Hill landscapes offer diverse ecosystems that support a wide variety of flora and fauna, contributing significantly to environmental balance. Exploring hills can enhance your appreciation of nature and provide unique recreational opportunities such as hiking and birdwatching. Discover more about the fascinating features and benefits of hills in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
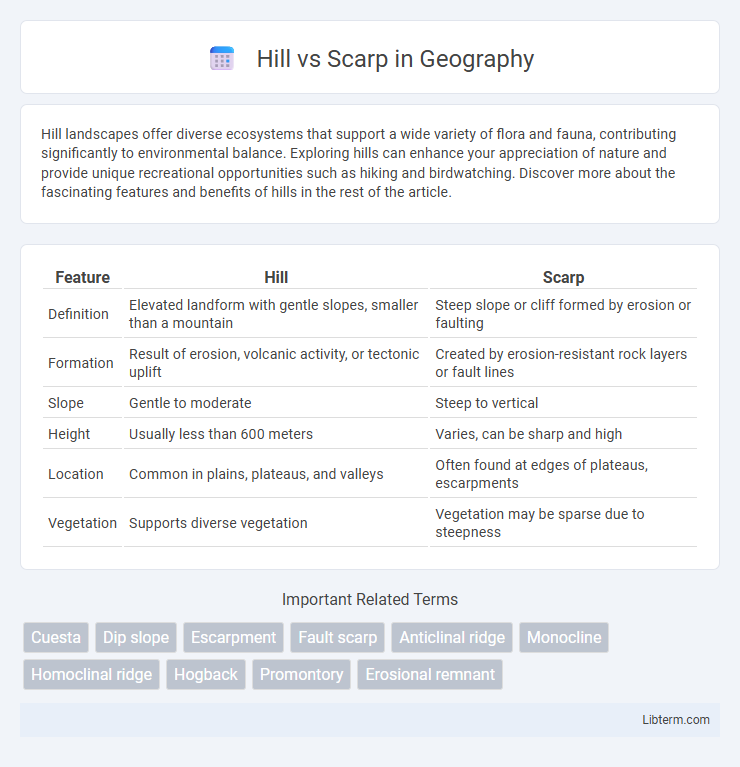
| Feature | Hill | Scarp |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated landform with gentle slopes, smaller than a mountain | Steep slope or cliff formed by erosion or faulting |
| Formation | Result of erosion, volcanic activity, or tectonic uplift | Created by erosion-resistant rock layers or fault lines |
| Slope | Gentle to moderate | Steep to vertical |
| Height | Usually less than 600 meters | Varies, can be sharp and high |
| Location | Common in plains, plateaus, and valleys | Often found at edges of plateaus, escarpments |
| Vegetation | Supports diverse vegetation | Vegetation may be sparse due to steepness |
Introduction to Hill and Scarp
Hill and Scarp are geological terms describing landforms shaped by erosion and tectonic activity. A hill is a naturally raised area of land, typically less steep and lower in elevation than a mountain, formed through processes like weathering and sediment deposition. A scarp, or escarpment, is a steep slope or long cliff resulting from faulting or erosion, often marking the boundary between different geological formations or elevations.
Defining Hills: Features and Formation
Hills are elevated landforms with gentle slopes and rounded summits, typically lower and less steep than mountains. They form through various geological processes including erosion, sediment deposition, and tectonic activity, shaping distinct topographical features. Understanding these natural formations aids in distinguishing hills from structures like scarps, which are steep slopes or cliffs resulting from faulting or erosion.
Understanding Scarps: Geological Overview
Scarps are steep slopes or cliffs formed through tectonic activity, erosion, or faulting, significant in geological studies and landscape evolution. In Hill vs Scarp cases, understanding scarp morphology helps clarify natural versus anthropogenic influences on landforms. These features often indicate underlying fault lines or geological faults critical for assessing seismic hazards and stability issues.
Key Differences Between Hills and Scarps
Hills are natural elevations of the earth's surface, typically characterized by gentle slopes and moderate heights, while scarps are steep slopes or cliffs formed by faulting or erosion processes. Hills generally have rounded tops and gradual inclines, making them less abrupt compared to scarps, which feature sharp, vertical or near-vertical faces. The key difference lies in their formation: hills result from gradual geological processes such as sediment accumulation or tectonic uplift, whereas scarps are often created by sudden earth movements like fault displacement or erosion along faults.
Formation Processes: Erosion vs Faulting
Hill formations primarily result from erosion processes where wind, water, and ice gradually wear down rock and soil, shaping elevated landforms over time. In contrast, scarps form due to faulting, which involves tectonic movements causing fractures and vertical displacement in the Earth's crust, leading to steep slopes or cliffs. Understanding these distinct formation processes highlights erosion's gradual sculpting compared to faulting's sudden geological shifts.
Geographic Examples of Hills and Scarps
Hills such as the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States and the Black Hills in South Dakota exemplify elevated landforms with gentle slopes and rounded summits. Scarps, in contrast, are steep cliffs or escarpments like the Niagara Escarpment in Canada and the Sierra Madre Oriental fault scarps in Mexico, formed by tectonic activity or erosion. These geographic examples highlight the distinct formation processes and topographical characteristics that differentiate hills from scarps.
Ecological Impact of Hills and Scarps
Hills and scarps significantly influence local ecosystems by shaping habitat diversity and microclimates; hills often support diverse plant communities due to variations in elevation, slope, and sunlight exposure, while scarps create abrupt environmental gradients that can serve as natural barriers for species movement. The ecological impact of hills includes promoting soil retention and water infiltration, which enhances biodiversity and carbon sequestration, whereas scarps contribute to soil erosion risk but also provide unique niches for specialized flora and fauna. Understanding these geomorphological features is critical for conservation planning and managing landscape connectivity to protect ecological functions.
Human Interaction and Land Use
Hill vs Scarp addresses the legal boundaries and rights concerning human interaction with landforms, emphasizing how land use impacts property ownership and access rights. The case clarifies the interaction between developed land on a hill and adjacent scarp slopes, influencing zoning regulations and environmental conservation efforts. Understanding these distinctions helps manage land use conflicts and supports sustainable development practices in hilly terrains.
Importance in Landscape Classification
Hill vs Scarp distinction plays a crucial role in landscape classification by clearly differentiating between elevated landforms with gradual slopes and steep, cliff-like escarpments. Understanding this difference enhances topographic mapping accuracy and informs ecological zoning, soil distribution analysis, and watershed management. Accurate identification of hills and scarps supports environmental planning, land use decisions, and hazard risk assessments in geomorphology.
Conclusion: Hill vs Scarp Explained
Hill vs Scarp clarified the legal distinction between ownership rights and obligations in property boundaries, emphasizing the importance of precise boundary definitions under property law. The court concluded that easements and licenses could not override established ownership rights without explicit agreements, reinforcing property holders' control over their land. This case set a precedent for resolving disputes by prioritizing clear title and formal documentation in boundary conflicts.
Hill Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com