Division is a fundamental mathematical operation that splits a number into equal parts or groups, helping you understand how quantities relate to each other. Mastering division enhances problem-solving skills and is essential for tasks ranging from budgeting to data analysis. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding and apply division effectively in various scenarios.
Table of Comparison
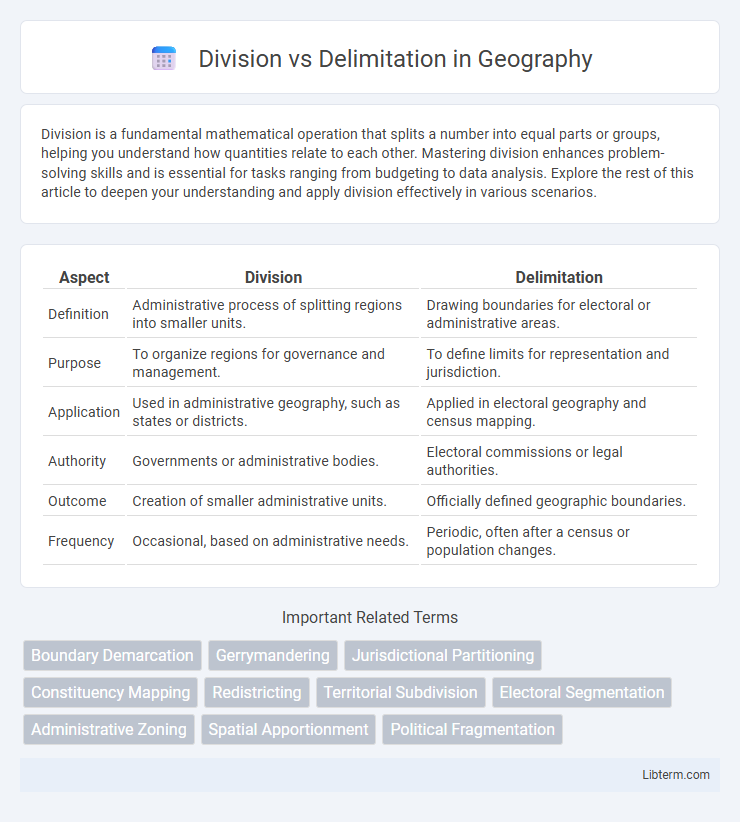
| Aspect | Division | Delimitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Administrative process of splitting regions into smaller units. | Drawing boundaries for electoral or administrative areas. |
| Purpose | To organize regions for governance and management. | To define limits for representation and jurisdiction. |
| Application | Used in administrative geography, such as states or districts. | Applied in electoral geography and census mapping. |
| Authority | Governments or administrative bodies. | Electoral commissions or legal authorities. |
| Outcome | Creation of smaller administrative units. | Officially defined geographic boundaries. |
| Frequency | Occasional, based on administrative needs. | Periodic, often after a census or population changes. |
Understanding Division and Delimitation
Division refers to the process of separating a whole into distinct parts based on defined criteria, often used in mathematics or organizational structures to create manageable sections. Delimitation involves establishing clear boundaries or limits within a given space or concept to clarify scope and avoid overlap. Understanding the differences between division and delimitation is essential for accurate classification, spatial mapping, and effective resource allocation.
Key Differences Between Division and Delimitation
Division involves splitting a geographic or administrative area into smaller parts based on existing boundaries, while delimitation defines the exact boundaries between these parts using legal or official frameworks. Division is primarily concerned with allocation and organization, whereas delimitation emphasizes precise boundary establishment to prevent disputes. Key differences include division's role in segmenting areas for governance or management and delimitation's function in legally drawing boundary lines for clarity and jurisdiction.
Legal Framework Governing Division and Delimitation
The legal framework governing division and delimitation primarily involves statutory laws and regulations that define the processes for territorial subdivision and boundary determination within a jurisdiction. Division pertains to the lawful segmentation of administrative areas or property, often regulated by legislation such as municipal codes or land use statutes, while delimitation refers to the precise establishment of boundaries, guided by legal principles and treaties in cases of international borders or by cadastral laws in domestic contexts. Courts and governmental agencies play crucial roles in interpreting and enforcing these legal provisions to resolve disputes and ensure adherence to established norms.
Historical Context of Division and Delimitation
Division and delimitation have historically shaped political boundaries and administrative jurisdictions, often influenced by colonial powers and treaties. Division refers to the physical or political separation of territories into distinct units, while delimitation focuses on defining precise boundaries through legal or cartographic means. Understanding the historical context reveals how divisions frequently resulted from conflicts or negotiations, with delimitation serving as the formal process to establish recognized borders.
Purposes and Objectives of Division and Delimitation
Division aims to subdivide a larger geographic area into smaller, manageable units primarily to facilitate effective governance, resource allocation, and administrative convenience. Delimitation focuses on defining precise boundaries of electoral constituencies to ensure equitable representation based on population distribution and demographic changes. Both processes serve distinct purposes: division enhances administrative efficiency, while delimitation safeguards the principle of fair political representation.
Processes Involved in Division
Division involves the systematic process of separating a whole into distinct parts based on set criteria or characteristics, often used in administrative, biological, or mathematical contexts. The key steps include identifying the entity to be divided, establishing clear boundaries or categories, and applying consistent rules or methods to ensure each part is distinct and functional. Tools such as geographic information systems (GIS) for territorial division or classification algorithms in data analysis play a crucial role in enhancing accuracy and efficiency during the division process.
Steps of the Delimitation Process
Delimitation involves the precise definition of territorial boundaries through a series of methodical steps, including the collection of relevant legal documents, historical treaties, and cartographic evidence. Experts analyze geographic features and apply international law principles to draft an agreed boundary line, which is then reviewed and accepted by all parties involved. The process concludes with formal documentation and, often, the erection of physical markers to clearly indicate the agreed boundary.
Impacts on Governance and Representation
Division alters administrative boundaries, potentially creating smaller, more manageable governance units that enhance local representation and resource allocation. Delimitation adjusts electoral boundaries to reflect population changes, ensuring equitable representation in legislative bodies and preventing vote dilution. Both processes significantly influence political power distribution and the effectiveness of public service delivery within affected regions.
Challenges and Controversies
Division and delimitation processes often face significant challenges due to competing territorial claims and ambiguous boundary definitions. Controversies arise from differing interpretations of legal frameworks, historical treaties, and resource allocations, complicating conflict resolution between states or regions. Disputes over maritime delimitation and internal administrative boundaries further exacerbate tensions, impacting political stability and international relations.
Future Trends in Division and Delimitation
Future trends in division and delimitation emphasize the integration of advanced geographic information systems (GIS) and artificial intelligence to enhance precision and efficiency. These technologies enable dynamic boundary adjustments based on real-time demographic, environmental, and political data, fostering more equitable representation and resource allocation. Increasing emphasis on participatory approaches and digital mapping platforms drives transparency and inclusivity in the delimitation process.
Division Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com