The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth and their interactions with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere, forming a dynamic and complex system essential for sustaining life. Understanding the intricate balance within the biosphere reveals how ecosystems adapt and respond to environmental changes that impact biodiversity and global health. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these processes affect your environment and the planet's future.
Table of Comparison
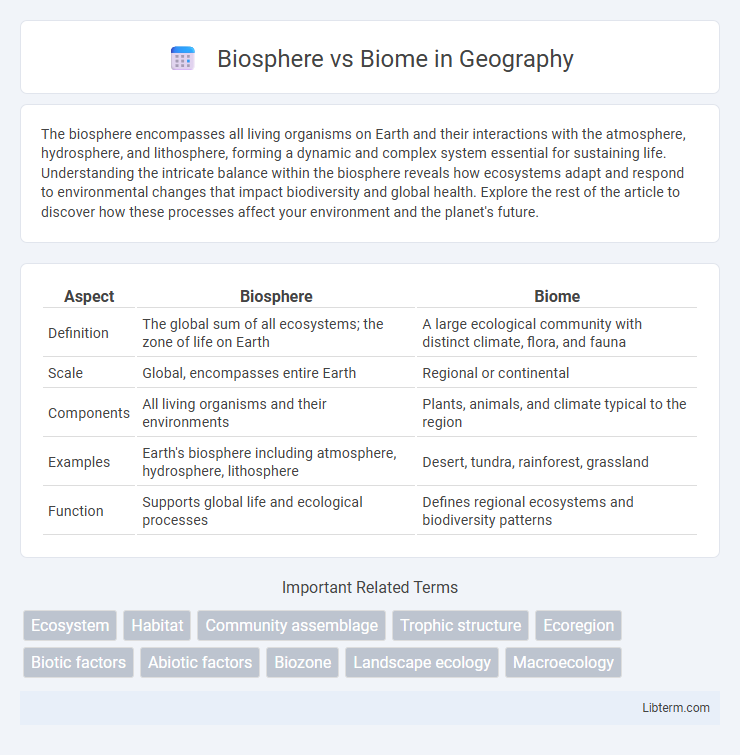
| Aspect | Biosphere | Biome |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The global sum of all ecosystems; the zone of life on Earth | A large ecological community with distinct climate, flora, and fauna |
| Scale | Global, encompasses entire Earth | Regional or continental |
| Components | All living organisms and their environments | Plants, animals, and climate typical to the region |
| Examples | Earth's biosphere including atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere | Desert, tundra, rainforest, grassland |
| Function | Supports global life and ecological processes | Defines regional ecosystems and biodiversity patterns |
Introduction to Biosphere and Biome
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth along with the environments they inhabit, representing the global sum of ecosystems. A biome is a large ecological area characterized by distinct climate conditions, flora, and fauna, such as forests, deserts, and tundras. Understanding the biosphere requires analyzing interactions across multiple biomes and their contributions to Earth's life-supporting systems.
Defining the Biosphere
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, integrating living organisms with their physical environment across land, water, and atmosphere. It represents the global sum of all biomes, including forests, deserts, grasslands, and aquatic systems, forming a complex and interconnected network of life. Defining the biosphere highlights its role as the planet's life-supporting layer, sustaining biodiversity and ecological processes on a planetary scale.
What is a Biome?
A biome is a large ecological area characterized by distinct climate conditions, plant communities, and animal species, such as deserts, tundras, and tropical rainforests. It represents a classification of ecosystems sharing similar environmental conditions and biological communities on a regional scale. Unlike the biosphere, which encompasses all Earth's ecosystems, a biome focuses on specific terrestrial or aquatic habitats defined by dominant vegetation and climate patterns.
Key Differences Between Biosphere and Biome
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems and living organisms on Earth, representing the global sum of all biomes, whereas a biome is a specific regional or global community of plants and animals adapted to a particular climate and environment, such as tundra, rainforest, or desert. Biosphere integrates interactions among biotic and abiotic components across the planet, while biomes categorize life forms based on geographic and climatic conditions. Key differences include scale--biosphere is global, biomes are localized--and complexity, with the biosphere involving broader ecological processes and biomes focusing on specific habitat types.
Structure and Components of the Biosphere
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, integrating living organisms and their environments into a global ecological system that includes the atmosphere, lithosphere, and hydrosphere. Its structure is characterized by interconnected biomes, which are large ecological units defined by dominant vegetation, climate, and animal life. Key components of the biosphere consist of producers, consumers, decomposers, along with abiotic factors such as sunlight, water, and nutrients that support life processes across terrestrial and aquatic regions.
Types of Biomes: An Overview
Biomes are large ecological areas on Earth's surface, each characterized by distinct climate, flora, and fauna, including types such as tundra, tropical rainforest, grassland, desert, and temperate forest. The biosphere encompasses all biomes, representing the global sum of ecosystems where life exists, integrating terrestrial, aquatic, and atmospheric zones. Understanding the specific attributes and distribution of biomes provides insights into biodiversity patterns and ecological processes within the biosphere.
How Biomes Interact Within the Biosphere
Biomes represent large ecological areas with distinct climate, flora, and fauna, while the biosphere encompasses all biomes on Earth, creating a complex network of life and environmental interactions. Energy flow, nutrient cycles, and species migration connect biomes, influencing global climate regulation and biodiversity within the biosphere. Understanding these interactions is crucial for predicting ecological responses to environmental changes and implementing effective conservation strategies.
Importance of Biosphere and Biomes in Ecology
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems and living organisms on Earth, playing a crucial role in maintaining global ecological balance and supporting life through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Biomes, defined by distinct climate conditions and vegetation types, enable the study of regional biodiversity and adaptation strategies critical for ecosystem resilience. Understanding both biosphere and biomes aids in conserving habitats, predicting environmental changes, and sustaining ecosystem services essential for human survival.
Human Impact on the Biosphere and Biomes
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, while biomes are large regions characterized by specific climate and vegetation. Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, have drastically altered both the biosphere and individual biomes, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline. Climate change driven by greenhouse gas emissions disrupts biome distributions and ecosystem services critical to global environmental health.
Conclusion: Interconnectedness of Biosphere and Biomes
The biosphere encompasses all biomes, integrating diverse ecosystems into a global network of life that supports planetary health. Each biome contributes unique biological and climatic characteristics essential for maintaining ecological balance within the biosphere. Understanding the interconnectedness highlights the critical need for preserving biome diversity to sustain the biosphere's resilience and functionality.
Biosphere Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com