Delimitation defines the boundaries and scope of a research project, clarifying what the study will and will not cover. It helps streamline your focus by setting clear parameters, ensuring relevant and manageable data collection. Explore the rest of the article to understand how setting precise delimitations enhances your research effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
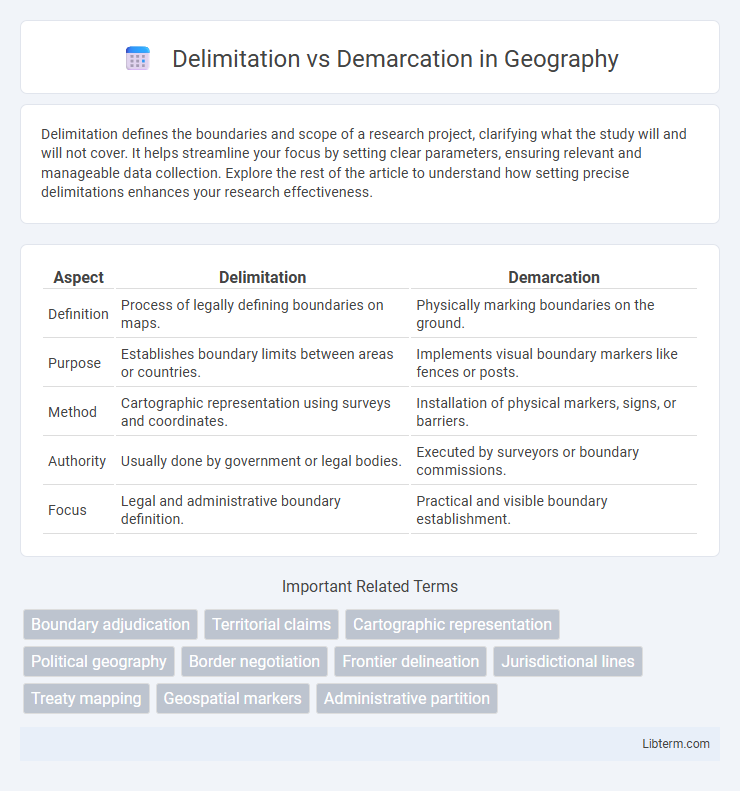
| Aspect | Delimitation | Demarcation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of legally defining boundaries on maps. | Physically marking boundaries on the ground. |
| Purpose | Establishes boundary limits between areas or countries. | Implements visual boundary markers like fences or posts. |
| Method | Cartographic representation using surveys and coordinates. | Installation of physical markers, signs, or barriers. |
| Authority | Usually done by government or legal bodies. | Executed by surveyors or boundary commissions. |
| Focus | Legal and administrative boundary definition. | Practical and visible boundary establishment. |
Understanding Delimitation and Demarcation
Delimitation is the process of legally defining boundaries through treaties or agreements, establishing clear limits between territories or properties. Demarcation follows delimitation and involves physically marking these boundaries on the ground using markers or fences. Understanding the distinction is crucial for resolving territorial disputes and ensuring precise boundary management.
Historical Context of Boundary Setting
Historical context of boundary setting reveals delimitation as the formal process of defining territorial limits through negotiation and treaties, often based on natural landmarks or coordinates. Demarcation follows as the physical manifestation of these agreed boundaries, marked by fences, posts, or markers on the ground to prevent disputes. Colonial-era boundary setting frequently involved delimitation without accurate demarcation, contributing to later conflicts in regions such as Africa and the Middle East.
Key Differences Between Delimitation and Demarcation
Delimitation refers to the legal process of defining territorial boundaries on a map, establishing official border lines between states or regions. Demarcation is the physical act of marking these boundaries on the ground using markers, fences, or boundary stones to make the limits visibly identifiable. Key differences include that delimitation is a cartographic and legal procedure, while demarcation involves tangible, on-site implementation and enforcement of those boundaries.
Legal Frameworks Governing Boundaries
Delimitation involves the legal process of defining boundary lines between states or territories through treaties or agreements, establishing clear jurisdictional limits under international law. Demarcation refers to the physical marking of these legally defined boundaries on the ground using boundary markers, fences, or natural landmarks to prevent disputes. Legal frameworks such as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and bilateral boundary treaties provide the authoritative basis for delimitation, while demarcation ensures enforceable and recognized boundary implementation.
The Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as the United Nations and the International Court of Justice play a crucial role in delimitation by facilitating negotiations and providing legal frameworks for boundary agreements between states. These organizations contribute to demarcation by overseeing the physical marking of boundaries on the ground to ensure compliance with treaties and prevent conflicts. Their involvement enhances boundary clarity, promotes peaceful resolution, and supports international stability through standardized conflict resolution mechanisms.
Processes Involved in Delimitation
The delimitation process involves defining territorial boundaries through legal and political agreements, often using maps and treaties to specify the limits between states or administrative units. This stage requires diplomatic negotiations, data analysis of geographical features, and consultations with relevant stakeholders to reach a consensual boundary framework. Delimitation sets the theoretical or legal boundary line, which is later physically marked during demarcation with visible signs like boundary stones or fences.
Steps in Physical Demarcation
Physical demarcation involves precise steps such as surveying the land to identify boundaries, placing visible markers like boundary stones or fences, and recording these positions on official maps and documents to prevent future disputes. Surveyors use tools like GPS and total stations to measure and map the exact coordinates of the boundary lines established during delimitation. This process ensures the legal recognition and physical visibility of boundaries for landowners and authorities.
Common Challenges and Disputes
Delimitation involves legally defining boundary lines between states or territories using treaties or agreements, while demarcation physically marks these boundaries on the ground with monuments or markers. Common challenges in delimitation include ambiguous legal language, historical claims, and overlapping territorial assertions that fuel disputes. Demarcation problems often arise from difficult terrain, environmental changes, and lack of maintenance, which contribute to ongoing boundary conflicts and disagreements.
Case Studies: Notable Boundary Resolutions
Delimitation involves legally defining boundaries on maps, while demarcation refers to physically marking those boundaries on the ground, critical in resolving territorial disputes such as the India-Bangladesh Land Boundary Agreement which successfully addressed enclaves. The Ethiopia-Eritrea Boundary Commission exemplifies the challenges of demarcation following the legal delimitation after the Algiers Agreement, highlighting complexities in implementing peaceful resolutions. The Rwanda-Uganda border dispute resolution illustrates how joint boundary delimitation and demarcation can foster bilateral cooperation and reduce cross-border tensions.
Future Trends in Boundary Management
Delimitation involves defining boundary lines through legal agreements, while demarcation refers to the physical marking of those boundaries on the ground. Future trends in boundary management emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as GIS, satellite imagery, and blockchain to enhance accuracy, transparency, and dispute resolution. These innovations aim to streamline international boundary negotiations and improve real-time monitoring of border areas.
Delimitation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com