A plateau is a flat elevated landform that rises sharply above the surrounding area, often formed by geological processes such as volcanic activity or erosion. Plateaus can vary in size and are significant for their unique ecosystems and potential for agriculture and human settlement. Discover more about the fascinating features and types of plateaus in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
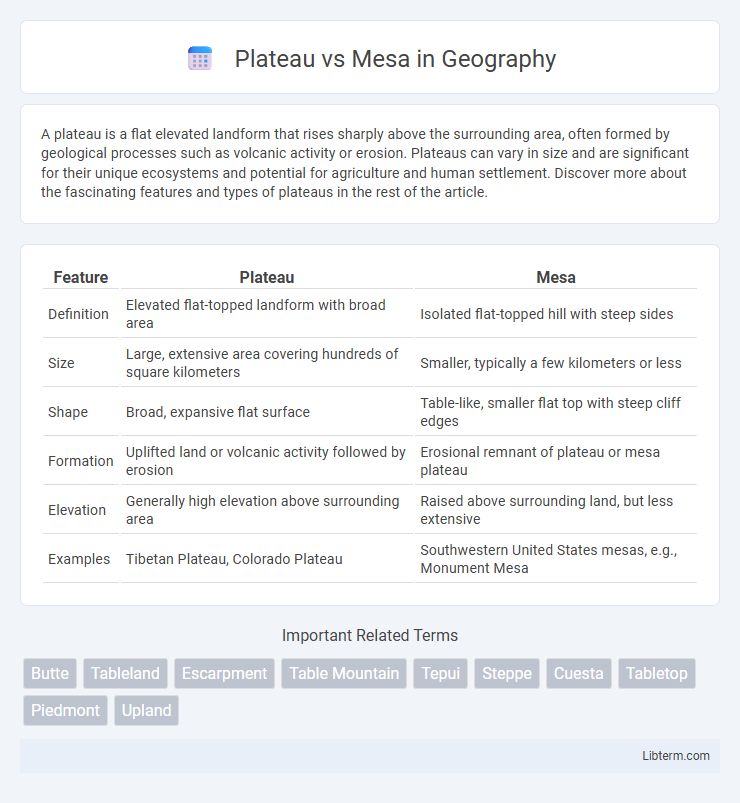
| Feature | Plateau | Mesa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated flat-topped landform with broad area | Isolated flat-topped hill with steep sides |
| Size | Large, extensive area covering hundreds of square kilometers | Smaller, typically a few kilometers or less |
| Shape | Broad, expansive flat surface | Table-like, smaller flat top with steep cliff edges |
| Formation | Uplifted land or volcanic activity followed by erosion | Erosional remnant of plateau or mesa plateau |
| Elevation | Generally high elevation above surrounding area | Raised above surrounding land, but less extensive |
| Examples | Tibetan Plateau, Colorado Plateau | Southwestern United States mesas, e.g., Monument Mesa |
Introduction to Plateaus and Mesas
Plateaus are elevated flatlands with extensive horizontal surfaces, often formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity, covering vast areas with steep sides. Mesas are smaller, isolated landforms with flat tops and steep, cliff-like edges, typically resulting from erosion that isolates a section of a plateau or plateau-like terrain. Both landforms showcase distinct geological processes and contribute to diverse landscapes in regions such as the Colorado Plateau and the American Southwest.
Defining a Plateau
A plateau is a broad, elevated landform with a relatively flat top and steep sides, often formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity. It covers extensive areas and can be characterized by its high elevation compared to surrounding terrain. Unlike mesas, which are smaller and more isolated, plateaus stretch across larger regions and support diverse ecosystems and human settlements.
What is a Mesa?
A mesa is a landform characterized by a flat-topped hill with steep, often vertical sides, typically formed through erosion-resistant rock layers that protect the summit from weathering. Unlike plateaus, which are extensive elevated areas, mesas are smaller and more isolated with distinct edges. Commonly found in arid regions such as the southwestern United States, mesas are significant geological features resulting from differential erosion processes.
Geological Formation Differences
Plateaus are broad, elevated landforms with relatively flat tops formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity, often covering extensive areas. Mesas are smaller, flat-topped hills with steep, often cliff-like sides, created primarily through erosion that isolates these features from surrounding terrain. The key geological difference is that plateaus result from large-scale uplift and volcanic processes, while mesas form from erosional remnants of once larger plateaus or plateaus' edges.
Key Physical Characteristics
Plateaus are vast, elevated flatlands that rise sharply above surrounding areas with steep sides, often formed by volcanic activity or erosion-resistant rock layers. Mesas exhibit a distinct flat top with steep, cliff-like edges and are typically smaller and more isolated than plateaus. Both landforms result from erosion processes but differ primarily in scale, with plateaus covering extensive regions and mesas appearing as isolated flat-topped hills.
Global Examples of Plateaus and Mesas
The Colorado Plateau in the United States spans over 130,000 square miles, featuring extensive flat-topped highlands with deep canyons, while the Mesas of the American Southwest, such as Monument Valley, showcase isolated flat-topped hills with steep sides formed by erosion. The Deccan Plateau in India, covering approximately 1.9 million square kilometers, represents one of the world's largest volcanic plateaus known for its rich basaltic soil. In contrast, the Mexican Plateau, or Central Plateau, is a highland region characterized by large mesas and broad valleys supporting diverse ecosystems and dense human settlements.
Ecological and Environmental Significance
Plateaus and mesas both provide unique habitats that support diverse ecosystems due to their elevation, soil types, and climatic conditions. Plateaus often sustain extensive grasslands and forests, playing a critical role in water catchment and carbon storage, while mesas, with their isolated flat tops and steep cliffs, serve as refuges for specialized plant and animal species. These landforms contribute to biodiversity conservation and act as natural barriers against soil erosion and desertification.
Human Activities and Land Use
Plateaus, with their extensive flat surfaces and fertile soil, support diverse human activities such as agriculture, urban development, and mining, often hosting large populations due to their resources and accessibility. Mesas, characterized by their isolated, steep sides and limited flat tops, are less suitable for widespread farming or settlements but are frequently used for grazing, tourism, and conservation purposes. Land use on plateaus tends to be more intensive and varied, while mesas often maintain natural vegetation and serve as landmarks or protected areas.
Comparing Erosion Processes
Plateaus and mesas both result from erosion but differ significantly in scale and formation. Plateaus are extensive elevated flatlands shaped primarily by widespread horizontal erosion of sedimentary rock layers, while mesas are smaller, isolated flat-topped hills with steep sides formed by differential erosion, where harder caprock resists weathering more effectively than surrounding softer rock. The erosional process in mesas concentrates vertically, leading to their distinctive cliff-like edges, whereas plateaus experience more uniform surface erosion across vast areas.
Conclusion: Plateau vs Mesa
A plateau is an extensive, elevated flat area with significant horizontal dimensions, while a mesa is a smaller, isolated flat-topped hill with steep sides. Both landforms result from erosion processes, but plateaus cover larger regions, often spanning hundreds of kilometers. Understanding the scale and formation differences between plateaus and mesas aids in geological classification and environmental studies.
Plateau Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com