Mesa formations are flat-topped hills with steep sides, commonly found in arid landscapes as a result of erosion-resistant rock layers. These geological structures offer unique insights into Earth's history and are often popular destinations for hiking and photography. Explore this article to uncover fascinating facts about mesas and their significance in nature.
Table of Comparison
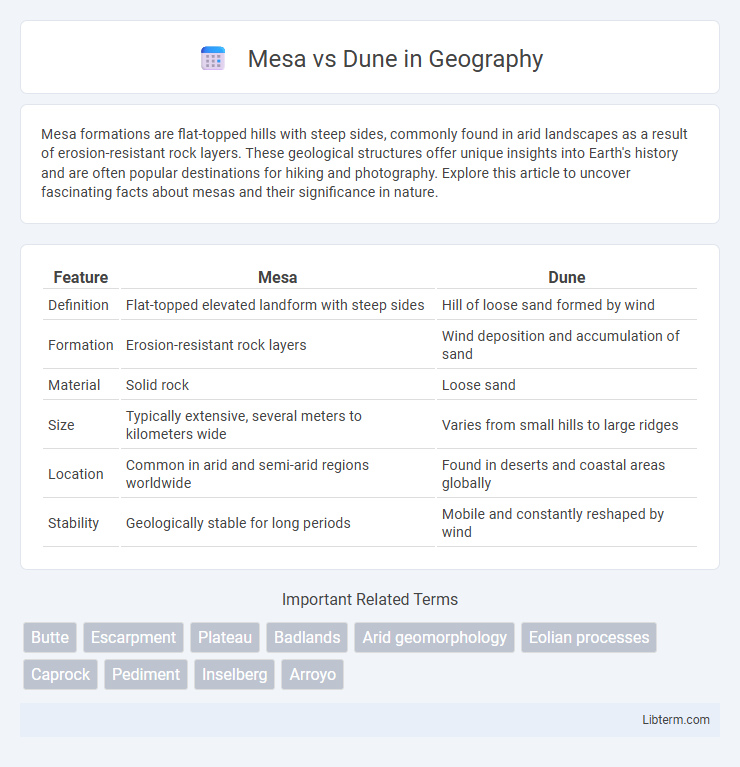
| Feature | Mesa | Dune |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flat-topped elevated landform with steep sides | Hill of loose sand formed by wind |
| Formation | Erosion-resistant rock layers | Wind deposition and accumulation of sand |
| Material | Solid rock | Loose sand |
| Size | Typically extensive, several meters to kilometers wide | Varies from small hills to large ridges |
| Location | Common in arid and semi-arid regions worldwide | Found in deserts and coastal areas globally |
| Stability | Geologically stable for long periods | Mobile and constantly reshaped by wind |
Introduction to Mesa and Dune
Mesa is an open-source project that provides a collection of graphics drivers and a framework for rendering APIs like OpenGL and Vulkan, primarily supporting Linux and Unix-like operating systems. Dune is a modular, extensible library designed for solving partial differential equations with grid-based methods, commonly used in scientific computing and engineering simulations. While Mesa focuses on graphics rendering and hardware acceleration, Dune emphasizes numerical computation and parallel processing for large-scale scientific applications.
Key Differences Between Mesa and Dune
Mesa is a cross-platform graphics library primarily used for OpenGL implementation, enabling hardware-accelerated rendering on multiple operating systems. Dune is a modular software framework focused on solving partial differential equations with grid-based methods, emphasizing numerical simulations rather than graphics rendering. The key difference lies in Mesa's role in graphics rendering infrastructure versus Dune's specialization in scientific computing and numerical analysis frameworks.
Performance Comparison: Mesa vs Dune
Mesa delivers efficient graphics driver performance through its open-source implementations targeting a wide range of hardware, emphasizing compatibility and stability. Dune provides a lightweight, secure runtime environment aimed at isolating applications for improved performance in security-sensitive contexts, though it is less focused on raw graphics throughput. Benchmark analyses reveal Mesa outperforms Dune in graphics-intensive workloads, while Dune excels in minimizing overhead for isolated computing tasks.
Installation and Setup Processes
Mesa features a straightforward installation process with pre-compiled binaries available for most Linux distributions, making it easy to set up and update via package managers like apt or rpm. In contrast, Dune requires a more involved setup involving OCaml environment configuration, dependencies installation, and manual compilation steps, which may necessitate familiarity with build systems. Mesa's ease of installation benefits users seeking quick deployment, while Dune's setup offers greater customization for advanced build automation in OCaml projects.
Compatibility With Hardware and Software
Mesa offers extensive hardware compatibility by supporting a wide range of GPUs from AMD, Intel, and NVIDIA through its open-source drivers, making it ideal for Linux-based systems and diverse software environments. Dune specializes in GPU virtualization and cloud-based graphics acceleration, providing compatibility mainly with NVIDIA GPUs and software stacks optimized for virtualized infrastructure. Mesa excels in native hardware integration for desktops and laptops, while Dune targets cloud-native applications requiring efficient GPU partitioning and remote graphical workloads.
Feature Set and Capabilities
Mesa provides a comprehensive open-source 3D graphics library with robust support for OpenGL, Vulkan, and Gallium3D drivers, enabling advanced rendering and hardware acceleration across multiple platforms. Dune, in contrast, emphasizes scalable grid-based numerical simulations with powerful support for finite element, finite volume, and finite difference methods, offering extensive flexibility for solving partial differential equations in scientific computing. Mesa excels in graphics rendering capabilities, while Dune focuses on numerical solvers and computational frameworks for high-performance scientific applications.
Community Support and Documentation
Mesa offers extensive community support through an active mailing list, GitHub discussions, and frequent contributions from developers across various research institutions, ensuring real-time problem-solving and collaborative development. Dune boasts comprehensive, well-structured documentation with detailed tutorials, user guides, and API references, making it accessible for both beginners and advanced users. Strong community forums and consistent maintenance updates further enhance Dune's usability and reliability for large-scale scientific computing projects.
Use Cases: When to Choose Mesa or Dune
Choose Mesa for real-time analytics and interactive data exploration when dealing with large-scale datasets that require fast querying and customizable visualizations. Opt for Dune when focusing on decentralized finance (DeFi) insights, blockchain analytics, and community-driven data dashboards tailored to Ethereum and other blockchain networks. Mesa excels in general-purpose business intelligence, while Dune specializes in on-chain data transparency and collaborative analysis.
Pros and Cons Analysis
Mesa offers a user-friendly interface with extensive customization options, making it ideal for those seeking flexibility in project management. However, its complexity can overwhelm beginners and requires time to master. Dune excels in real-time data visualization and collaborative features, enhancing team productivity, but it may lack the depth of customization found in Mesa, potentially limiting advanced users.
Conclusion: Which Is Better for Your Needs?
Mesa offers a user-friendly interface and strong community support, making it ideal for beginners and developers seeking rapid prototyping in AI and robotics. Dune provides advanced optimization tools and high-performance capabilities suited for researchers and enterprises requiring scalable and precise data analysis. Choosing between Mesa and Dune depends on your project complexity, technical expertise, and scalability requirements.
Mesa Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com