Divide can refer to the act of separating or distributing something into parts, whether it's numbers, land, or resources. Understanding how to divide efficiently improves problem-solving skills and promotes fair sharing in various contexts. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical examples and techniques for mastering division in your daily life.
Table of Comparison
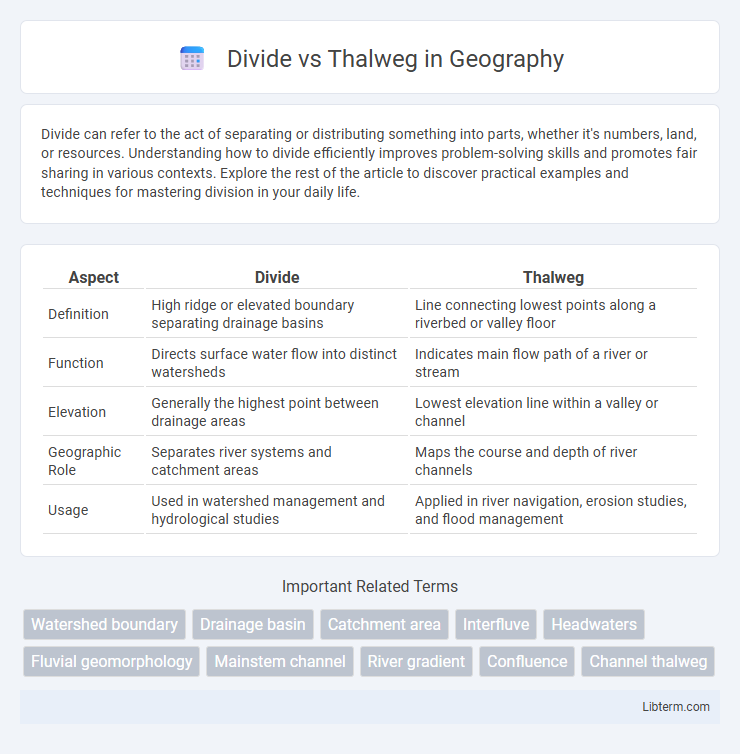
| Aspect | Divide | Thalweg |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High ridge or elevated boundary separating drainage basins | Line connecting lowest points along a riverbed or valley floor |
| Function | Directs surface water flow into distinct watersheds | Indicates main flow path of a river or stream |
| Elevation | Generally the highest point between drainage areas | Lowest elevation line within a valley or channel |
| Geographic Role | Separates river systems and catchment areas | Maps the course and depth of river channels |
| Usage | Used in watershed management and hydrological studies | Applied in river navigation, erosion studies, and flood management |
Understanding Divide and Thalweg: Key Concepts
A divide refers to the elevated boundary separating adjacent drainage basins, directing surface water flow toward distinct watersheds, while a thalweg marks the line connecting the lowest points along a valley or riverbed, illustrating the path of deepest channel flow. Understanding these features is crucial in watershed management, hydrology, and geomorphology, as divides determine drainage patterns and thalwegs influence sediment transport and river navigation. Analyzing divides and thalwegs helps optimize flood control strategies and environmental conservation by accurately mapping water flow and landscape changes.
Geographical Significance of Divides and Thalwegs
Divides represent elevated boundaries separating adjacent drainage basins, guiding the flow direction of surface water and influencing watershed management and hydrological patterns. Thalwegs are the lowest points along a valley or riverbed, marking the natural channels of water flow and often serving as critical reference lines in defining political or property boundaries. Their geographical significance lies in divides controlling watershed extents and runoff distribution, while thalwegs determine river navigation routes and boundary delineations in fluvial environments.
Formation Processes: Divide vs Thalweg
Divides form through tectonic uplift, erosion, and sediment deposition, creating elevated boundaries that separate adjacent drainage basins. Thalwegs develop from fluvial processes where water flow concentrates along the lowest points in a valley or river channel, continuously eroding and deepening the path over time. The formation of divides is predominantly influenced by geological forces shaping the landscape, while thalwegs evolve primarily through hydrological dynamics and sediment transport.
Roles in River and Watershed Dynamics
Divides serve as elevated boundary lines that separate adjacent watersheds, directing surface water flow into distinct drainage basins and influencing the overall watershed dynamics by controlling runoff distribution. The thalweg represents the deepest continuous line along a river channel, crucial for determining flow paths, sediment transport, and river morphology within the watershed. Together, divides and thalwegs regulate hydrological and geomorphological processes that shape river networks and watershed interactions.
Legal and Political Implications
The divide and thalweg principles represent distinct approaches to boundary delimitation in international law, where the divide refers to the watershed line separating river basins, and the thalweg represents the deepest navigable channel of a river. Legal disputes often arise in transboundary watercourses, as the thalweg method favors navigational rights and access, while the divide emphasizes sovereign control over distinct drainage areas. Politically, selecting either approach can affect resource allocation, water security, and regional stability, making these concepts central to treaties and negotiations between riparian states.
Importance in Boundary Delimitation
The divide represents the highest points of terrain separating distinct drainage basins, often serving as natural boundary lines between territories or countries, ensuring clear and undisputed territorial limits. The thalweg, defined as the deepest continuous line along a river channel, plays a crucial role in defining boundaries where watercourses act as borders, providing precise demarcation especially in navigable rivers. Understanding the geographic and hydrological characteristics of divides and thalwegs is fundamental in international boundary delimitation to prevent conflicts and facilitate equitable resource sharing.
Key Differences Between Divide and Thalweg
The key differences between divide and thalweg lie in their geographical and hydrological significance: a divide is a ridge or elevated boundary separating adjacent drainage basins, whereas a thalweg is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or river channel, often indicating the deepest part of a stream bed. While divides determine watershed boundaries influencing water flow direction, thalwegs trace the path of maximum flow velocity and erosion within a watercourse. Understanding these distinctions aids in hydrological studies, watershed management, and legal boundary definitions.
Real-World Examples of Divides and Thalwegs
The Continental Divide in North America serves as a classic example of a drainage divide, separating waters flowing to the Pacific Ocean from those draining into the Atlantic. In contrast, the thalweg of the Rhine River marks the deepest continuous line along the river channel, often used as a natural boundary between Germany and France. These real-world instances illustrate divides delineating major watershed boundaries and thalwegs defining river navigation and political borders.
Applications in Environmental Management
In environmental management, divides and thalwegs play critical roles in watershed delineation and water resource planning. Divides, which are elevated land boundaries separating drainage basins, guide the allocation of water flow and pollutant migration, affecting land use decisions and ecosystem conservation. Thalwegs, representing the deepest continuous line of a stream channel, are essential for monitoring sediment transport, flood management, and habitat restoration within riparian environments.
Challenges and Controversies
The distinction between divide and thalweg often presents challenges in international boundary delimitation due to varying interpretations of natural landscape features. Disputes arise when determining whether borders should follow the watershed divide or the deepest continuous line of a riverbed, especially in regions with complex hydrography. Ambiguities in legal definitions and the dynamic nature of river systems further complicate negotiations, leading to controversies over resource control and territorial sovereignty.
Divide Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com