Biogeography explores the distribution of species and ecosystems across geographic locations, revealing patterns shaped by environmental factors and evolutionary history. Understanding these patterns is essential for conserving biodiversity and managing natural resources effectively. Discover how biogeography impacts your world by reading the rest of the article.
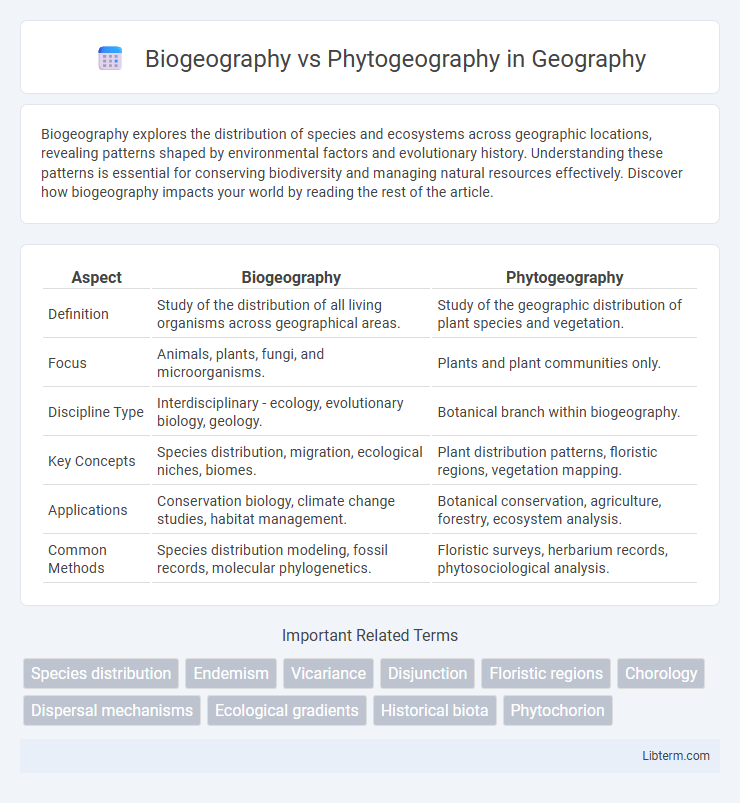
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Biogeography | Phytogeography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of the distribution of all living organisms across geographical areas. | Study of the geographic distribution of plant species and vegetation. |
| Focus | Animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. | Plants and plant communities only. |
| Discipline Type | Interdisciplinary - ecology, evolutionary biology, geology. | Botanical branch within biogeography. |
| Key Concepts | Species distribution, migration, ecological niches, biomes. | Plant distribution patterns, floristic regions, vegetation mapping. |
| Applications | Conservation biology, climate change studies, habitat management. | Botanical conservation, agriculture, forestry, ecosystem analysis. |
| Common Methods | Species distribution modeling, fossil records, molecular phylogenetics. | Floristic surveys, herbarium records, phytosociological analysis. |
Introduction to Biogeography and Phytogeography
Biogeography studies the distribution of living organisms across geographic spaces and through geological time, integrating ecology, evolution, and environmental factors. Phytogeography, a sub-discipline of biogeography, specifically examines the spatial distribution of plant species and vegetation patterns in relation to climate, soil, and topography. Both fields utilize mapping and classification techniques to understand biodiversity patterns and the influence of historical and ecological processes on species distribution.
Defining Biogeography
Biogeography is the scientific study of the geographic distribution of living organisms, encompassing patterns of species distribution across various spatial scales and ecosystems. It integrates data from ecology, evolutionary biology, and geology to understand factors influencing biodiversity and the historical processes shaping the presence of flora and fauna. In contrast, phytogeography specifically examines the spatial distribution and patterns of plant species, focusing on vegetation regions and plant community dynamics.
Understanding Phytogeography
Phytogeography examines the spatial distribution of plant species and ecosystems, focusing on patterns influenced by climate, soil, and evolutionary history. It provides insights into plant biodiversity, ecological relationships, and environmental changes over time. Understanding phytogeography aids in conservation planning, habitat restoration, and predicting vegetation responses to global climate shifts.
Historical Development of Biogeography
Biogeography originated in the 18th century with explorers such as Alexander von Humboldt, who documented species distributions and environmental relationships. Charles Darwin's theory of evolution further shaped biogeographical studies by explaining patterns of species diversification and migration over geological time. Phytogeography, a branch of biogeography, specifically examines the historical and ecological distribution of plant species, tracing plant origins and adaptations to different environments.
Evolution of Phytogeography
Phytogeography, the study of plant distribution, evolved as a specialized branch of biogeography, concentrating on patterns influenced by evolutionary processes, climate, and geological history. The evolution of phytogeography traces back to early botanical explorations and advances in evolutionary theory, emphasizing the role of speciation, migration, and extinction in shaping plant distributions. Modern phytogeography integrates molecular phylogenetics and paleobotanical data, offering insights into how evolutionary adaptations have driven plant community assemblages across different biomes globally.
Key Distinctions Between Biogeography and Phytogeography
Biogeography studies the spatial distribution of all living organisms across the Earth, including animals, plants, and microorganisms, while phytogeography specifically focuses on the distribution of plant species and vegetation patterns. Biogeography integrates ecological, evolutionary, and geological factors influencing species distribution, whereas phytogeography concentrates on botanical data, plant community characteristics, and environmental interactions. Key distinctions include the scope of organisms studied and specialized methodologies used, with phytogeography employing vegetation mapping and floristic analysis to understand plant-specific distribution.
Methodologies in Biogeographical Studies
Biogeographical studies employ methodologies such as species distribution modeling, phylogenetic analysis, and geographic information systems (GIS) to analyze the spatial patterns of biodiversity across ecosystems and geological timescales. Unlike phytogeography, which primarily focuses on plant distribution through vegetation mapping and floristic surveys, biogeography integrates multi-taxa data sets including animals, microbes, and plants to understand ecological and evolutionary processes. Techniques like paleobiogeography and landscape genetics further enhance insights into historical biogeographical patterns and species dispersal mechanisms.
Approaches in Phytogeographical Research
Phytogeographical research primarily employs field surveys, herbarium studies, and remote sensing to analyze plant distribution patterns and ecological relationships. It integrates climatic, edaphic, and biotic factors to understand vegetation dynamics and species adaptation within specific geographic regions. Molecular techniques and GIS mapping enhance the precision of phytogeographical analyses, facilitating comprehensive studies of plant biodiversity and biogeographical zonation.
Applications and Implications in Ecology
Biogeography and phytogeography are essential for understanding species distribution, with biogeography covering all living organisms and phytogeography focusing specifically on plant distribution. Applications in ecology include habitat conservation planning, predicting responses to climate change, and managing invasive species by analyzing spatial patterns of biodiversity. These fields provide crucial insights for ecosystem restoration and sustainable resource management by identifying key biotic and abiotic factors influencing plant and animal communities.
Future Trends in Biogeography and Phytogeography
Future trends in biogeography emphasize integrating advanced spatial analysis technologies and climate modeling to predict species distribution shifts due to global change. Phytogeography focuses on refining genetic and ecological data to understand plant migration patterns and adaptation mechanisms. Both fields increasingly leverage big data and machine learning to enhance biodiversity conservation strategies and ecosystem management.
Biogeography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com