Elevation Point offers breathtaking views and serene hiking trails that immerse you in nature's beauty. This destination provides the perfect escape for outdoor enthusiasts seeking adventure and tranquility. Discover everything you need to plan your visit by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
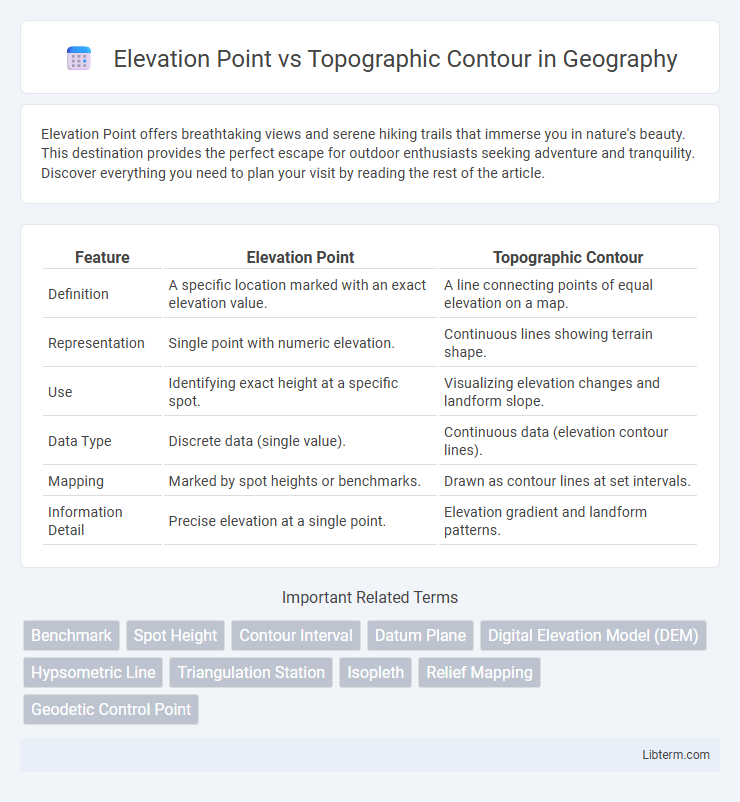
| Feature | Elevation Point | Topographic Contour |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A specific location marked with an exact elevation value. | A line connecting points of equal elevation on a map. |
| Representation | Single point with numeric elevation. | Continuous lines showing terrain shape. |
| Use | Identifying exact height at a specific spot. | Visualizing elevation changes and landform slope. |
| Data Type | Discrete data (single value). | Continuous data (elevation contour lines). |
| Mapping | Marked by spot heights or benchmarks. | Drawn as contour lines at set intervals. |
| Information Detail | Precise elevation at a single point. | Elevation gradient and landform patterns. |
Understanding Elevation Points
Elevation points represent specific locations on a map where the exact height above sea level is marked, providing precise vertical data crucial for detailed terrain analysis. Unlike topographic contours that illustrate continuous elevation lines to visualize slopes and landforms, elevation points offer definitive altitude measurements essential for surveying and construction projects. Understanding these precise elevation markers enables accurate assessment of terrain features and supports informed decision-making in environmental planning and engineering.
What Are Topographic Contours?
Topographic contours are lines on a map that connect points of equal elevation, representing the three-dimensional shape of the terrain on a two-dimensional surface. These contour lines illustrate elevation changes, slope steepness, and landforms, making it easier to interpret the landscape's relief and gradients. Elevation points provide specific height measurements at exact locations, while topographic contours offer a continuous representation of terrain elevation changes across a broader area.
Key Differences Between Elevation Points and Topographic Contours
Elevation points represent specific spots on a map with exact altitude values, providing precise vertical measurements at individual locations. Topographic contours are continuous lines connecting points of equal elevation, illustrating the shape and slope of the terrain across an area. The key difference lies in elevation points offering discrete height data, while contours convey spatial patterns of elevation changes.
Methods of Measuring Elevation Points
Measuring elevation points involves precise methods such as leveling, GPS surveying, and total station use, which directly determine specific vertical positions on a terrain. In contrast, topographic contour lines represent continuous elevation data derived from interpolating multiple elevation points, often generated through digital elevation models (DEMs) or photogrammetry. Advanced techniques like LiDAR scanning also enable high-resolution mapping of elevation points, enhancing the accuracy of contour mapping.
How Topographic Contours Are Created
Topographic contours are created by connecting points of equal elevation on a map to represent the 3D terrain in 2D form, allowing for visualization of landforms and slopes. Elevation points provide specific altitude data at precise locations, serving as reference markers during the contouring process. Surveying techniques and digital elevation models (DEMs) help generate accurate contour lines by interpolating between these elevation points.
Applications of Elevation Point Data
Elevation point data provides precise altitude measurements crucial for urban planning, infrastructure design, and flood risk assessment, enabling accurate modeling of terrain features. Unlike topographic contour lines, which represent elevation in continuous intervals, elevation points offer granular data essential for GIS mapping, construction site analysis, and environmental monitoring. This precision facilitates detailed land surveying, aids in transportation route optimization, and supports natural resource management.
Uses of Topographic Contour Maps
Topographic contour maps are essential tools in environmental planning, hiking, and geological studies due to their precise representation of land elevation and terrain features. These maps use contour lines to connect points of equal elevation, allowing users to visualize slopes, valleys, and peaks for navigation and land assessment. Elevation point data complements contour maps by providing exact height measurements, enhancing the accuracy of terrain analysis and engineering projects.
Accuracy Comparison: Elevation Point vs Topographic Contour
Elevation points provide precise vertical positioning with accuracy often within centimeters, making them reliable for detailed topographic analysis. Topographic contours represent elevation as continuous lines, which can introduce interpolation errors and reduce accuracy, especially in areas with steep or complex terrain. Comparing both, elevation points deliver higher accuracy for specific locations, while contours offer a generalized overview that may sacrifice detail.
Visualization Techniques in Elevation Mapping
Elevation points represent specific locations with exact altitude values, enabling precise visualization through 3D modeling and digital elevation models (DEMs) for detailed terrain analysis. Topographic contours connect points of equal elevation, forming continuous lines that effectively illustrate terrain shape and gradient on 2D maps, facilitating slope and landform interpretation. Combining both techniques enhances elevation mapping by providing detailed point-based accuracy alongside comprehensive contour visualization for nuanced spatial understanding.
Choosing Between Elevation Points and Contour Lines
Choosing between elevation points and topographic contour lines depends on the level of detail and visualization needed for terrain analysis. Elevation points provide precise altitude data at specific locations, ideal for pinpointing exact heights or analyzing discrete features. Contour lines offer a continuous representation of terrain shape, making them more suitable for understanding slopes, gradients, and overall landform patterns efficiently.
Elevation Point Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com