Isoamplitude refers to signals or waveforms that maintain a constant amplitude over time, which is crucial in fields like acoustics and signal processing to ensure uniform signal strength and accurate data interpretation. Maintaining isoamplitude helps reduce distortion and improve the clarity of transmitted information, directly impacting the performance of communication systems and audio devices. Discover more about the applications and importance of isoamplitude in this detailed article.
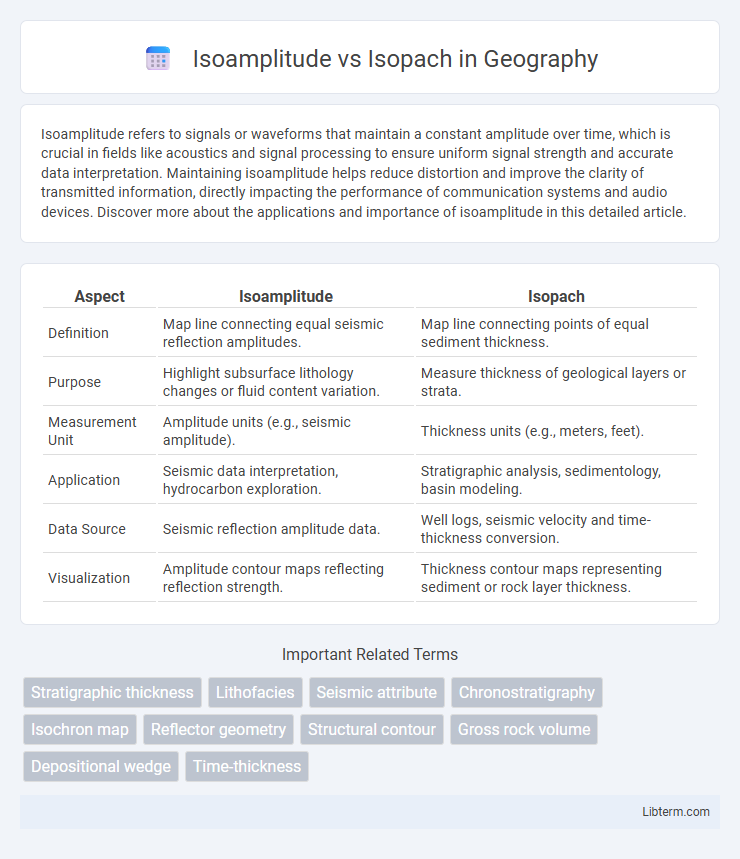
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Isoamplitude | Isopach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Map line connecting equal seismic reflection amplitudes. | Map line connecting points of equal sediment thickness. |
| Purpose | Highlight subsurface lithology changes or fluid content variation. | Measure thickness of geological layers or strata. |
| Measurement Unit | Amplitude units (e.g., seismic amplitude). | Thickness units (e.g., meters, feet). |
| Application | Seismic data interpretation, hydrocarbon exploration. | Stratigraphic analysis, sedimentology, basin modeling. |
| Data Source | Seismic reflection amplitude data. | Well logs, seismic velocity and time-thickness conversion. |
| Visualization | Amplitude contour maps reflecting reflection strength. | Thickness contour maps representing sediment or rock layer thickness. |
Understanding Isoamplitude and Isopach: Key Definitions
Isoamplitude maps represent surfaces of equal reflection amplitude in seismic data, crucial for identifying variations in rock properties and fluid content within subsurface formations. Isopach maps illustrate thickness variations of geological layers by connecting points of equal stratigraphic thickness, essential for sedimentological and reservoir characterization studies. Distinguishing between isoamplitude, which highlights seismic response attributes, and isopach, which measures physical thickness, provides a comprehensive understanding of subsurface geology and aids in accurate reservoir evaluation.
Geological Significance of Isoamplitude and Isopach Maps
Isoamplitude maps illustrate variations in seismic reflection amplitude, which are crucial for identifying lithology changes, fluid content, and reservoir heterogeneity in subsurface formations. Isopach maps represent thickness variations of geological layers, helping to interpret sediment deposition patterns, subsidence rates, and structural deformation. Together, these maps provide complementary insights into stratigraphic architecture, reservoir quality, and tectonic evolution in hydrocarbon exploration and geotechnical studies.
How Isoamplitude Differs from Isopach in Subsurface Mapping
Isoamplitude maps display equal reflection amplitude values from seismic data, highlighting changes in lithology or fluid content, whereas isopach maps represent thickness variations of sedimentary layers or formations. Isoamplitude focuses on seismic attribute analysis sensitive to rock properties, while isopach quantifies geological thickness based on stratigraphic boundaries. The distinction lies in isopach measuring physical thickness, and isoamplitude detecting changes in seismic response due to subsurface heterogeneities.
Methods for Constructing Isoamplitude Contours
Isoamplitude contours are constructed by mapping seismic amplitude values at a consistent time or depth level across a survey area, typically using amplitude extraction techniques combined with seismic attribute analysis software. Common methods involve picking amplitude values from amplitude slices, horizon slices, or time windows, then interpolating these points using geostatistical approaches like kriging or inverse distance weighting to generate continuous amplitude surfaces. Accurate construction depends on careful data conditioning, including gain correction, noise filtering, and ensuring amplitude preservation during processing workflows.
Techniques for Creating Isopach Maps
Isopach maps, which represent thickness variations of geological units, are created using techniques such as seismic interpretation, well log correlation, and geostatistical modeling. Seismic horizon picking allows for the identification of stratigraphic surfaces, while well logs provide precise thickness measurements to calibrate seismic data. Advanced software tools integrate these data sources to generate detailed isopach maps crucial for reservoir characterization and geological analysis.
Applications of Isoamplitude in Hydrocarbon Exploration
Isoamplitude maps represent constant reflection amplitude values on seismic sections, which are crucial for identifying hydrocarbon reservoirs by highlighting fluid and lithology contrasts. These maps enable geophysicists to detect bright spots and amplitude anomalies associated with gas or oil accumulations, improving direct hydrocarbon indicator (DHI) reliability. Unlike isopach maps that measure sediment thickness variations, isoamplitude maps focus on seismic response attributes, enhancing stratigraphic and structural interpretation in hydrocarbon exploration.
Isopach Mapping for Reservoir Thickness Estimation
Isopach mapping is a critical technique in reservoir thickness estimation, representing contours of equal stratigraphic thickness which directly reflect the thickness variation of sedimentary layers. Unlike isoamplitude maps that display seismic amplitude variations related to lithology or fluid content, isopach maps provide quantitative measurement essential for volumetric calculations and resource evaluation. Accurate isopach mapping integrates well log data and seismic horizons, enabling precise reservoir geometry modeling and enhanced hydrocarbon volume estimation.
Integrating Isoamplitude and Isopach Data in Geological Interpretation
Integrating Isoamplitude and Isopach data enhances geological interpretation by combining amplitude variations with thickness measurements, offering a comprehensive subsurface model. Isoamplitude maps highlight seismic reflection strength changes related to lithology or fluid content, while Isopach maps provide accurate thickness distribution of sedimentary layers. Combining these datasets improves reservoir characterization, structural analysis, and hydrocarbon prospect identification, leading to more precise exploration and development decisions.
Advantages and Limitations of Isoamplitude vs. Isopach Analysis
Isoamplitude maps highlight areas of consistent seismic reflection strength, aiding in detecting lithological changes and fluid contacts, but may be affected by noise and variable seismic acquisition parameters. Isopach maps provide precise thickness measurements of sedimentary units, crucial for reservoir volume estimation, yet can misrepresent thickness in areas with complex structural deformation or seismic velocity anomalies. Combining isoamplitude and isopach analyses enhances subsurface interpretations by integrating amplitude variations with stratigraphic thickness, mitigating individual limitations.
Case Studies: Isoamplitude and Isopach in Real-World Geology
Case studies demonstrate that isoamplitude maps effectively highlight variations in seismic reflection strength, aiding in the identification of lithological changes and fluid content within reservoirs. Isopach maps provide precise thickness measurements of sedimentary layers, essential for stratigraphic analysis and resource estimation. Combining isoamplitude and isopach data enhances geological interpretation by correlating amplitude anomalies with depositional thickness, improving reservoir characterization and exploration accuracy.
Isoamplitude Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com