Hydrogeography examines the distribution and movement of water across Earth's surface and underground, influencing environmental and human systems. Understanding watersheds, aquifers, and river basins is essential for managing water resources sustainably. Discover how hydrogeography shapes your environment and impacts water availability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
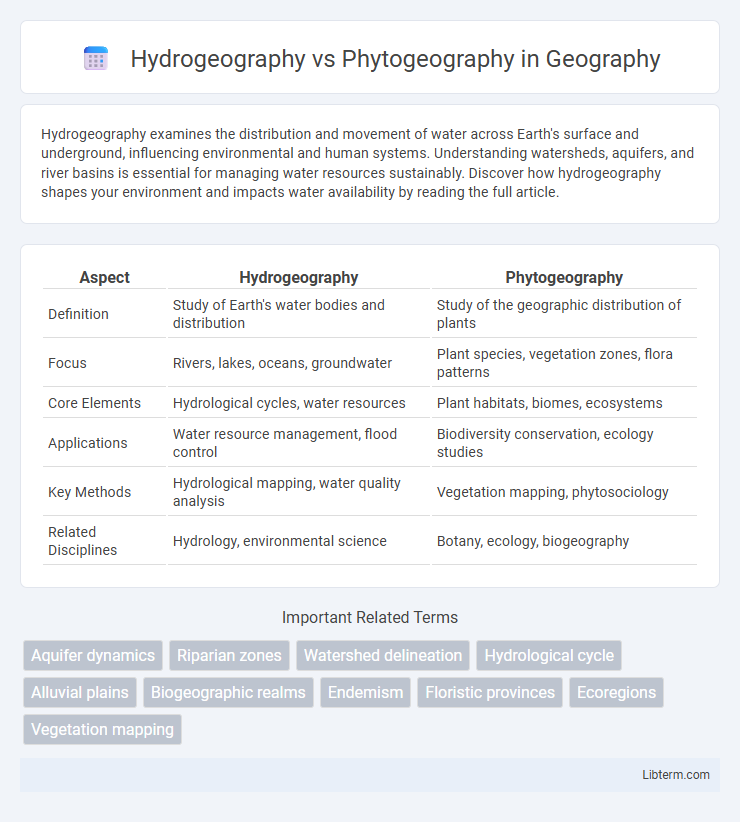
| Aspect | Hydrogeography | Phytogeography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of Earth's water bodies and distribution | Study of the geographic distribution of plants |
| Focus | Rivers, lakes, oceans, groundwater | Plant species, vegetation zones, flora patterns |
| Core Elements | Hydrological cycles, water resources | Plant habitats, biomes, ecosystems |
| Applications | Water resource management, flood control | Biodiversity conservation, ecology studies |
| Key Methods | Hydrological mapping, water quality analysis | Vegetation mapping, phytosociology |
| Related Disciplines | Hydrology, environmental science | Botany, ecology, biogeography |
Introduction to Hydrogeography and Phytogeography
Hydrogeography studies the distribution and movement of water across Earth's surface, highlighting rivers, lakes, groundwater, and oceans within physical landscapes. Phytogeography examines the spatial distribution of plant species and vegetation patterns, analyzing environmental factors influencing flora across different regions. Both fields integrate ecological and geographical data to understand natural resource dynamics and ecosystem interactions.
Defining Hydrogeography: Scope and Focus
Hydrogeography studies the distribution, movement, and quality of Earth's freshwater resources, including rivers, lakes, groundwater, and wetlands, emphasizing hydrological processes and aquatic ecosystems. Phytogeography, in contrast, examines the geographic distribution of plant species and vegetation patterns, focusing on ecological and evolutionary factors influencing plant biomes. The scope of hydrogeography encompasses water cycle dynamics and human interactions with water bodies, while phytogeography centers on plant diversity and biogeographical regions.
Defining Phytogeography: Scope and Focus
Phytogeography, also known as plant geography, examines the distribution patterns of plant species and communities across various geographic regions, emphasizing ecological and evolutionary factors influencing vegetation. Unlike hydrogeography, which studies the spatial distribution and movement of water bodies, phytogeography focuses on terrestrial and aquatic plants in relation to climate, soil, and topography. This discipline integrates biogeographical data to map vegetation zones, assess biodiversity hotspots, and understand plant migration and adaptation trends over time.
Key Differences Between Hydrogeography and Phytogeography
Hydrogeography studies the distribution, movement, and quality of Earth's water resources, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater systems, while phytogeography focuses on the geographic distribution of plant species and vegetation patterns. Hydrogeography emphasizes hydrological processes and water cycle dynamics, whereas phytogeography investigates ecological factors influencing plant habitats and biogeographical zones. The key difference lies in hydrogeography's concentration on water bodies and their physical properties, contrasting with phytogeography's analysis of plant distribution shaped by climatic and environmental variables.
Methods and Tools in Hydrogeographical Research
Hydrogeographical research primarily employs remote sensing technologies, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and hydrological modeling to analyze water distribution, flow patterns, and watershed management. Methods such as groundwater mapping, isotopic tracing, and hydrochemical analysis enable detailed assessment of aquifer properties and water quality. Tools like satellite imagery, digital elevation models (DEM), and hydrogeological survey instruments optimize data collection and spatial analysis in hydrogeography, distinguishing it from phytogeographical methods that focus more on vegetation distribution and ecological zones.
Methods and Tools in Phytogeographical Research
Phytogeographical research primarily employs remote sensing, GIS mapping, and vegetation sampling methods to analyze plant distribution patterns and ecosystem dynamics. Molecular tools such as DNA barcoding and phylogenetic analysis are increasingly used to assess genetic diversity and evolutionary relationships of plant species. Statistical modeling and niche modeling software enhance predictions of plant responses to environmental changes, integrating climatic, soil, and topographical data.
Interconnections: Water Systems and Plant Distribution
Hydrogeography examines the spatial distribution and dynamics of water bodies, influencing soil moisture and microclimates essential for plant growth, while phytogeography studies the distribution of plants in relation to these environmental factors. The interconnection between water systems and plant distribution is evident in riparian zones, wetlands, and aquatic ecosystems, where water availability and quality directly shape vegetation patterns and biodiversity. Understanding these relationships aids in predicting the impacts of hydrological changes on plant communities, crucial for conservation and ecological management.
Applications in Environmental Management
Hydrogeography, which studies the distribution and movement of water resources, plays a crucial role in environmental management by informing sustainable water use, flood control, and watershed protection strategies. Phytogeography examines plant distribution patterns influenced by environmental factors, aiding habitat conservation, restoration projects, and biodiversity management. Integrating hydrogeographic and phytogeographic data enhances ecosystem resilience planning and supports adaptive management practices in response to climate change impacts.
Challenges in Studying Hydrogeography and Phytogeography
Challenges in studying hydrogeography include variable water flow patterns, complex underground aquifer systems, and the impact of climate change on water distribution. In phytogeography, difficulties arise from the vast diversity of plant species, overlapping ecological niches, and rapid environmental changes affecting plant distribution. Both fields require integrating remote sensing, GIS technology, and long-term ecological data for accurate mapping and analysis.
Future Trends in Hydrogeographical and Phytogeographical Studies
Emerging technologies such as remote sensing and GIS are revolutionizing hydrogeographical and phytogeographical studies, enabling precise mapping of water resources and vegetation patterns under climate change scenarios. Future research will increasingly integrate big data analytics and machine learning to predict ecosystem responses to hydrological variability and shifts in plant distribution. Interdisciplinary approaches combining hydrogeology and plant ecology will drive sustainable management of natural resources amid growing environmental challenges.
Hydrogeography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com