Gigabyte technology delivers powerful performance and reliable hardware solutions for gaming, content creation, and business applications. Their cutting-edge motherboards, graphics cards, and components optimize your system's speed and efficiency, ensuring a seamless computing experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Gigabyte products can elevate your setup.
Table of Comparison
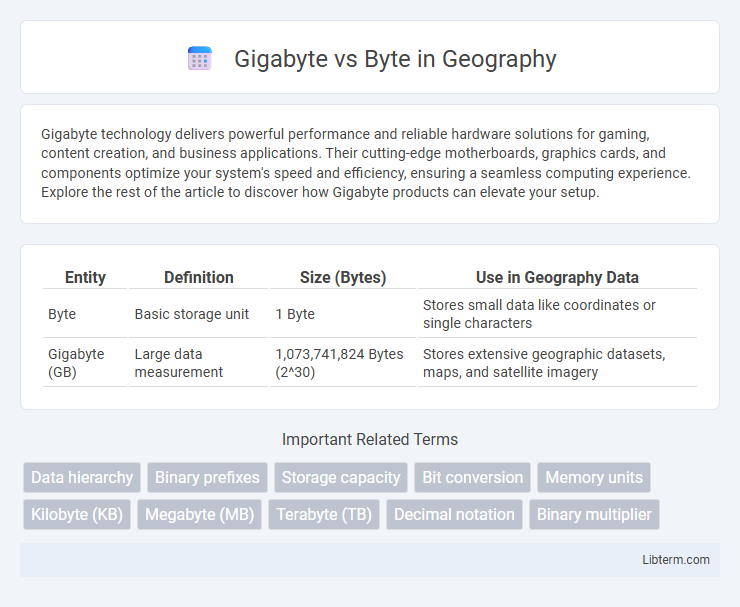
| Entity | Definition | Size (Bytes) | Use in Geography Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Byte | Basic storage unit | 1 Byte | Stores small data like coordinates or single characters |
| Gigabyte (GB) | Large data measurement | 1,073,741,824 Bytes (2^30) | Stores extensive geographic datasets, maps, and satellite imagery |
Understanding the Basics: What is a Byte?
A byte is a fundamental unit of digital information storage, typically consisting of 8 bits, each representing a binary value of 0 or 1. It is the basic building block for encoding a single character, such as a letter, number, or symbol, in computer systems. Understanding bytes is essential, as larger data measurements like kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes are all multiples of bytes, with one gigabyte equaling approximately one billion bytes.
Defining a Gigabyte: How Many Bytes?
A gigabyte (GB) is a unit of digital information storage commonly used to quantify data capacity in computing. Technically, one gigabyte equals 1,073,741,824 bytes when using the binary system (2^30 bytes), often referred to as a gibibyte in some contexts. However, in the decimal system used by most storage manufacturers, a gigabyte is defined as 1,000,000,000 bytes, leading to differences in how storage size is reported.
Byte vs Gigabyte: Key Differences Explained
A byte is the basic unit of digital information, typically representing one character, while a gigabyte equals approximately 1 billion bytes, used to measure larger data sizes like storage capacity. The difference lies in scale; bytes measure small amounts of data, whereas gigabytes handle substantial volumes commonly seen in hard drives and file sizes. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately assessing data storage and file transfer requirements.
Historical Evolution of Data Measurement Units
The historical evolution of data measurement units began with the byte, originally defined in the 1950s as a group of bits representing a single character, typically consisting of 8 bits. Over time, as digital storage expanded, the gigabyte emerged to quantify approximately one billion bytes (1,073,741,824 bytes in binary systems), reflecting the exponential growth in computing capacity. This shift from byte to gigabyte marks the progression from early computing's basic data units to modern high-capacity data storage standards essential for handling multimedia and large-scale databases.
Real-World Examples: Bytes and Gigabytes in Everyday Life
A byte represents a single character of data, such as a letter or number, commonly used to measure file sizes like a text document or an email, typically ranging from a few bytes to several kilobytes. Gigabytes, equivalent to approximately one billion bytes, are used to quantify larger digital storage capacities such as smartphone memory, laptop hard drives, or streaming video files, with common devices offering storage from 64GB to 512GB or more. For instance, a high-definition movie might be around 2-4GB, while a regular photo file usually occupies 2-5MB, clearly illustrating the scale difference between bytes and gigabytes in everyday technology use.
Conversion Guide: From Bytes to Gigabytes
A gigabyte (GB) equals 1,073,741,824 bytes, based on the binary system used in computing where 1 gigabyte is 2^30 bytes. Converting bytes to gigabytes requires dividing the total byte value by 1,073,741,824, enabling accurate measurement of data storage and file sizes. Understanding this conversion is crucial for optimizing storage capacity and managing digital data effectively.
Storage Devices: How Bytes and Gigabytes Matter
Storage devices use bytes as the fundamental unit to measure capacity, with gigabytes (GB) representing 1 billion bytes, crucial for quantifying data size and performance. Understanding the difference between bytes and gigabytes helps users gauge the actual storage available on devices like SSDs, HDDs, and flash drives. Manufacturers often advertise storage in gigabytes to provide a clearer and more manageable representation of device capacity for consumers.
Importance of Knowing Data Units in Technology
Understanding the difference between a gigabyte (GB) and a byte is crucial for accurately managing data storage and transfer in technology. A gigabyte equals 1,073,741,824 bytes, highlighting the vast scale difference important for tasks like file sizing, memory capacity, and network bandwidth. Mastery of data units ensures optimized system performance, efficient resource allocation, and precise communication in computing environments.
Common Misconceptions: Gigabyte vs Byte
A gigabyte (GB) is often mistakenly thought to be simply 1,000 bytes, but it actually represents 1 billion bytes in decimal systems or 1,073,741,824 bytes (2^30) in binary systems used by computers. Common misconceptions arise from confusing the gigabyte with the byte, the fundamental unit of digital information storage that equals a single character of text or a small data element. Misunderstanding these differences can lead to errors in data storage calculation, software requirements, and memory specifications.
Future Trends: Increasing Data Sizes and Storage Needs
Gigabyte (GB) and byte represent different scales of digital information, with a gigabyte equaling approximately one billion bytes, making it crucial to understand their roles in future data storage. As data sizes grow exponentially due to advancements in AI, IoT, and high-resolution media, storage solutions must evolve to handle multi-gigabyte and terabyte datasets efficiently. Emerging technologies such as cloud storage expansion, solid-state drives (SSD) innovations, and data compression algorithms will address the escalating storage needs driven by increasing gigabyte-scale data volumes.
Gigabyte Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com