A port serves as a crucial hub for maritime trade, enabling the efficient transfer of goods between ships and land transportation. It plays a significant role in global supply chains, supporting economic growth and connectivity between regions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your business can benefit from strategic port operations and infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
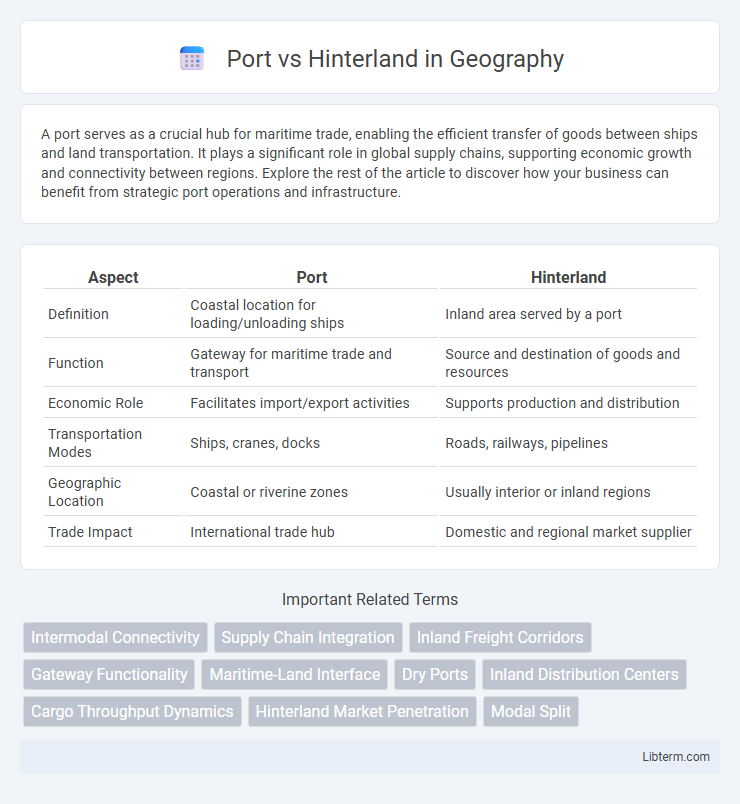
| Aspect | Port | Hinterland |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coastal location for loading/unloading ships | Inland area served by a port |
| Function | Gateway for maritime trade and transport | Source and destination of goods and resources |
| Economic Role | Facilitates import/export activities | Supports production and distribution |
| Transportation Modes | Ships, cranes, docks | Roads, railways, pipelines |
| Geographic Location | Coastal or riverine zones | Usually interior or inland regions |
| Trade Impact | International trade hub | Domestic and regional market supplier |
Introduction to Port and Hinterland
Ports serve as critical maritime gateways facilitating the transfer of goods between sea and land, acting as hubs for shipping containers, bulk cargo, and passenger traffic. Hinterlands refer to the inland regions connected to ports through transport networks such as railways, highways, and waterways, where goods are distributed or aggregated. Efficient port-hinterland linkages optimize supply chains, reduce transit times, and enhance trade competitiveness by integrating maritime and terrestrial logistics.
Defining Ports: Gateways of Trade
Ports serve as critical gateways of trade, facilitating the transfer of goods between sea routes and inland transportation networks. They consist of docks, terminals, and handling facilities designed to optimize cargo loading, unloading, and storage processes. Efficient port operations enhance global supply chains by enabling smooth connectivity with hinterlands, supporting economic growth and regional development.
Understanding the Hinterland: The Economic Heartland
The hinterland serves as the economic heartland by providing essential goods, raw materials, and market access to the port, thereby sustaining its operational viability. Efficient transportation networks and logistical connections between the port and its hinterland stimulate regional trade and economic growth. The integration of hinterland economies with port activities enhances supply chain resilience and drives value-added services in maritime commerce.
Historical Evolution of Port-Hinterland Relationships
The historical evolution of port-hinterland relationships reveals a dynamic shift from simple maritime trade points to complex logistics hubs integrating inland transport networks. Early ports served as local exchange centers, but industrialization and technological advances expanded hinterlands, creating extensive rail and road systems that enhanced cargo reach and efficiency. Modern ports now function within global supply chains, leveraging digital infrastructure to optimize connectivity and streamline the flow of goods between sea and inland markets.
Key Functions of Ports in Global Logistics
Ports serve as critical nodes in global logistics, facilitating the transfer of goods between maritime and inland transportation networks. Key functions include cargo handling, storage, and customs clearance, ensuring efficient movement and regulatory compliance. Hinterlands depend on ports for access to international markets, making seamless connectivity essential for supply chain optimization and economic growth.
Hinterland Connectivity and Transportation Networks
Hinterland connectivity refers to the efficient transportation and logistical links between a port and its surrounding inland regions, facilitating the smooth movement of goods to and from the port. Robust transportation networks, including rail, road, and inland waterways, are critical for reducing transit times and costs, enhancing the port's competitiveness and economic impact. Advanced intermodal solutions and infrastructure investments in hinterland corridors directly influence throughput capacity and supply chain resilience.
Port-Hinterland Integration: Strategies and Challenges
Port-Hinterland integration involves optimizing the connectivity between seaports and their inland regions to enhance the flow of goods, reduce logistics costs, and improve supply chain efficiency. Key strategies include developing multimodal transport networks, investing in advanced IT systems for real-time data sharing, and fostering public-private partnerships to streamline customs and regulatory processes. Challenges in this integration encompass infrastructural bottlenecks, fragmented governance structures, and inconsistent regulatory standards across jurisdictions that hinder seamless cargo movement.
Economic Impacts of Ports on Hinterland Regions
Ports significantly boost the economic development of hinterland regions by facilitating efficient trade flows and reducing transportation costs. Enhanced connectivity through multimodal transport networks enables hinterland industries to access global markets, attract investment, and stimulate job creation. The increased cargo throughput at ports directly correlates with regional economic growth, infrastructure development, and improved competitiveness of hinterland economies.
Technological Innovations Influencing Port-Hinterland Linkages
Technological innovations such as blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and automated container handling systems are transforming port-hinterland linkages by enhancing real-time data exchange and operational efficiency. Advanced analytics and digital twin technologies enable optimized route planning and cargo tracking, reducing transit times and costs between ports and inland logistics hubs. Integration of smart transportation networks and electrified rail systems further strengthens connectivity and sustainability within global supply chains.
Future Trends in Port and Hinterland Development
Future trends in port and hinterland development emphasize smart infrastructure integration, leveraging IoT and AI to enhance operational efficiency and real-time logistics management. Investment in multimodal transport corridors and sustainable energy solutions strengthens connectivity between ports and inland terminals, reducing carbon footprints and congestion. Digital twin technology and blockchain adoption facilitate transparent cargo tracking and secure data exchange, driving resilience in global supply chains.
Port Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com