Hot springs offer naturally heated mineral-rich water that provides numerous health benefits, including relaxation, improved circulation, and skin rejuvenation. These geothermal wonders are often found in volcanic regions, where underground water is heated by the Earth's magma, creating a soothing and therapeutic experience. Discover how these natural pools can enhance your well-being by exploring the full article on hot springs.
Table of Comparison
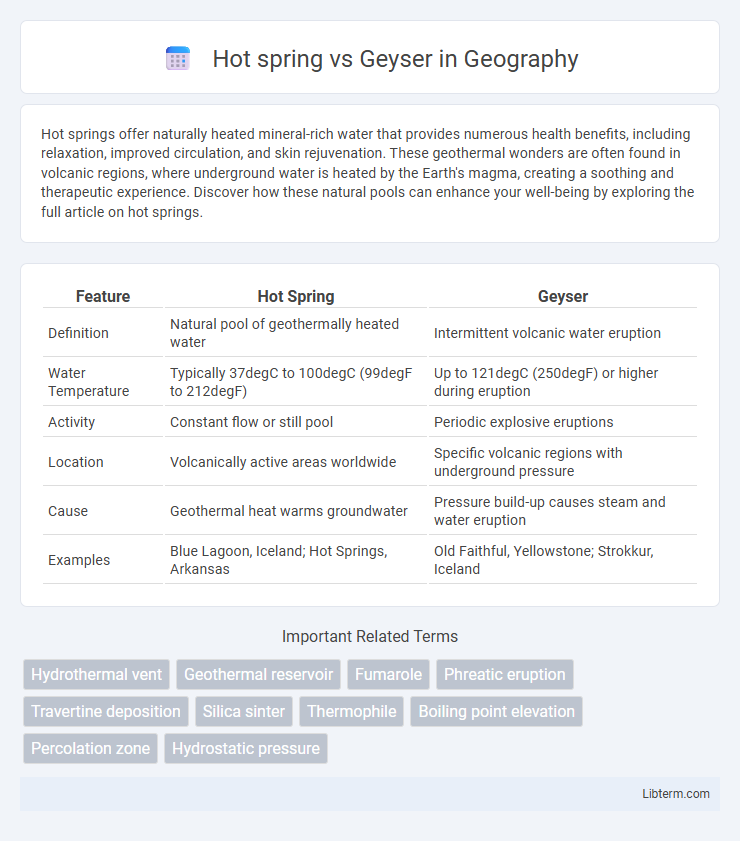
| Feature | Hot Spring | Geyser |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural pool of geothermally heated water | Intermittent volcanic water eruption |
| Water Temperature | Typically 37degC to 100degC (99degF to 212degF) | Up to 121degC (250degF) or higher during eruption |
| Activity | Constant flow or still pool | Periodic explosive eruptions |
| Location | Volcanically active areas worldwide | Specific volcanic regions with underground pressure |
| Cause | Geothermal heat warms groundwater | Pressure build-up causes steam and water eruption |
| Examples | Blue Lagoon, Iceland; Hot Springs, Arkansas | Old Faithful, Yellowstone; Strokkur, Iceland |
Introduction to Hot Springs and Geysers
Hot springs are natural pools of geothermally heated groundwater, often rich in minerals and known for their therapeutic properties. Geysers are a specific type of hot spring characterized by intermittent eruptions of steam and hot water due to pressure buildup underground. Both phenomena occur in volcanic regions where heat from the Earth's mantle warms subterranean water.
Defining Hot Springs: What Are They?
Hot springs are natural pools of geothermally heated groundwater that emerge at the Earth's surface, maintaining consistently warm temperatures due to heat from underlying magma or hot rocks. Unlike geysers, hot springs flow steadily without erupting steam or water bursts, creating a soothing environment rich in minerals such as sulfur, calcium, and magnesium. These mineral-rich waters offer therapeutic benefits and support unique ecosystems, distinguishing them ecologically and geochemically from geysers.
Understanding Geysers: Key Features
Geysers are natural hot springs characterized by intermittent eruptions of steam and boiling water caused by underground heat and pressure. Key features include a narrow vent, a reservoir of water, and a heat source typically from volcanic activity, which create periodic bursts of water and steam. Unlike hot springs that provide continuous warm water, geysers have distinct eruptive cycles influenced by hydrothermal dynamics and geological formations.
Geological Formation: How Hot Springs and Geysers Develop
Hot springs develop when groundwater is heated by geothermal heat from the Earth's mantle, rising through permeable rock fractures and emerging on the surface as warm or hot water. Geysers form in similar geothermal areas but require a unique underground plumbing system with constrictions that trap steam and water, causing periodic eruptions. The key geological difference lies in geysers' superheated water becoming trapped under pressure, leading to explosive release, while hot springs allow continuous flow without eruptions.
Temperature Differences Between Hot Springs and Geysers
Hot springs generally maintain stable temperatures ranging from 30degC to 60degC, while geysers experience rapid temperature fluctuations, often exceeding 100degC during eruptions. The temperature in geysers rises sharply due to pressurized steam trapped underground, leading to explosive releases of boiling water. In contrast, hot springs allow heat to dissipate more gradually, resulting in consistently warm but less variable temperatures.
Water Movement and Eruption Patterns
Hot springs exhibit steady water movement as groundwater is continuously heated by geothermal energy, causing a gentle flow of warm water to the surface without dramatic eruptions. Geysers, in contrast, experience periodic and forceful eruptions due to the buildup of steam pressure in underground cavities, resulting in intermittent bursts of hot water and steam. The eruption patterns of geysers are highly variable and depend on specific subsurface conditions, unlike the relatively constant flow seen in hot springs.
Locations Around the World: Hot Springs vs. Geysers
Hot springs and geysers are found in geothermally active regions worldwide, with famous hot springs located in places like Iceland's Blue Lagoon, Japan's Beppu, and California's Mammoth Lakes, offering natural warm water pools for relaxation. Geysers are more rare and spectacular, with notable examples including Yellowstone National Park in the USA, known for Old Faithful, and New Zealand's Rotorua area where geothermal activity creates powerful water eruptions. These distinct features highlight the diversity of geothermal landscapes and attract millions of visitors seeking unique natural phenomena globally.
Health and Recreational Benefits Comparisons
Hot springs offer therapeutic mineral-rich waters that promote relaxation, alleviate muscle pain, and improve skin conditions through consistent soaking. Geysers, while less accessible for bathing, provide unique recreational interest and educational value due to their dramatic geothermal eruptions and natural beauty. Both geothermal features support tourism and wellness activities but differ significantly in their direct health applications, with hot springs being preferable for hydrotherapy benefits.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Hot springs release naturally heated water rich in minerals, supporting unique ecosystems but posing minimal hazards when accessed responsibly, whereas geysers intermittently eject boiling water and steam, creating dynamic yet potentially dangerous environments due to sudden eruptions. Both geothermal features contribute to local biodiversity and geothermal energy potential but require careful management to prevent habitat disruption and human injury. Safety measures around geysers emphasize maintaining distance and respecting thermal instability, while hot springs demand monitoring contamination risks and ensuring sustainable tourism practices.
Hot Spring or Geyser: Which Should You Visit?
Hot springs offer soothing, warm mineral-rich waters ideal for relaxation and therapeutic benefits, making them perfect for a calming getaway. Geysers provide a spectacular natural show with erupting hot water and steam, attracting visitors interested in geological phenomena and photography. Choose hot springs for a tranquil experience focused on wellness, or geysers for dynamic, awe-inspiring natural displays.
Hot spring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com