Alpine landscapes offer breathtaking views and unique opportunities for outdoor adventure and relaxation. Exploring these high-altitude environments can enhance your appreciation for nature's beauty and challenge your physical limits. Discover how experiencing the Alpine region can transform your next travel adventure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
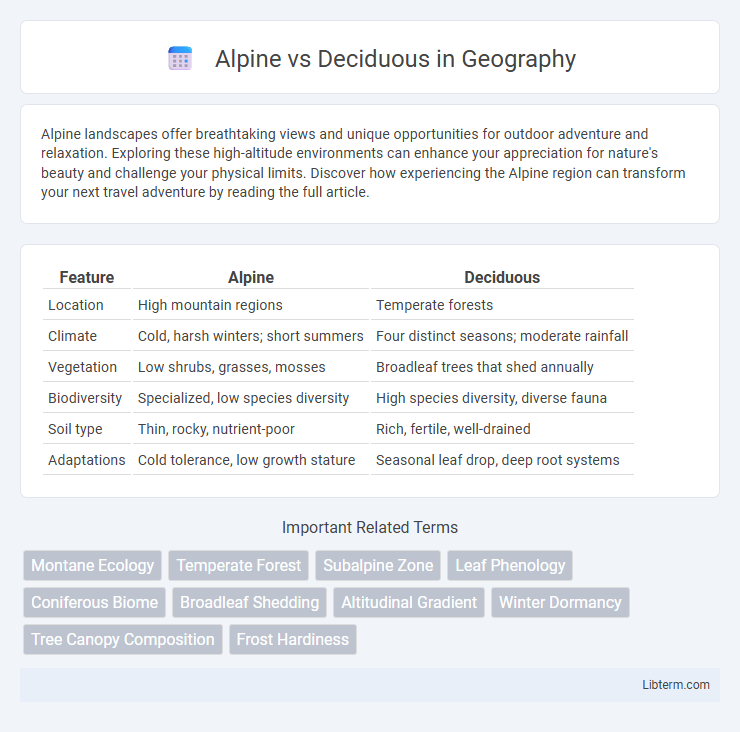
| Feature | Alpine | Deciduous |
|---|---|---|
| Location | High mountain regions | Temperate forests |
| Climate | Cold, harsh winters; short summers | Four distinct seasons; moderate rainfall |
| Vegetation | Low shrubs, grasses, mosses | Broadleaf trees that shed annually |
| Biodiversity | Specialized, low species diversity | High species diversity, diverse fauna |
| Soil type | Thin, rocky, nutrient-poor | Rich, fertile, well-drained |
| Adaptations | Cold tolerance, low growth stature | Seasonal leaf drop, deep root systems |
Introduction to Alpine and Deciduous Ecosystems
Alpine ecosystems are characterized by high elevations, cold temperatures, and a short growing season, supporting specialized flora such as dwarf shrubs and hardy grasses. Deciduous ecosystems, found in temperate regions, feature trees that shed their leaves seasonally to adapt to varying climates, promoting rich biodiversity. These ecosystems contrast sharply in vegetation structure, climate adaptation, and species composition, highlighting their ecological significance.
Key Characteristics of Alpine Environments
Alpine environments are characterized by high elevation, cold temperatures, and a short growing season, distinguishing them from deciduous forests that experience moderate elevation and seasonal leaf shedding. Vegetation in alpine zones primarily consists of low-growing, hardy plants such as grasses, mosses, and lichens adapted to harsh winds, intense sunlight, and nutrient-poor soils. These ecosystems exhibit unique adaptations like cushion plants and permafrost presence, contrasting with the broad-leaved trees and rich undergrowth typical of deciduous zones.
Key Traits of Deciduous Forests
Deciduous forests are characterized by broadleaf trees that shed their leaves seasonally to conserve water during winter or dry periods. These forests exhibit rich biodiversity, with distinct layers including a dense canopy, understory, and forest floor covered in nutrient-rich leaf litter. The temperate climate supports diverse wildlife adapted to seasonal changes and facilitates nutrient cycling through the decomposition of fallen leaves.
Climate Differences: Alpine vs Deciduous
Alpine regions experience cold temperatures year-round with short growing seasons, while deciduous forests have moderate climates with distinct seasonal changes including warm summers and cold winters. Alpine climates are characterized by high altitudes, resulting in heavy snowfall and strong winds, contrasting with the more temperate and humid conditions of deciduous areas. These climatic differences dictate unique adaptations in flora and fauna, with alpine species tolerating extreme cold and low oxygen, whereas deciduous species undergo seasonal leaf shedding to conserve resources.
Flora Diversity in Alpine Regions
Alpine regions exhibit unique flora diversity characterized by hardy, low-growing plants adapted to extreme cold, high UV radiation, and short growing seasons, contrasting with the broadleaf dominance found in deciduous forests. Species such as alpine asters, sedges, and dwarf shrubs thrive in rocky soils and nutrient-poor environments typical of high-altitude zones. This specialized vegetation supports distinct ecological niches and contributes to biodiversity hotspots despite the harsh climatic conditions.
Plant Life in Deciduous Forests
Deciduous forests feature a diverse plant life dominated by broadleaf trees such as oak, maple, and birch, which shed their leaves annually to conserve water and survive cold winters. The understory supports shrubs, ferns, and wildflowers adapted to seasonal light changes, creating rich biodiversity. Deciduous forests exhibit nutrient-rich soil due to leaf litter decomposition, fostering robust plant growth and sustained ecosystems.
Wildlife Adaptations in Alpine Habitats
Wildlife in alpine habitats exhibits specialized adaptations such as thick insulating fur, compact body shapes to minimize heat loss, and enhanced oxygen-carrying blood to survive extreme cold and low oxygen levels. Species like the snow leopard and mountain goat have developed strong limbs and hooves for navigating rocky, steep terrain. Behavioral adaptations include seasonal migrations and hibernation to cope with harsh alpine winters and limited food availability.
Faunal Diversity in Deciduous Biomes
Deciduous biomes exhibit higher faunal diversity compared to alpine regions due to their rich vegetation layers that provide ample food and shelter for a variety of species. Mammals like white-tailed deer, black bears, and numerous bird species thrive in these temperate forests, supported by seasonal availability of fruits, nuts, and insects. This biodiversity contrasts with alpine biomes, where harsh climate conditions limit faunal presence primarily to specialized species such as mountain goats and pika.
Environmental Challenges: Alpine and Deciduous Comparisons
Alpine environments face extreme cold, high winds, and low oxygen levels that limit plant growth to specialized, hardy species, while deciduous forests experience seasonal temperature variations with nutrient-rich soils supporting diverse tree species. Alpine plants adapt through slow growth, compact forms, and protective features, contrasting with deciduous trees that rely on shedding leaves to conserve water during cold or dry seasons. Environmental challenges in alpine regions also include shorter growing seasons and higher UV radiation, whereas deciduous ecosystems contend more with pests and seasonal flooding.
Conservation Efforts for Alpine and Deciduous Ecosystems
Conservation efforts for alpine ecosystems prioritize protecting fragile high-altitude habitats from climate change impacts and human disturbances by implementing strict land-use regulations and promoting restoration projects. Deciduous forest conservation focuses on preserving biodiversity through sustainable forestry practices, habitat connectivity, and combating invasive species. Both ecosystems benefit from community engagement and scientific research to monitor environmental changes and enhance resilience.
Alpine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com