Cliffs are steep rock faces that offer dramatic landscapes and unique ecosystems formed by natural erosion and geological processes. These striking landforms provide crucial habitats for various wildlife species and attract adventure seekers for activities like climbing and hiking. Discover more about the formation, ecological importance, and recreational opportunities cliffs offer in the full article.
Table of Comparison
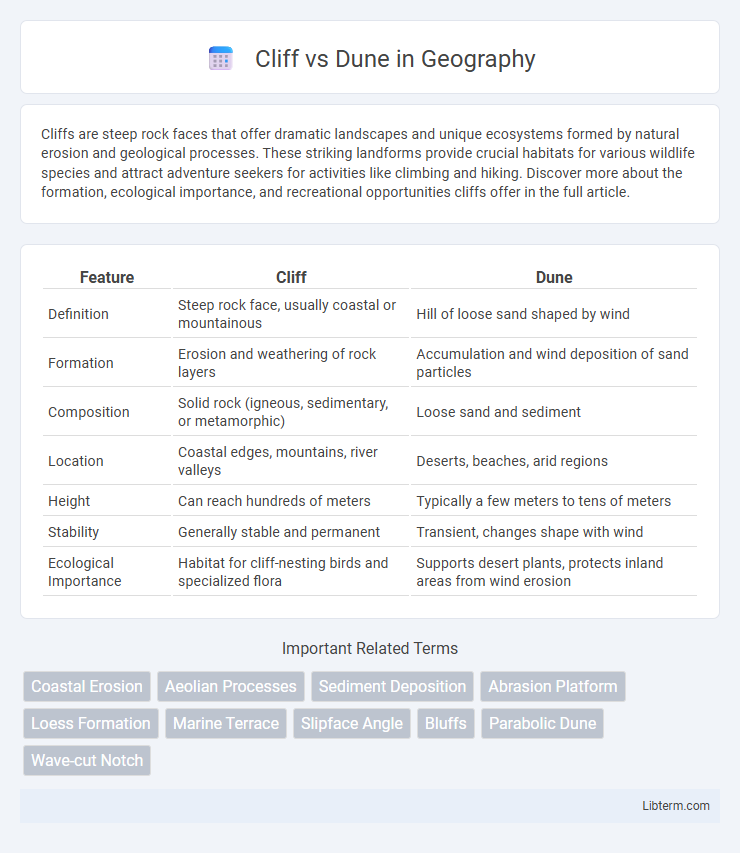
| Feature | Cliff | Dune |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steep rock face, usually coastal or mountainous | Hill of loose sand shaped by wind |
| Formation | Erosion and weathering of rock layers | Accumulation and wind deposition of sand particles |
| Composition | Solid rock (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) | Loose sand and sediment |
| Location | Coastal edges, mountains, river valleys | Deserts, beaches, arid regions |
| Height | Can reach hundreds of meters | Typically a few meters to tens of meters |
| Stability | Generally stable and permanent | Transient, changes shape with wind |
| Ecological Importance | Habitat for cliff-nesting birds and specialized flora | Supports desert plants, protects inland areas from wind erosion |
Understanding Cliffs and Dunes: Key Definitions
Cliffs are steep rock faces formed by erosion or tectonic activity, often found along coastlines or mountainous regions, characterized by vertical or near-vertical slopes. Dunes are mounds or ridges of sand shaped by wind action, primarily found in deserts or coastal areas, exhibiting dynamic forms that shift over time. Understanding cliffs involves geological processes and rock composition, while dunes require knowledge of sediment transport and wind patterns.
Geological Formation: Cliffs vs Dunes
Cliffs are steep rock faces formed through processes such as erosion, weathering, and tectonic activity, often revealing layers of sedimentary rock that provide insights into geological history. Dunes consist of accumulations of sand shaped by wind patterns in arid or coastal environments, constantly shifting and evolving due to sediment transport. The stability of cliffs contrasts with the dynamic nature of dunes, highlighting differences in composition, formation processes, and ecological impact.
Physical Characteristics: Height, Shape, and Composition
Cliffs typically rise vertically or near-vertically, with heights ranging from a few meters to several hundred meters, often composed of hard rock such as limestone, sandstone, or granite, which resists erosion. Dunes are mound-like hills of loose sand shaped by wind, with heights varying from a few meters up to hundreds of meters, characterized by soft, shifting sand grains primarily composed of quartz. Unlike the solid, rocky structure of cliffs, dunes constantly change shape due to wind movement and lack significant mineral cementation.
Locations: Where Cliffs and Dunes Are Found
Cliffs are prominent along coastlines, mountainous regions, and river valleys, typically forming where resistant rock meets erosion forces. Dunes are commonly found in arid deserts, coastal beaches, and large sandy inland areas where wind activity shapes loose sand into mounds or ridges. Both landforms highlight the dynamic interaction between natural elements and the earth's surface across diverse environments.
Processes Behind Cliff and Dune Formation
Cliff formation results from tectonic activity, erosion, and weathering processes that gradually wear away softer rock layers, leaving steep, exposed faces. Dunes form through the accumulation and migration of wind-blown sand particles, shaped by wind velocity, direction, and vegetation that stabilizes the sand deposits. Both processes are influenced by climatic conditions and geological factors, but cliffs are primarily shaped by mechanical forces acting on solid rock, while dunes develop through aeolian sediment transport in arid or coastal environments.
Ecological Importance of Cliffs and Dunes
Cliffs provide critical habitats for unique plant and animal species adapted to harsh, rocky environments while serving as natural barriers against coastal erosion and storms. Dunes act as dynamic sand reservoirs, supporting specialized vegetation that stabilizes the landscape and protects inland ecosystems from wind and saltwater intrusion. Both cliffs and dunes contribute to biodiversity conservation and coastline resilience, playing essential roles in maintaining ecological balance in coastal regions.
Human Impact on Cliffs and Dunes
Human activity significantly alters the structure and stability of both cliffs and dunes through construction, tourism, and resource extraction. Coastal cliffs face increased erosion due to foot traffic and development, while dunes suffer from vegetation removal and trampling, which reduces their natural defense against wind and water erosion. Restoration efforts, such as planting native vegetation and restricting access, are critical to mitigating human impact and preserving these dynamic landscapes.
Erosion and Conservation: Comparing Risks
Cliffs face intense erosion due to wave action, weathering, and gravity, leading to occasional landslides and loss of landmass along coastal regions. Dunes, composed primarily of sand, are highly susceptible to wind erosion but can continuously regenerate through natural processes and vegetation stabilization, which helps trap sediments and reduce movement. Conservation efforts for cliffs often involve engineered solutions like sea walls, whereas dune conservation emphasizes planting native grasses and controlling foot traffic to maintain ecological balance and prevent habitat degradation.
Notable Cliff and Dune Landforms Worldwide
Cliffs like the towering White Cliffs of Dover in England and the dramatic Preikestolen in Norway showcase breathtaking vertical rock faces shaped by erosion and tectonic activity. In contrast, dune landforms such as the vast Namib Sand Sea in Namibia and the towering Great Sand Dunes of Colorado feature wind-sculpted sand ridges and waves that shift over time. Both cliffs and dunes represent dynamic natural landscapes formed by distinct geological and environmental processes, offering unique ecosystems and striking visual contrasts worldwide.
Cliff or Dune: Which Landscape Dominates Coastal Regions?
Dune landscapes dominate many coastal regions due to their role in stabilizing shorelines and providing habitats for diverse flora and fauna. Cliffs are prominent where erosion-resistant rock meets the ocean, creating dramatic vertical landscapes but are less widespread than sand dunes. The prevalence of dunes correlates with sandy shorelines and wind patterns, making them the primary coastal feature in temperate and arid regions.
Cliff Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com