A biome is a large ecological area on Earth's surface with distinct plant and animal groups adapted to its environment, such as forests, deserts, or tundras. Understanding biomes is essential for recognizing how ecosystems function and the impact of climate change on biodiversity. Explore the rest of the article to discover how different biomes shape our planet and influence your world.
Table of Comparison
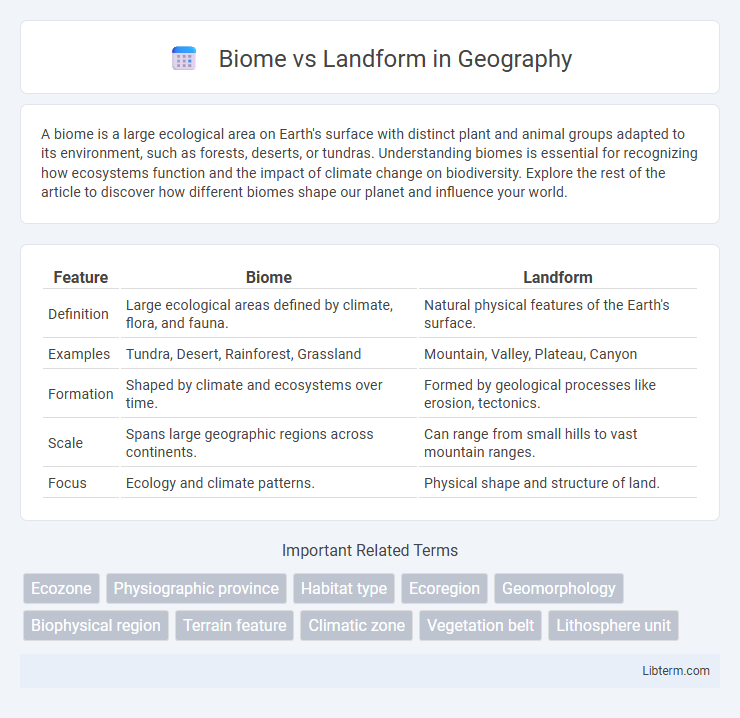
| Feature | Biome | Landform |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large ecological areas defined by climate, flora, and fauna. | Natural physical features of the Earth's surface. |
| Examples | Tundra, Desert, Rainforest, Grassland | Mountain, Valley, Plateau, Canyon |
| Formation | Shaped by climate and ecosystems over time. | Formed by geological processes like erosion, tectonics. |
| Scale | Spans large geographic regions across continents. | Can range from small hills to vast mountain ranges. |
| Focus | Ecology and climate patterns. | Physical shape and structure of land. |
Understanding Biomes and Landforms
Biomes are large ecological areas characterized by distinct climate conditions, flora, and fauna, such as tundras, rainforests, and deserts. Landforms refer to the physical features on Earth's surface like mountains, valleys, plateaus, and plains, shaped by geological processes. Understanding biomes involves studying ecosystems and biological diversity, while understanding landforms requires knowledge of Earth's topography and geological history.
Defining Biomes: Characteristics and Types
Biomes are vast ecological areas defined by distinct climate conditions, flora, and fauna, such as tropical rainforests, deserts, tundra, and grasslands, each characterized by unique temperature and precipitation patterns. Unlike landforms, which are physical features of the Earth's surface like mountains, valleys, and plateaus shaped by geological processes, biomes represent biological communities adapted to specific environmental conditions. Understanding biomes involves studying ecosystem dynamics, species adaptations, and climatic influences that govern the distribution and sustainability of life across the planet.
What Are Landforms? Key Features and Examples
Landforms are natural physical features on the Earth's surface formed by geological processes such as tectonic activity, erosion, and sediment deposition. Key features include mountains, valleys, plateaus, and plains, each distinguished by unique shapes and elevations. Examples of prominent landforms are the Himalayas, Grand Canyon, and Great Plains, representing diverse terrains that influence climate and ecosystems.
Distinctions Between Biomes and Landforms
Biomes are large ecological areas defined by their climate, vegetation, and animal life, such as tundras, rainforests, and deserts, whereas landforms refer to the physical features of the Earth's surface like mountains, valleys, and plateaus. Biomes represent biological communities shaped by environmental conditions, while landforms are geological structures formed through tectonic activity, erosion, and sediment deposition. Understanding the distinction highlights how biomes emphasize living ecosystems, whereas landforms focus on the Earth's topographical characteristics.
How Climate Influences Biomes and Landforms
Climate plays a critical role in shaping both biomes and landforms by determining temperature, precipitation, and seasonal patterns that influence vegetation types and soil development. Varied climate zones result in distinct biomes such as tropical rainforests, deserts, and tundras, each supporting specific ecosystems adapted to moisture and temperature regimes. Simultaneously, climate-driven processes like glaciation, erosion, and weathering contribute to the formation and alteration of physical landforms including mountains, valleys, and dunes.
The Role of Geography in Shaping Landforms and Biomes
Geography plays a crucial role in shaping both landforms and biomes by influencing climate patterns, soil composition, and elevation, which determine the physical characteristics and biological communities of an area. Landforms such as mountains, valleys, and plateaus are products of geological processes like tectonic activity and erosion, while biomes are defined by the interaction of temperature, precipitation, and vegetation across these landforms. The spatial distribution of biomes is thus closely tied to the underlying landforms, as geographic features control environmental conditions vital for ecosystem development and biodiversity.
Interactions Between Biomes and Landforms
Biomes and landforms interact dynamically, influencing each other's development and characteristics through factors such as climate, vegetation, and soil composition. Landforms like mountains affect biome distribution by creating microclimates and varied precipitation patterns that support diverse ecosystems. Conversely, biome vegetation can impact landform stability by reducing erosion and shaping soil profiles over time.
Human Impact on Biomes and Landforms
Human activities drastically alter biomes by deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture, leading to habitat loss and reduced biodiversity. Landforms experience significant changes through mining, construction, and dam building, which reshape natural terrain and disrupt ecosystems. These modifications result in soil erosion, altered water cycles, and increased vulnerability of both biomes and landforms to environmental stressors.
Importance of Studying Biomes and Landforms
Studying biomes and landforms is essential for understanding Earth's ecological and geological diversity, enabling better conservation efforts and natural resource management. Biomes reveal patterns of climate, vegetation, and wildlife that support biodiversity, while landforms shape habitats and influence human settlement and agriculture. Comprehensive knowledge of both enhances environmental planning and climate change adaptation strategies.
Biomes vs Landforms: Key Takeaways and Summary
Biomes represent large ecological communities defined by climate, vegetation, and animal life, such as deserts, tundras, and rainforests, while landforms are physical features of the Earth's surface like mountains, valleys, and plateaus shaped by geological processes. Biomes are primarily biological and climatic classifications influencing ecosystems, whereas landforms focus on topographical structures formed by erosion, tectonic activity, and sedimentation. Understanding the distinction aids in studying environmental patterns, as biomes describe living conditions and biodiversity, and landforms determine habitat physical characteristics and geological context.
Biome Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com