Map analysis reveals geographic patterns, spatial relationships, and data distribution essential for decision-making and planning across various fields. Understanding these elements enhances Your ability to interpret physical and thematic maps accurately. Explore the rest of the article to deepen Your insight into effective map analysis techniques and applications.
Table of Comparison
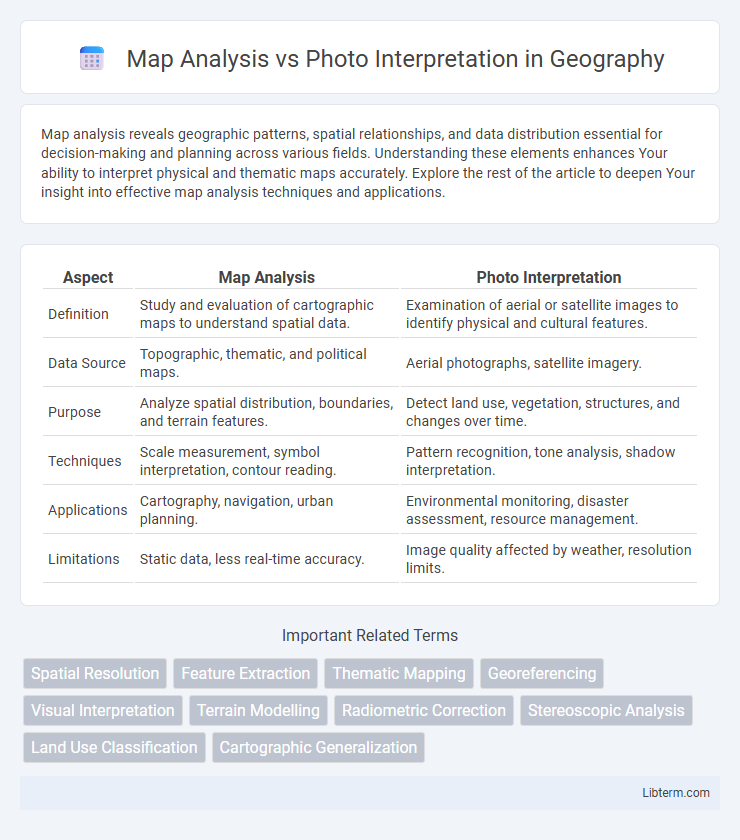
| Aspect | Map Analysis | Photo Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study and evaluation of cartographic maps to understand spatial data. | Examination of aerial or satellite images to identify physical and cultural features. |
| Data Source | Topographic, thematic, and political maps. | Aerial photographs, satellite imagery. |
| Purpose | Analyze spatial distribution, boundaries, and terrain features. | Detect land use, vegetation, structures, and changes over time. |
| Techniques | Scale measurement, symbol interpretation, contour reading. | Pattern recognition, tone analysis, shadow interpretation. |
| Applications | Cartography, navigation, urban planning. | Environmental monitoring, disaster assessment, resource management. |
| Limitations | Static data, less real-time accuracy. | Image quality affected by weather, resolution limits. |
Introduction to Map Analysis and Photo Interpretation
Map analysis involves examining spatial data presented through cartographic symbols, scales, and legends to extract information about geographic features and relationships. Photo interpretation refers to the process of identifying and assessing objects and patterns in aerial or satellite imagery by analyzing tone, texture, shape, and shadow. Both techniques are essential for geospatial analysis, with map analysis emphasizing structural data and photo interpretation focusing on visual and spectral details.
Defining Map Analysis: Key Concepts
Map analysis involves examining spatial data represented through symbols, colors, and contours to understand geographic patterns and relationships. Key concepts include scale, projection, legend interpretation, and topology, which allow for accurate reading and inference of spatial information. This process aids in identifying terrain features, land use, and spatial trends without relying on photographic imagery.
Understanding Photo Interpretation: Essential Elements
Photo interpretation involves analyzing aerial or satellite images to extract information about land use, vegetation, and urban development, emphasizing key elements such as tone, texture, shape, and shadow. Understanding spatial relationships, scale, and image resolution enhances accurate identification of features and environmental conditions. This process relies on integrating multispectral data and contextual knowledge to improve the precision of feature recognition and thematic mapping.
Historical Evolution of Map Analysis and Photo Interpretation
Map analysis originated in the early 20th century with advancements in cartography and geographic information systems, enabling detailed spatial data examination. Photo interpretation evolved alongside aerial photography during World War I, dramatically enhancing reconnaissance and environmental monitoring capabilities. Both techniques have progressively integrated remote sensing technologies, expanding their applications in fields such as urban planning, military intelligence, and natural resource management.
Methodologies in Map Analysis
Map analysis methodologies emphasize spatial data interpretation through techniques such as topographic evaluation, contour mapping, and thematic layering to reveal terrain features and human-made structures. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) facilitate quantitative assessments by integrating multiple data sources, enabling precise spatial patterns and relationships analysis. These methods contrast with photo interpretation, which relies primarily on visual recognition of surface features captured in aerial or satellite imagery.
Techniques Used in Photo Interpretation
Photo interpretation techniques involve analyzing imagery by identifying shapes, patterns, textures, shadows, and tone variations to extract meaningful information about the subject. Methods such as stereoscopic viewing enhance depth perception, while multispectral analysis allows differentiation of features based on wavelength reflectance. These techniques enable accurate classification and assessment of land use, vegetation health, and environmental changes directly from aerial or satellite photographs.
Comparative Advantages of Map Analysis vs Photo Interpretation
Map analysis offers precise spatial data with standardized symbols, enabling detailed measurement of distances, elevations, and boundaries not easily discernible in photo interpretation. Photo interpretation provides real-time visual context and texture information, capturing current environmental conditions and subtle variations in land use patterns. Map analysis is advantageous for planning and navigation due to its accuracy and scalability, while photo interpretation excels in identifying immediate landscape changes and surface features.
Applications in Modern Geographic Studies
Map analysis offers precise spatial data visualization essential for urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource management, while photo interpretation provides detailed, real-time insights into land use changes, vegetation health, and disaster assessment through aerial and satellite imagery. Combining map analysis with remote sensing techniques enhances accuracy in geographic information systems (GIS) applications, enabling more effective decision-making in climate change studies and habitat conservation. Modern geographic studies leverage both methods to integrate multi-source data for comprehensive spatial analysis and dynamic environmental monitoring.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Map analysis faces challenges such as outdated information and scale limitations that can obscure fine details, making it difficult to interpret current conditions accurately. Photo interpretation struggles with issues like image resolution, oblique angles, and atmospheric conditions, which can distort features and complicate precise analysis. Both approaches have limitations in temporal relevance and require complementary data sources to improve accuracy and contextual understanding.
Future Trends in Spatial Data Analysis
Future trends in spatial data analysis emphasize the integration of AI and machine learning for enhanced map analysis and photo interpretation, enabling real-time processing and higher accuracy in identifying geographic patterns. Advances in remote sensing technologies and high-resolution satellite imagery contribute to more detailed and dynamic spatial datasets, facilitating predictive modeling and automated feature extraction. The convergence of big data analytics with GIS platforms supports scalable and efficient analysis, driving innovations in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
Map Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com