Merge technology enables you to combine multiple data sets or software files into a single, cohesive unit, improving efficiency and organization in digital workflows. This process minimizes redundancy and enhances data accuracy, facilitating smoother project management and collaboration. Discover how to leverage merge techniques effectively by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
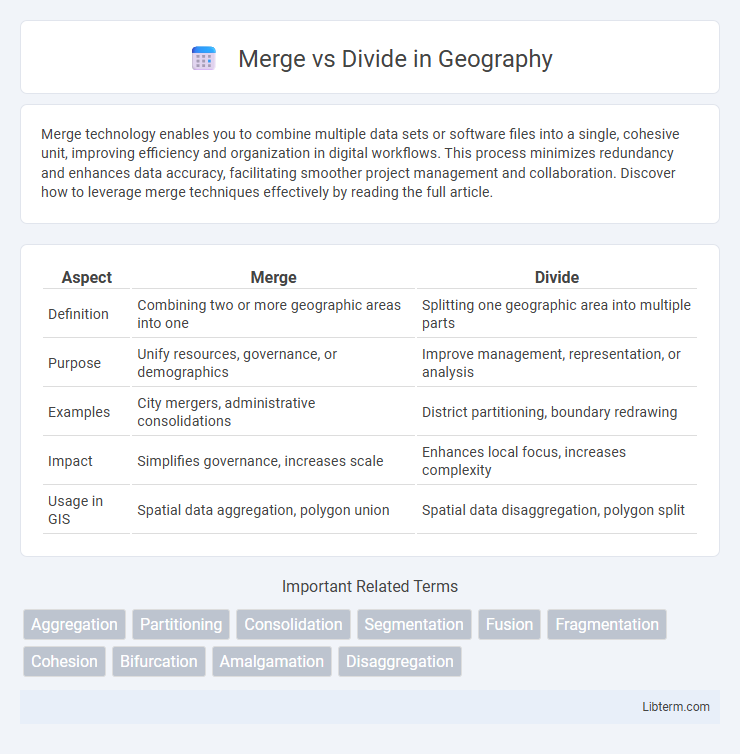
| Aspect | Merge | Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining two or more geographic areas into one | Splitting one geographic area into multiple parts |
| Purpose | Unify resources, governance, or demographics | Improve management, representation, or analysis |
| Examples | City mergers, administrative consolidations | District partitioning, boundary redrawing |
| Impact | Simplifies governance, increases scale | Enhances local focus, increases complexity |
| Usage in GIS | Spatial data aggregation, polygon union | Spatial data disaggregation, polygon split |
Understanding the Concepts: Merge and Divide
Merge combines multiple data sets or entities into a single, unified whole, enhancing cohesion and streamlining information processing. Divide separates a complex data set or entity into smaller, manageable parts to facilitate detailed analysis and targeted operations. Understanding the core principles of merge and divide enables efficient data manipulation, improving computational performance and accuracy.
Historical Perspectives on Merging and Dividing
Historical perspectives on merging and dividing reveal patterns of geopolitical shifts driven by economic, cultural, and political factors. Empires such as the Roman and Ottoman empires expanded through mergers of diverse territories, while the breakup of the Soviet Union exemplifies strategic divisions rooted in ethnic and ideological distinctions. These processes often reflect the quest for stability, identity, and governance efficiency across different eras.
Key Differences Between Merging and Dividing
Merging combines two or more entities into a single unified organization, consolidating resources, operations, and management to improve efficiency and market share. Dividing involves splitting one organization into multiple separate entities, each with distinct assets, responsibilities, and goals to enhance focus and agility. Key differences include the direction of structural change--merging expands integration, while dividing increases specialization and independence.
When to Merge: Benefits and Opportunities
Merging companies can create economies of scale, enhanced market share, and increased operational efficiency, providing significant competitive advantages. When firms have complementary strengths or overlapping customer bases, merging enables resource consolidation and innovation acceleration. Strategic mergers often unlock new growth opportunities, optimize costs, and improve financial performance through synergies and shared expertise.
When to Divide: Advantages and Use Cases
Dividing data or tasks enhances parallel processing by enabling simultaneous workflows that improve efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. It supports scalability in distributed systems, particularly in big data analytics and cloud computing, where workloads must be managed across multiple nodes. Common use cases include database sharding, map-reduce algorithms, and microservices architecture, where division optimizes performance and resource utilization.
Potential Challenges of Merging and Dividing
Merging and dividing organizations present potential challenges such as culture clashes, misaligned goals, and operational disruptions that can hinder integration success. Financial complexities arise from asset reallocation, valuation discrepancies, and unforeseen liabilities, impacting overall stability. Employee uncertainty and communication gaps often lead to decreased morale and productivity during both processes.
Impact on Team Dynamics: Merge vs Divide
Merging teams fosters collaboration, combining diverse skills to enhance creativity and problem-solving, which often strengthens trust and communication. Dividing teams can increase focus and efficiency on specific tasks, allowing smaller groups to develop closer bonds and faster decision-making processes. Both approaches significantly influence team dynamics by shaping interaction patterns and collective performance outcomes.
Real-Life Examples: Successful Merges and Divides
Successful mergers like the Disney and Pixar union in 2006 combined creative strengths and expanded market reach, boosting revenue and innovation in animation. Conversely, the 2015 eBay and PayPal split enabled both companies to focus on core competencies, resulting in increased shareholder value and operational efficiency. Real-life corporate divides and merges demonstrate strategic restructuring's impact on growth, market adaptation, and competitive advantage.
Strategic Decision-Making: Merge or Divide?
Strategic decision-making in the context of merging versus dividing requires careful evaluation of organizational goals, market conditions, and resource optimization. Merging can enhance competitive advantage by consolidating assets, streamlining operations, and expanding market share, while dividing may foster agility, focus on core competencies, and risk mitigation. Effective analysis of financial metrics, cultural alignment, and long-term strategic vision is essential to determine whether merging or dividing aligns best with sustained business growth.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Merge vs Divide
Future trends in the merge vs divide landscape highlight increased integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies to enhance data management and decision-making processes. Companies are leveraging cloud-based platforms that allow seamless merging of datasets for comprehensive analytics while promoting modular division for agile scalability. Emerging market demands drive innovations in hybrid models, balancing centralized control with decentralized responsiveness to optimize operational efficiency.
Merge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com