Benchmark is a critical tool for measuring and comparing performance across industries, enabling businesses to identify best practices and improve efficiency. By analyzing benchmark data, you can gain valuable insights into competitive standards and set achievable goals for growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how benchmarking can transform your strategy and drive success.
Table of Comparison
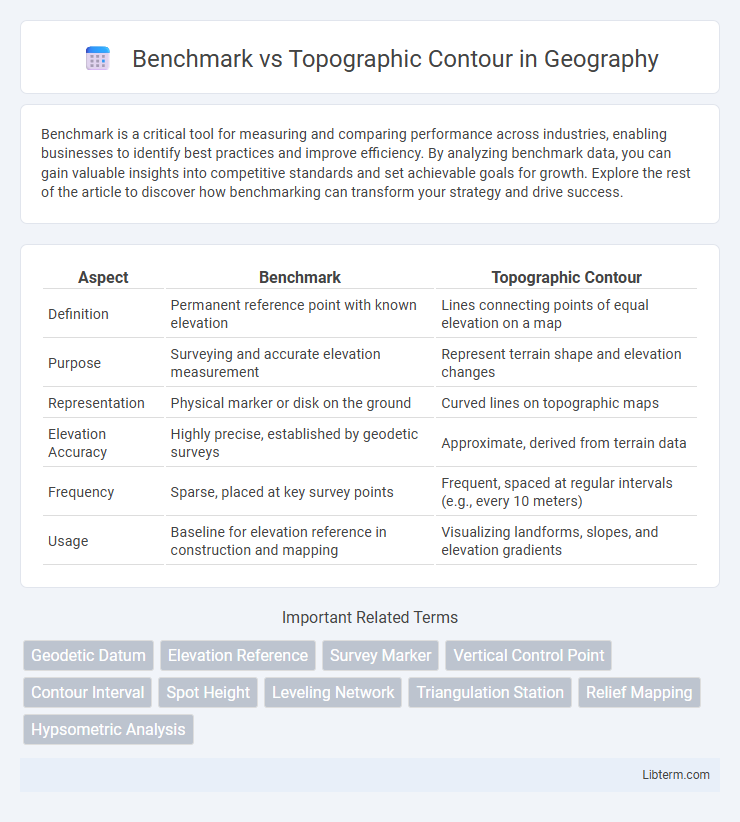
| Aspect | Benchmark | Topographic Contour |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent reference point with known elevation | Lines connecting points of equal elevation on a map |
| Purpose | Surveying and accurate elevation measurement | Represent terrain shape and elevation changes |
| Representation | Physical marker or disk on the ground | Curved lines on topographic maps |
| Elevation Accuracy | Highly precise, established by geodetic surveys | Approximate, derived from terrain data |
| Frequency | Sparse, placed at key survey points | Frequent, spaced at regular intervals (e.g., every 10 meters) |
| Usage | Baseline for elevation reference in construction and mapping | Visualizing landforms, slopes, and elevation gradients |
Introduction to Benchmarks and Topographic Contours
Benchmarks serve as fixed reference points with known elevation used primarily in surveying and mapping for accurate vertical control. Topographic contours represent continuous lines on maps connecting points of equal elevation, illustrating terrain shape and elevation changes. Together, benchmarks provide precise elevation data points, while contours visualize the overall landscape's relief and slope.
Definition of Benchmark in Surveying
A benchmark in surveying is a fixed reference point with a precisely known elevation used as a starting point for leveling measurements. It serves as a control mark to ensure accuracy and consistency across topographic surveys by providing a stable datum for contour mapping. Unlike topographic contours that represent elevation changes graphically, benchmarks offer exact elevation values essential for precise land surveying and construction projects.
Understanding Topographic Contours
Topographic contours represent continuous lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation, providing a detailed visualization of terrain shape and slope. Each contour line indicates a specific elevation above sea level, allowing users to interpret the gradient and form of hills, valleys, and plateaus accurately. Understanding topographic contours is essential for navigation, land surveying, and environmental planning, as they convey precise information about elevation changes across a geographic area.
Purpose and Importance of Benchmarks
Benchmarks serve as fixed reference points with precisely determined elevations, essential for ensuring accuracy in surveying, construction, and mapping projects. They provide a reliable standard for measuring height differences and establishing consistent vertical control across different sites. Unlike topographic contours, which depict elevation changes on maps, benchmarks guarantee precise and stable elevation data critical for engineering and land development accuracy.
Roles of Topographic Contours in Mapping
Topographic contours play a critical role in mapping by representing elevation and the shape of the terrain through continuous lines connecting points of equal altitude. These contours enable accurate visualization of landforms, slope gradients, and relief patterns, facilitating terrain analysis and navigation. Unlike benchmarks, which provide precise elevation data at fixed points, topographic contours offer a comprehensive spatial understanding of elevation changes across the mapped area.
Key Differences: Benchmark vs. Topographic Contour
Benchmarks represent fixed reference points with precisely known elevations used for surveying and mapping accuracy, while topographic contours depict continuous lines connecting points of equal elevation on a map, illustrating terrain shape. Benchmarks provide exact elevation data at a specific location, whereas topographic contours offer a visual representation of the land's slope and relief. The key difference lies in benchmarks serving as factual elevation markers, while contours are interpretative lines used to understand topography.
Methods for Identifying Benchmarks and Contours
Benchmarks are identified using precise geodetic surveys or GPS measurements to establish exact elevation points, often marked physically on durable structures. Topographic contours are derived by interpolating elevation data from surveys, photogrammetry, or LiDAR, producing continuous lines that represent constant elevation across the terrain. Both methods rely on accurate spatial data collection, but benchmarks provide reference points while contours map the three-dimensional shape of the landscape.
Applications in Civil Engineering and Land Development
Benchmarks provide precise elevation reference points critical for surveying and construction, ensuring accuracy in civil engineering projects such as roadways, bridges, and foundations. Topographic contours depict continuous elevation changes across a landscape, aiding in site planning, drainage design, and grading for land development. Combining benchmarks with contour maps allows engineers to accurately model terrain, optimize earthworks, and manage stormwater systems effectively.
Interpreting Maps: Benchmark and Contour Integration
Benchmarks provide exact elevation points marked on maps, serving as reference locations for accurate height measurement. Topographic contour lines illustrate continuous elevation changes, enabling visualization of terrain shape and slopes. Integrating benchmarks with contour lines enhances map interpretation by anchoring elevation data to precise, verified points, improving navigation and terrain analysis accuracy.
Summary: Choosing Between Benchmark and Topographic Contour
Selecting between a benchmark and a topographic contour depends on the precision and type of elevation data required. Benchmarks provide exact, fixed reference points with known elevations ideal for surveying and construction projects. Topographic contours offer continuous elevation information across terrain, useful for mapping and landscape analysis where relative elevation changes are important.
Benchmark Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com