Beach drift refers to the natural movement of sand and sediments along the shoreline caused by wave action and currents. Understanding beach drift is essential for managing coastal erosion and maintaining the stability of your favorite beaches. Explore the rest of the article to learn how beach drift impacts coastal environments and what measures can be taken to protect them.
Table of Comparison
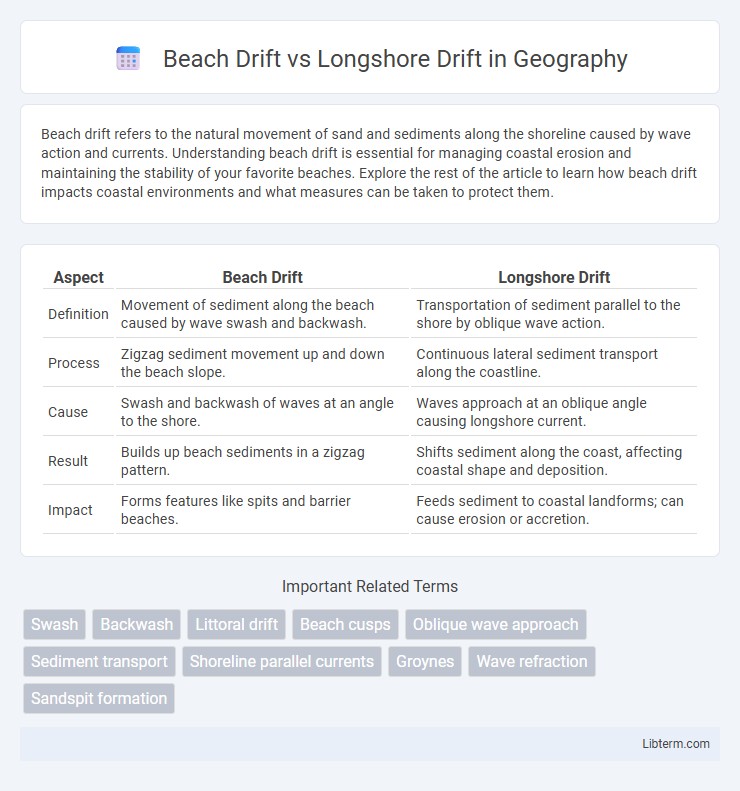
| Aspect | Beach Drift | Longshore Drift |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Movement of sediment along the beach caused by wave swash and backwash. | Transportation of sediment parallel to the shore by oblique wave action. |
| Process | Zigzag sediment movement up and down the beach slope. | Continuous lateral sediment transport along the coastline. |
| Cause | Swash and backwash of waves at an angle to the shore. | Waves approach at an oblique angle causing longshore current. |
| Result | Builds up beach sediments in a zigzag pattern. | Shifts sediment along the coast, affecting coastal shape and deposition. |
| Impact | Forms features like spits and barrier beaches. | Feeds sediment to coastal landforms; can cause erosion or accretion. |
Understanding Beach Drift: Definition and Process
Beach drift refers to the movement of sediment along a coast caused by waves approaching the shore at an angle, resulting in a zigzag transport of sand and pebbles parallel to the shoreline. This process occurs due to swash carrying materials up the beach at an angle, followed by backwash pulling them down perpendicularly, facilitating lateral sediment displacement. Unlike longshore drift, which involves sediment movement along the coastline driven by prevailing currents and wave energy, beach drift specifically describes the wave-induced sediment transport on the beach face itself.
What is Longshore Drift? Key Concepts Explained
Longshore drift is the process by which sediment, such as sand and pebbles, moves along the coastline due to the angled approach of waves. This movement occurs in a zigzag pattern, driven by the prevailing wind direction and wave energy, transporting materials parallel to the shore. It plays a crucial role in shaping coastal landforms, affecting beach erosion, deposition, and the formation of features like spits and bars.
Differences Between Beach Drift and Longshore Drift
Beach drift involves the zigzag movement of sand and sediment along the shoreline due to wave swash and backwash, whereas longshore drift refers to the overall transportation of sediment parallel to the coast driven by wave angle and current flow. Beach drift specifically describes particle movement on the shore's edge, while longshore drift encompasses the broader sediment transport along the coastal zone. The key difference lies in beach drift describing localized sediment motion on the beach, and longshore drift signifying continuous sediment displacement along the shoreline over longer distances.
How Beach Drift and Longshore Drift Shape Coastlines
Beach drift and longshore drift collaboratively shape coastlines by transporting sand and sediments along the shore, contributing to beach formation and erosion patterns. Beach drift moves particles in a zigzag motion driven by wave swash and backwash, while longshore drift transports sediment parallel to the coast through angled wave energy. Together, these processes redistribute coastal materials, influencing shoreline alignment, creating spits, and modifying coastal landforms over time.
Causes Behind Beach Drift and Longshore Drift
Beach drift occurs due to the angled approach of breaking waves, which transports sediment along the shoreline through the swash and backwash action. Longshore drift is driven by prevailing wind directions that generate waves at an oblique angle to the coast, causing sediment to move laterally down the shore. Both processes are influenced by wave energy, coastal topography, and sediment type, shaping the dynamic movement of beach materials.
Effects of Beach Drift on Coastal Environments
Beach drift moves sediment along the shoreline through the zigzag motion of waves, significantly shaping beach profiles and influencing sediment distribution patterns. This process promotes the formation of spits, bars, and other coastal landforms by transporting sand and pebbles parallel to the coast. Continuous beach drift can lead to beach erosion or accretion, impacting coastal habitats and human infrastructure.
Impact of Longshore Drift on Sediment Transport
Longshore drift significantly influences sediment transport by moving sand and other sediments parallel to the coastline due to the angle of wave approach. This process contributes to the gradual shaping and realignment of shorelines, affecting beach drift patterns by redistributing sediment deposits along the shore. The continuous sediment transport caused by longshore drift can lead to the formation of features such as spits, bars, and tombolos, impacting coastal ecosystems and human infrastructure.
Human Activities Influencing Beach and Longshore Drift
Human activities such as coastal development, construction of groynes, and harbor engineering significantly alter natural beach drift and longshore drift patterns by disrupting sediment transport and wave energy distribution. Beach nourishment projects and seawalls can stabilize shorelines but often interfere with sediment supply, leading to erosion downstream. Marine traffic and dredging also modify hydrodynamic conditions, further impacting longshore sediment movement and beach morphology.
Strategies for Managing Coastal Drift Processes
Managing coastal drift processes requires targeted strategies to address both beach drift and longshore drift effectively. Hard engineering solutions such as groynes and breakwaters are implemented to interrupt longshore drift, trapping sediment to preserve beaches and reduce erosion. Soft engineering approaches like beach nourishment and dune restoration enhance natural sediment deposition, supporting the management of beach drift while promoting sustainable coastal resilience.
Comparative Summary: Beach Drift vs Longshore Drift
Beach drift and longshore drift both describe sediment transport along coastlines but differ in mechanism and scale. Beach drift involves zigzag movement of sediment grains along the beach due to wave swash and backwash, whereas longshore drift transports sediment parallel to the shore driven by oblique wave angles and longshore currents. Longshore drift typically affects larger sediment volumes and influences coastal landforms more significantly compared to the localized sediment movement of beach drift.
Beach Drift Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com