Oxbow lakes form when a river creates a meander, which eventually gets cut off from the main channel, leaving a crescent-shaped body of water. These unique freshwater ecosystems support diverse wildlife and play a crucial role in maintaining natural water flow and quality. Explore the article to learn more about how oxbow lakes develop and their environmental significance.
Table of Comparison
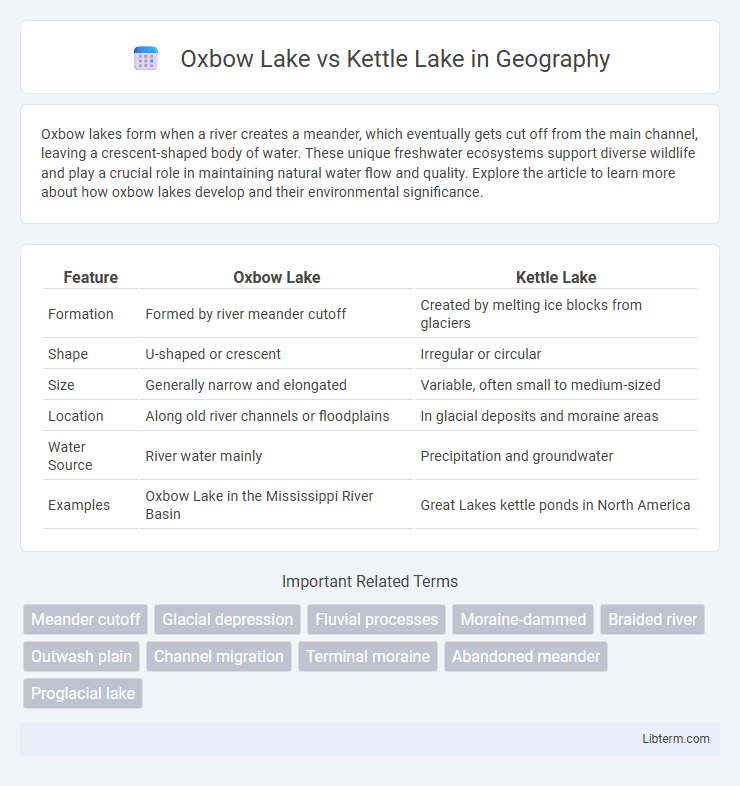
| Feature | Oxbow Lake | Kettle Lake |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Formed by river meander cutoff | Created by melting ice blocks from glaciers |
| Shape | U-shaped or crescent | Irregular or circular |
| Size | Generally narrow and elongated | Variable, often small to medium-sized |
| Location | Along old river channels or floodplains | In glacial deposits and moraine areas |
| Water Source | River water mainly | Precipitation and groundwater |
| Examples | Oxbow Lake in the Mississippi River Basin | Great Lakes kettle ponds in North America |
Introduction to Oxbow and Kettle Lakes
Oxbow lakes form when a river meander is cut off, creating a crescent-shaped body of water often surrounded by rich sediment deposits. Kettle lakes develop in glacial regions when large ice blocks become buried in sediments and melt, leaving behind depressions filled with water. Both lakes play vital roles in their ecosystems and serve as important indicators of geological and hydrological processes.
Formation Processes: Oxbow Lake
Oxbow lakes form through the natural evolution of meandering rivers, created when a wide river bend is cut off, isolating a crescent-shaped water body from the main channel. Sediment deposition during flood events seals the former river path, leading to the characteristic oxbow shape. These lakes often develop in low-gradient floodplains with active lateral river erosion and deposition.
Formation Processes: Kettle Lake
Kettle lakes form when large blocks of ice break off glaciers and become buried in sediment, eventually melting and creating depressions that fill with water. These depressions, called kettles, result from the uneven deposition of glacial till and outwash materials during glacial retreat. Unlike oxbow lakes formed by river meanders, kettle lakes are primarily glacial features formed through the dynamics of ice melt and sedimentation.
Key Physical Differences
Oxbow lakes form from meandering rivers when a curve is cut off, resulting in a crescent-shaped, shallow water body with rich sediment deposits. Kettle lakes originate from retreating glaciers, created by large blocks of ice left behind that melt and form deep, often circular depressions with minimal inflow or outflow. The key physical difference lies in their formation processes, shapes, and depths, with oxbow lakes being shallow and irregular, while kettle lakes are typically deeper and rounder.
Unique Characteristics of Oxbow Lakes
Oxbow lakes form from the meandering bends of rivers that become cut off, creating a distinct crescent shape often surrounded by rich alluvial soil. These lakes are characterized by their dynamic formation process, which contrasts with kettle lakes formed by retreating glaciers leaving behind isolated ice blocks. The unique hydrological patterns of oxbow lakes support diverse wetland ecosystems and serve as natural flood control features in riverine landscapes.
Distinct Features of Kettle Lakes
Kettle lakes are formed by retreating glaciers that leave behind large blocks of ice, which then melt and create depressions filled with water, distinguishing them from oxbow lakes formed by river meanders. Their often irregular, steep-sided basins and variable depths contrast with the typically crescent-shaped, shallow oxbow lakes. Kettle lakes commonly occur in glacial landscapes and can range from small ponds to large lakes, providing unique ecological habitats due to their isolation and nutrient input.
Ecological Significance
Oxbow lakes, formed by river meander cutoffs, create unique habitats with slow-moving water supporting diverse aquatic plants and providing critical breeding grounds for fish and amphibians. Kettle lakes, originating from retreating glaciers leaving behind ice blocks, host cold, nutrient-poor waters that support specialized ecosystems including rare plant species and migratory bird habitats. Both lake types play vital roles in maintaining regional biodiversity and water quality, influencing surrounding terrestrial ecosystems through nutrient cycling and habitat connectivity.
Geographic Distribution
Oxbow lakes predominantly form along meandering river valleys, especially in floodplains of large rivers like the Mississippi in the United States, whereas kettle lakes are commonly found in glacial regions such as the northern United States and Canada, formed by retreating glaciers leaving behind sediment-filled depressions. The geographic distribution of oxbow lakes is closely tied to active fluvial environments with dynamic river channels, while kettle lakes are characteristic of past glacial landscapes with irregular terrain. These distinct geographic distributions reflect their differing formation processes: oxbow lakes from river meanders cutoff and kettle lakes from ice block melting in glacial deposits.
Human Impact and Uses
Oxbow lakes, formed from abandoned river meanders, are often impacted by agriculture and urban development, leading to water pollution and habitat disruption. Kettle lakes, created by retreating glaciers leaving blocks of ice embedded in sediment, frequently support recreational activities and groundwater recharge, with human impact focused on tourism and conservation efforts. Both lake types serve as critical freshwater resources but face varying challenges from human encroachment and land use practices.
Summary: Oxbow Lake vs Kettle Lake
Oxbow lakes form when a river meander is cut off, creating a crescent-shaped body of water typically found in floodplains, while kettle lakes result from retreating glaciers leaving behind ice blocks that melt, forming depressions filled with water. Oxbow lakes are generally shallow with sediment-rich water, supporting diverse wetland ecosystems, whereas kettle lakes often have variable depths and clear, nutrient-poor water, influencing their unique flora and fauna. Understanding these differences aids in ecological studies and water resource management in glacial and riverine landscapes.
Oxbow Lake Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com