Stalactites form as mineral-rich water drips from cave ceilings, depositing calcite that gradually builds into icicle-shaped formations. These geological structures reveal valuable information about past environmental conditions and the cave's development over time. Explore the rest of this article to discover how stalactites grow and their significance in Earth's subterranean landscape.
Table of Comparison
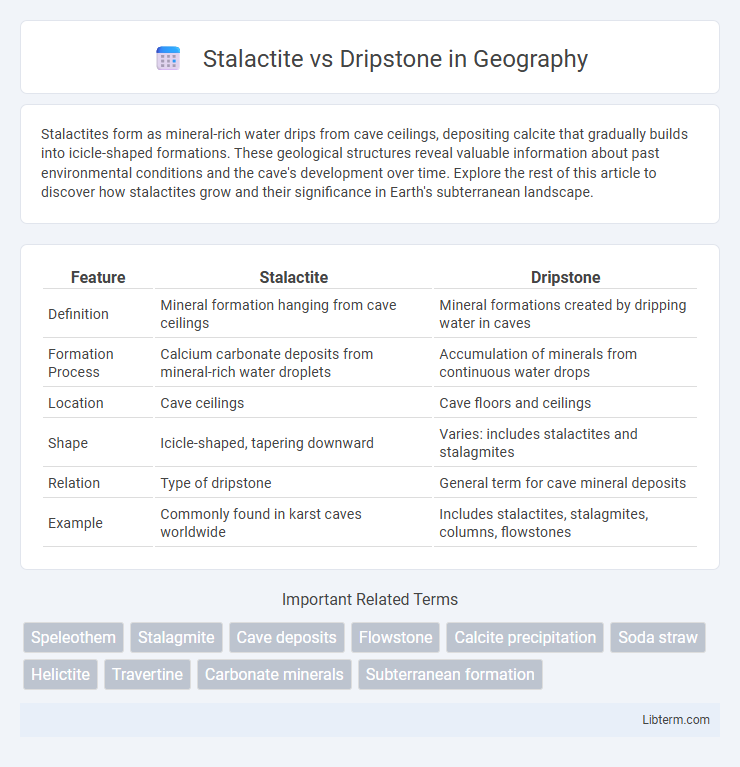
| Feature | Stalactite | Dripstone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mineral formation hanging from cave ceilings | Mineral formations created by dripping water in caves |
| Formation Process | Calcium carbonate deposits from mineral-rich water droplets | Accumulation of minerals from continuous water drops |
| Location | Cave ceilings | Cave floors and ceilings |
| Shape | Icicle-shaped, tapering downward | Varies: includes stalactites and stalagmites |
| Relation | Type of dripstone | General term for cave mineral deposits |
| Example | Commonly found in karst caves worldwide | Includes stalactites, stalagmites, columns, flowstones |
Introduction to Stalactites and Dripstones
Stalactites are icicle-shaped mineral formations that hang from cave ceilings, formed by the deposition of calcium carbonate from dripping water. Dripstones refer collectively to both stalactites and stalagmites, which develop through the slow accumulation of mineral deposits from dripping or flowing water in limestone caves. The distinguishing feature of stalactites is their downward growth, while dripstones encompass all speleothems created by mineral-laden water interactions within karst environments.
What are Stalactites?
Stalactites are icicle-shaped mineral formations that hang from the ceilings of caves, formed by the deposition of calcium carbonate from dripping water. These structures grow as mineral-rich water drips slowly, leaving behind tiny amounts of calcite that accumulate over thousands of years. Stalactites differ from dripstone by their distinctive hanging formation, specifically resulting from the deposition process on cave ceilings.
What are Dripstones?
Dripstones are mineral formations created by the deposition of calcium carbonate or other minerals from dripping water in caves. They include both stalactites, which hang from the ceiling, and stalagmites, which rise from the cave floor. These speleothems form through the continuous accumulation of minerals as water droplets evaporate, shaping intricate natural structures over thousands of years.
Formation Processes: Stalactites vs Dripstones
Stalactites form through the slow deposition of calcium carbonate as mineral-rich water drips from cave ceilings, creating icicle-shaped formations hanging downward. Dripstones encompass both stalactites and stalagmites, originating from similar mineral precipitation processes where water movement influences shape, size, and growth rate. Variations in drip rate, mineral concentration, and cave microclimate affect the formation dynamics of these speleothems, differentiating stalactites from broader dripstone structures.
Key Differences Between Stalactites and Dripstones
Stalactites are specific types of dripstones that form from mineral-rich water dripping from cave ceilings, creating icicle-shaped deposits. Unlike general dripstones, which include both stalactites and stalagmites, stalactites grow downward while stalagmites rise from cave floors. The key differences lie in their formation locations and shapes, with stalactites hanging from ceilings and dripstones encompassing a broader category of speleothems resulting from mineral deposition.
Similarities and Shared Features
Stalactites and dripstones are both speleothems formed by the deposition of calcium carbonate from mineral-rich water seeping through cave ceilings. They share similar growth processes involving the gradual accumulation of calcite as water drips and evaporates, creating elongated, icicle-like structures. Both formations contribute to the intricate and diverse cave morphology found in limestone environments worldwide.
Environmental Conditions for Formation
Stalactites and dripstones form in limestone caves through the deposition of calcium carbonate from dripping water, with stalactites hanging from cave ceilings and dripstones referring broadly to formations created by mineral-rich water deposits. The formation of stalactites requires a consistent supply of slightly acidic water rich in dissolved calcium bicarbonate, which precipitates as calcite when carbon dioxide escapes into the cave air. Environmental conditions such as stable temperature, humidity, and slow water flow rates are critical for the growth of these speleothems, promoting gradual mineral accumulation and distinct shapes.
Notable Examples Around the World
Notable examples of stalactites are found in the Carlsbad Caverns in New Mexico, where massive and intricate formations hang from cave ceilings, showcasing millions of years of mineral deposits. Dripstone formations are prominently featured in the Jenolan Caves in Australia, where both stalactites and stalagmites create stunning natural columns through continuous calcium carbonate deposits. The Postojna Cave in Slovenia is famous for its extensive dripstone decorations, demonstrating the dynamic processes of water seepage and mineral crystallization that sculpt these underground wonders.
Importance in Cave Ecosystems
Stalactites and dripstone formations play a crucial role in cave ecosystems by regulating water flow and providing habitats for specialized microorganisms and invertebrates. These mineral deposits influence cave humidity and microclimates, supporting diverse biological communities adapted to subterranean environments. Their presence also aids in preserving cave stability and contributes to nutrient cycling essential for ecosystem sustainability.
Conclusion: Stalactite vs Dripstone
Stalactites are a specific type of dripstone that hang from cave ceilings, formed by the deposition of calcium carbonate from dripping water. Dripstone encompasses a broader category of mineral formations created by mineral-rich water dripping or flowing in caves, including both stalactites and stalagmites. Understanding the distinction clarifies that all stalactites are dripstones, but not all dripstones are stalactites.
Stalactite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com