Climatogeography examines the relationship between climate patterns and geographic features, influencing ecosystems, human activities, and regional development. Understanding these interactions helps predict environmental changes and guide sustainable planning. Explore the rest of the article to discover how climatogeography impacts your surroundings and daily life.
Table of Comparison
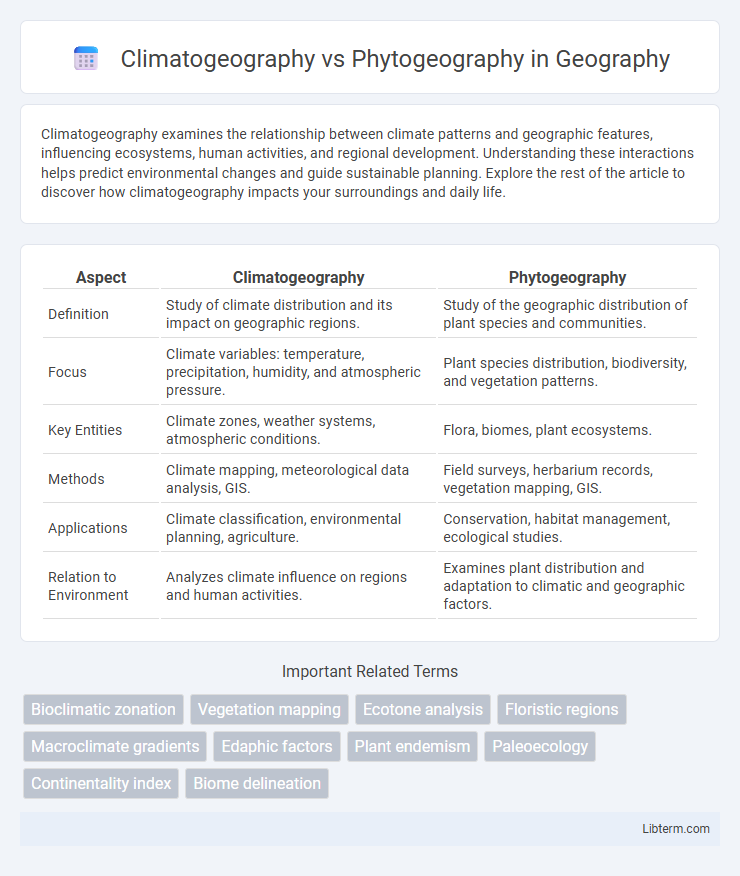
| Aspect | Climatogeography | Phytogeography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of climate distribution and its impact on geographic regions. | Study of the geographic distribution of plant species and communities. |
| Focus | Climate variables: temperature, precipitation, humidity, and atmospheric pressure. | Plant species distribution, biodiversity, and vegetation patterns. |
| Key Entities | Climate zones, weather systems, atmospheric conditions. | Flora, biomes, plant ecosystems. |
| Methods | Climate mapping, meteorological data analysis, GIS. | Field surveys, herbarium records, vegetation mapping, GIS. |
| Applications | Climate classification, environmental planning, agriculture. | Conservation, habitat management, ecological studies. |
| Relation to Environment | Analyzes climate influence on regions and human activities. | Examines plant distribution and adaptation to climatic and geographic factors. |
Introduction to Climatogeography and Phytogeography
Climatogeography studies the spatial distribution of climate patterns and their influence on the environment, emphasizing atmospheric conditions like temperature, precipitation, and wind across regions. Phytogeography examines the geographic distribution of plant species, analyzing factors such as habitat, climate, and soil that determine vegetation patterns. Both fields intersect by exploring how climate shapes the distribution of plant communities and ecosystems globally.
Defining Climatogeography: Scope and Key Concepts
Climatogeography studies the spatial distribution and patterns of climate elements such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity, emphasizing their influence on Earth's surface processes and ecosystems. This field integrates atmospheric science with geography to analyze climatic zones, microclimates, and their variability over time and space. Unlike phytogeography, which focuses on plant distribution, climatogeography addresses the climatic parameters shaping environmental conditions and landform interactions.
Understanding Phytogeography: Core Principles and Terminology
Phytogeography studies the spatial distribution of plant species and their ecological relationships, emphasizing how climatic factors influence vegetation patterns across different regions. Core principles include the concept of phytogeographical regions, endemism, and the role of climate zones in shaping plant communities. Understanding key terminology such as floristic provinces, biomes, and climatic gradients facilitates deeper insights into the complex interactions between plants and their environments.
Historical Development of Both Disciplines
Climatogeography and phytogeography both evolved through the 19th and early 20th centuries with key contributions from naturalists like Alexander von Humboldt and Otto Brunfels, who emphasized the relationships between climate patterns and plant distributions. Climatogeography developed as a branch of physical geography analyzing climatic influences on regional environments, while phytogeography, rooted in botanical exploration, focused on mapping plant species distribution and their ecological interactions. Historical advancement in both disciplines relied on empirical data collection and emerging theories in ecology and biogeography, establishing foundational knowledge for modern environmental and conservation sciences.
Major Methods Used in Climatogeography
Climatogeography primarily employs meteorological data analysis, including temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns, to study the spatial distribution of climates and their influence on ecosystems. Remote sensing technology and geographic information systems (GIS) are extensively used to map climate zones and analyze environmental changes over large areas. Statistical modeling and climate classification systems, such as the Koppen-Geiger classification, help in categorizing different climate types and understanding their geographic correlations.
Research Approaches in Phytogeography
Phytogeography research employs spatial analysis, field surveys, and remote sensing to study plant distributions and their environmental interactions. Techniques such as ecological niche modeling and molecular phylogenetics help elucidate historical biogeography and community assembly patterns. Emphasis is placed on understanding the influence of climate, soil, and biotic factors on vegetation distribution, distinguishing it from climatogeography's primary focus on climate variables.
Comparative Analysis: Areas of Overlap and Divergence
Climatogeography and phytogeography intersect in studying how climate influences plant distribution patterns, with both fields emphasizing temperature, precipitation, and seasonality effects on vegetation zones. Climatogeography primarily analyzes climatic variables shaping ecosystems at macro scales, while phytogeography focuses on the spatial distribution and evolutionary history of plant species and communities. Divergence arises as climatogeography integrates atmospheric sciences and climatology, whereas phytogeography incorporates ecological genetics and biogeography to explain plant diversity and endemism.
Influence of Climate Patterns on Plant Distribution
Climate patterns exert a significant influence on plant distribution by determining the temperature, precipitation, and seasonal variations that shape ecosystem characteristics in climatogeography. Phytogeography analyzes how these climatic factors influence species diversity, vegetation types, and biomes across different geographic regions. Both disciplines highlight the critical role of climate in controlling plant growth habits, migration, and adaptation within distinct ecological zones.
Applications in Environmental and Conservation Studies
Climatogeography analyzes climate patterns and their impact on ecosystems, providing critical data for predicting climate change effects on biodiversity. Phytogeography studies the distribution of plant species, essential for habitat conservation, restoration projects, and managing invasive species. Integrating climatogeography and phytogeography enhances environmental planning by aligning climate projections with plant distribution models to optimize conservation strategies.
Future Trends and Emerging Challenges
Future trends in climatogeography emphasize the integration of advanced climate modeling with spatial analysis to predict shifts in climatic zones, while phytogeography increasingly leverages genomic data and remote sensing to map vegetation changes. Emerging challenges include addressing the rapid pace of climate change impacting species distribution and ecosystem resilience, requiring interdisciplinary approaches that combine climatology, ecology, and geographic information systems (GIS). Both fields must adapt to data complexity and uncertainty in environmental predictions to effectively guide conservation and land-use planning.
Climatogeography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com