Solfatara is a volcanic crater located in the Campi Flegrei volcanic area near Naples, Italy, known for its active fumaroles and sulfur emissions. This geothermal hotspot offers a unique glimpse into volcanic activity with its boiling mud pools and steam vents, making it a fascinating destination for geology enthusiasts and adventurers alike. Discover more about Solfatara's intriguing natural phenomena and its significance in volcanic research by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
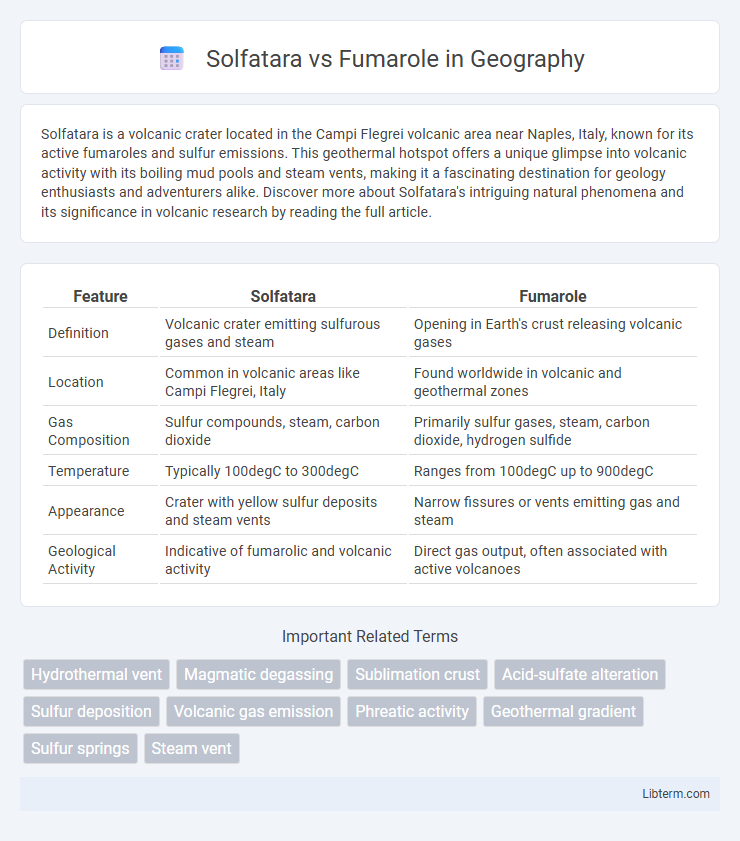
| Feature | Solfatara | Fumarole |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Volcanic crater emitting sulfurous gases and steam | Opening in Earth's crust releasing volcanic gases |
| Location | Common in volcanic areas like Campi Flegrei, Italy | Found worldwide in volcanic and geothermal zones |
| Gas Composition | Sulfur compounds, steam, carbon dioxide | Primarily sulfur gases, steam, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide |
| Temperature | Typically 100degC to 300degC | Ranges from 100degC up to 900degC |
| Appearance | Crater with yellow sulfur deposits and steam vents | Narrow fissures or vents emitting gas and steam |
| Geological Activity | Indicative of fumarolic and volcanic activity | Direct gas output, often associated with active volcanoes |
Introduction to Solfataras and Fumaroles
Solfataras are volcanic vents emitting sulfur-rich gases and steam, typically found in volcanic areas with moderate temperatures ranging from 100degC to 300degC. Fumaroles release various volcanic gases, mainly steam and carbon dioxide, often at higher temperatures exceeding 300degC and lacking significant sulfur deposits. Both features indicate active geothermal activity but differ in gas composition, temperature, and sulfur presence.
Defining Solfatara: Characteristics and Features
Solfatara is a volcanic crater characterized by its emission of sulfur-rich gases, primarily sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, which create distinctive yellow deposits around vent openings. Unlike fumaroles, which release steam and non-sulfurous gases, solfataras are specifically marked by intense sulfur emissions and higher temperatures, often exceeding 200degC. The acidic environment and fumarolic activity within solfatara craters contribute to unique geothermal landscapes commonly found in volcanic regions such as the Phlegraean Fields in Italy.
What is a Fumarole? Key Differences Explained
A fumarole is a vent in volcanic areas that emits steam and volcanic gases such as sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, often found in geothermal fields. Unlike Solfatara, which specifically refers to fumaroles rich in sulfur deposits creating intense sulfurous emissions and yellow crusts, a fumarole can emit a variety of gases and may not always produce visible sulfur deposits. The key difference lies in the composition and appearance: Solfatara is a type of fumarole characterized by high sulfur content, while fumaroles broadly denote steam and gas vents regardless of sulfur concentration.
Geological Formation: Solfataras vs Fumaroles
Solfataras are volcanic vents emitting sulfur-rich gases and steam at moderate temperatures, formed by the interaction of magma with underground water near volcanic fumaroles. Fumaroles are openings in the Earth's crust that release steam and volcanic gases directly from magma, often at higher temperatures and with a broader gas composition including sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide. The geological formation of solfataras typically involves sulfur deposition around vent areas, whereas fumaroles represent more direct volcanic gas escape points linked to deeper magma sources.
Gas Emissions: Composition and Environmental Impact
Solfataras emit sulfur-rich volcanic gases primarily composed of sulfur dioxide (SO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon dioxide (CO2), and steam, significantly impacting air quality and contributing to acid rain and vegetation damage in surrounding areas. Fumaroles release hotter gases dominated by water vapor (H2O), CO2, and trace amounts of sulfur compounds, affecting local microclimates and posing risks of toxic gas exposure. Both gas emissions influence atmospheric chemistry and can alter soil acidity and local ecosystems, necessitating monitoring to mitigate environmental and health hazards.
Temperature Ranges: Solfatara vs Fumarole Activity
Solfataras exhibit temperature ranges typically between 100degC and 300degC, where steam-rich emissions are accompanied by sulfurous gases like hydrogen sulfide, indicating intense hydrothermal activity. Fumaroles often reach higher temperatures, sometimes exceeding 400degC, with gas compositions dominated by water vapor, carbon dioxide, and trace sulfur compounds, reflecting deeper volcanic heat sources. The temperature difference highlights solfataras as cooler, sulfur-rich vents, while fumaroles represent hotter, more volatile-prone geothermal emissions.
Notable Locations Around the World
Solfatara is a shallow volcanic crater emitting sulfurous gases, with the famous Solfatara of Pozzuoli in Italy being a key geothermal site studied for its active fumarolic activity. Fumaroles, found worldwide, are steam vents releasing volcanic gases, notable examples include Yellowstone National Park in the USA, the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes in Alaska, and the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. Both phenomena serve as important indicators of volcanic activity and geothermal energy potential in regions with active volcanism.
Ecological and Geothermal Significance
Solfatara fields emit sulfur-rich gases that support unique extremophile ecosystems, while fumaroles release steam and gases that drive geothermal energy production. The acidic environment of solfataras fosters specialized microbial communities that contribute to biogeochemical cycling, contrasting with fumaroles' role in indicating subterranean volcanic activity and potential geothermal reservoirs. Both features are critical for studying volcanic activity's impact on local biodiversity and renewable geothermal energy resources.
Hazards and Safety Measures
Solfatara vents emit sulfur-rich gases like hydrogen sulfide, posing inhalation risks and skin irritation hazards, while fumaroles release primarily steam and volcanic gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide, which can cause respiratory issues and burns. Safety measures for solfatara include maintaining a safe distance, using gas detectors, and wearing protective masks to avoid toxic exposure. For fumaroles, precautions involve avoiding unstable ground, monitoring gas concentrations, and using protective gear to prevent inhalation injuries or thermal burns.
Summary: Comparing Solfatara and Fumarole Phenomena
Solfatara and fumaroles are volcanic features that emit gas, but solfataras specifically release sulfur-rich steam and gases, often creating yellow sulfur deposits. Fumaroles generally emit a variety of volcanic gases including water vapor, carbon dioxide, and sulfur compounds, but may not always produce sulfur deposits. Both phenomena indicate subterranean volcanic activity and contribute to understanding volcanic gas emissions and geothermal processes.
Solfatara Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com