia risk, and difficulty in rescue operations, exacerbated by their often concealed nature beneath snow bridges. Navigating glacier terrain requires specialized equipment and experienced judgment to identify and avoid these perilous features effectively.
Rifts vs Crevasses: Key Differences
Rifts and crevasses are distinct geological features formed by different tectonic processes; rifts are large-scale fractures where the Earth's crust is pulling apart, often resulting in the formation of rift valleys, while crevasses are narrow, deep cracks that form on glaciers due to tension in the ice. Rifts can span hundreds of kilometers and are associated with plate boundary divergence, whereas crevasses are typically a few meters wide and occur within the glacial ice. Understanding the scale, formation mechanism, and geological context is crucial for differentiating rifts from crevasses in earth science.
Scientific Studies and Exploration
Scientific studies of rifts and crevasses highlight their crucial differences in glaciology, with rifts being larger fractures that can lead to iceberg calving, while crevasses are smaller cracks formed due to stress in glacier ice. Explorations using remote sensing and GPS technology provide detailed mapping of rift propagation and crevasse patterns, enhancing understanding of glacier dynamics and ice shelf stability. Research on Antarctic ice shelves emphasizes rift monitoring as key to predicting large-scale ice loss, contrasting with crevasse studies that focus on localized glacier movement and structural integrity.
Impact on Human Activity and Safety
Rifts and crevasses both pose significant hazards to human activity, particularly in mountaineering and glaciology, but their impacts differ due to their formation and stability. Rift zones, often found along tectonic plate boundaries, can cause large-scale ground displacement affecting infrastructure and increasing earthquake risks, while crevasses, typically found on glaciers, represent localized, deep fractures that present immediate dangers such as falls for climbers and explorers. Safety measures must account for rifts' potential for sudden land shifts and crevasses' deceptive snow bridges, emphasizing the need for specialized equipment and site-specific risk assessments.
Preservation, Monitoring, and Climate Impact
Rifts and crevasses, both fractures in ice, exhibit critical differences in preservation and monitoring due to their formation and scale; rifts are larger and often precursor to iceberg calving, requiring extensive satellite and aerial surveillance to track their evolution. Preservation efforts focus on understanding glacier stability where rifts indicate significant structural weaknesses impacting ice shelf integrity, whereas crevasses, typically smaller and more transient, demand localized monitoring for immediate glacier dynamics assessment. Climate change accelerates the formation of rifts by increasing ice melt and thinning, while crevasses respond quickly to surface stress changes, making both features vital indicators of glacier response to warming temperatures.
Rift Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com