Natural landscapes offer breathtaking views and vital ecosystems that sustain biodiversity and regulate climate. Preserving these areas supports your well-being through clean air, water, and recreational opportunities. Discover how natural landscapes impact our planet and what you can do to protect them in the rest of the article.
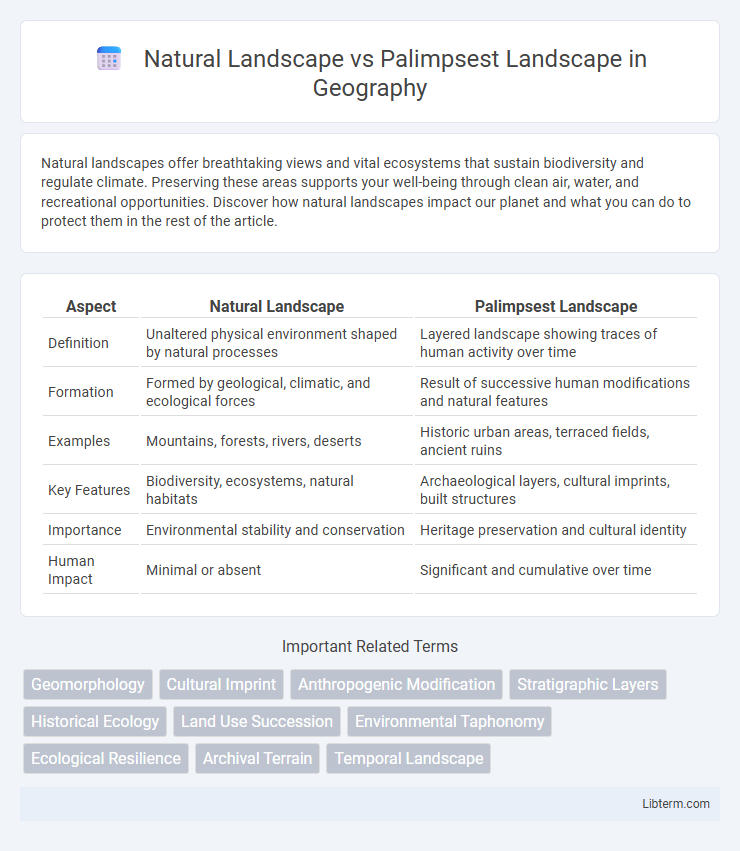
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Landscape | Palimpsest Landscape |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unaltered physical environment shaped by natural processes | Layered landscape showing traces of human activity over time |
| Formation | Formed by geological, climatic, and ecological forces | Result of successive human modifications and natural features |
| Examples | Mountains, forests, rivers, deserts | Historic urban areas, terraced fields, ancient ruins |
| Key Features | Biodiversity, ecosystems, natural habitats | Archaeological layers, cultural imprints, built structures |
| Importance | Environmental stability and conservation | Heritage preservation and cultural identity |
| Human Impact | Minimal or absent | Significant and cumulative over time |
Introduction to Natural and Palimpsest Landscapes
Natural landscapes are ecosystems shaped primarily by natural processes without significant human alteration, characterized by features such as forests, mountains, rivers, and wetlands that maintain biodiversity and ecological balance. Palimpsest landscapes, in contrast, represent layers of human history and activity superimposed on natural environments, where cultural, historical, and architectural elements coexist with natural features, reflecting continuous human interaction over time. These landscapes embody a complex interplay between natural elements and anthropogenic influences, serving as living records of environmental change and human legacy.
Defining Natural Landscapes: Characteristics and Examples
Natural landscapes consist of ecosystems that have developed without significant human intervention, showcasing features such as untouched forests, mountains, rivers, and wildlife habitats. Characterized by their biodiversity, geological formations, and climatic conditions, these landscapes include examples like the Amazon Rainforest, the Grand Canyon, and the Serengeti Plains. Their preservation is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, supporting species diversity, and providing ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration and water purification.
Understanding Palimpsest Landscapes: Layers of Human Influence
Palimpsest landscapes reveal complex layers of human influence superimposed on natural environments, reflecting historical, cultural, and ecological interactions over time. Unlike natural landscapes, which are primarily shaped by geological and ecological processes, palimpsest landscapes embody successive modifications such as agricultural terraces, ancient ruins, and urban development embedded within the terrain. These layered imprints provide valuable insights into past land use, social organization, and environmental adaptation, emphasizing the dynamic relationship between humans and their surroundings.
Historical Evolution of Landscapes: Nature and Culture Intertwined
Natural landscapes represent ecosystems shaped primarily by geological and ecological processes over millennia, reflecting biodiversity and environmental forces untouched by extensive human intervention. Palimpsest landscapes embody layered histories where cultural imprints, such as ancient agriculture, architecture, and urban development, intersect with natural features, revealing successive modifications by human societies across centuries. This historical evolution illustrates the dynamic interplay between nature and culture, highlighting how landscapes are continuously redefined by environmental changes and human activities.
Key Differences Between Natural and Palimpsest Landscapes
Natural landscapes are primarily shaped by ecological processes and consist of untouched environments such as forests, mountains, and wetlands, emphasizing biodiversity and geological formations. Palimpsest landscapes reflect layers of human history and cultural interventions, where past activities, structures, and land uses overlap, creating a complex tapestry of temporal and spatial narratives. The key difference lies in natural landscapes' dominance by natural elements versus palimpsest landscapes' integration of human-made modifications and historical imprinting on the environment.
Ecological Significance of Untouched Natural Landscapes
Untouched natural landscapes serve as critical reservoirs of biodiversity, providing habitat stability and ecological resilience against climate change and human disturbances. These areas maintain complex, self-regulating ecosystems that support endemic species and nutrient cycling essential for environmental health. In contrast, palimpsest landscapes, characterized by layers of historical human influence, often experience altered ecological functions and reduced biodiversity due to ongoing anthropogenic pressures.
Palimpsest Landscapes as Records of Human Activity
Palimpsest landscapes serve as layered records of human activity, where successive modifications overlay and interact with natural features, revealing complex histories through archaeological and cultural markers. These landscapes are dynamic archives, preserving evidence of past land use, settlement patterns, and environmental changes that contrast with untouched, natural landscapes characterized by minimal human intervention. Understanding palimpsest landscapes enhances our ability to interpret human-environment interactions over time, offering insights into heritage conservation and sustainable land management.
Impacts of Human Modification on Landscapes
Natural landscapes retain original ecological processes and biodiversity, providing habitats with minimal human disturbance. Palimpsest landscapes exhibit layers of human modifications over time, revealing cumulative impacts such as soil degradation, altered hydrology, and reduced native species diversity. These human-induced changes often fragment ecosystems, disrupt natural cycles, and diminish landscape resilience to environmental stresses.
Conservation Challenges: Preserving Nature and History
Natural landscapes face conservation challenges related to protecting biodiversity, ecosystems, and natural processes from human encroachment and climate change. Palimpsest landscapes present complex preservation issues by requiring the safeguarding of both tangible historical artifacts and intangible cultural heritage layered over time. Effective conservation strategies must balance ecological integrity with the need to maintain historical narratives embedded in these dynamic environments.
Future Perspectives on Landscape Management and Restoration
Future perspectives on landscape management emphasize integrating natural landscape dynamics with palimpsest landscapes' layered human imprints to enhance ecological resilience and cultural heritage preservation. Advanced remote sensing and GIS technologies enable precise monitoring and adaptive restoration strategies tailored to complex landscape interactions. Embracing multidisciplinary approaches fosters sustainable coexistence between natural processes and historic land use for climate adaptation and biodiversity conservation.
Natural Landscape Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com